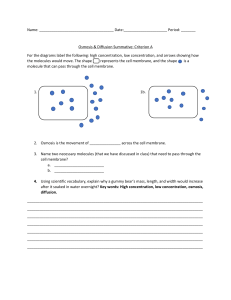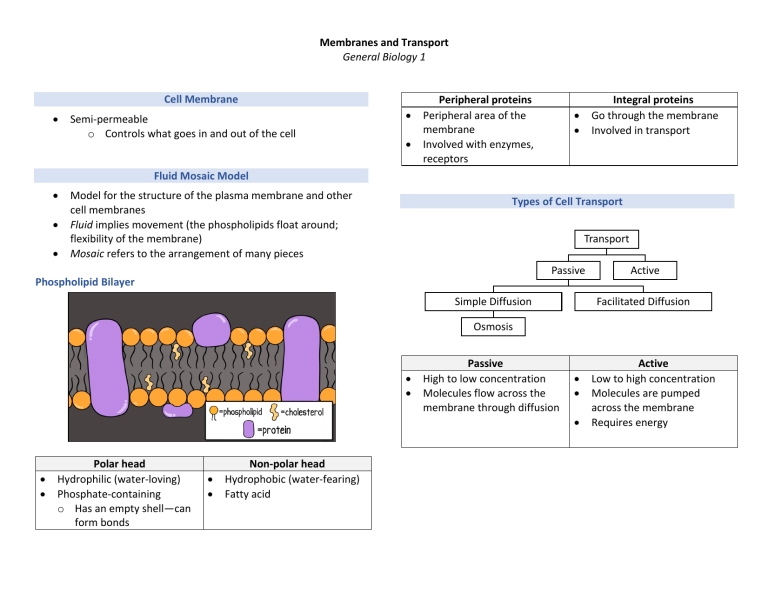
Membranes and Transport General Biology 1 Cell Membrane • Semi-permeable o Controls what goes in and out of the cell • • Peripheral proteins Peripheral area of the membrane Involved with enzymes, receptors Integral proteins Go through the membrane Involved in transport • • Fluid Mosaic Model • • • Model for the structure of the plasma membrane and other cell membranes Fluid implies movement (the phospholipids float around; flexibility of the membrane) Mosaic refers to the arrangement of many pieces Types of Cell Transport Transport Passive Phospholipid Bilayer Simple Diffusion Active Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis • • Passive High to low concentration Molecules flow across the membrane through diffusion • • • • • Polar head Hydrophilic (water-loving) Phosphate-containing o Has an empty shell—can form bonds • • Non-polar head Hydrophobic (water-fearing) Fatty acid Active Low to high concentration Molecules are pumped across the membrane Requires energy Passive Transport • • • • Involves water Moves from high water potential to low water potential Moves from low concentration gradient to high concentration gradient Terms: o Concentration gradient refers to the other molecules (i.e. solutes) Plant Cell in a: Hypotonic Solution Isotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Stable Low WP, High CG High WP, Low CG Cell will shrink Diagram Simple Diffusion • Net (overall) movement of a substance traveling down its concentration gradient • Moving from high concentration to low concentration • Small molecules such as water and oxygen High WP, Low CG Low WP, High CG Cell will expand Facilitated Diffusion • Requires a protein channel o Because the hydrophobic tails repel hydrophilic substances (e.g. charged ions and polar substances) Osmosis High Water Potential Low Concentration Gradient Solution Cell Effect à Low Water Potential High Concentration Gradient Active Transport • • Requires energy (i.e. ATP) o Adenosine triphosphate has three phosphates; when one phosphate breaks a bond, it releases energy Moving from low concentration to high concentration Sodium-Potassium Pump • Phosphate released by the ATP attaches to the membrane protein o The membrane protein then changes it shape