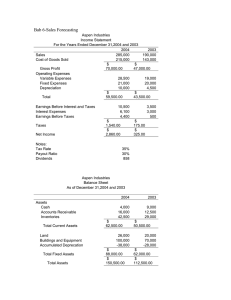
Date: 17th October 2018 MBA Financial Accounting Research Analysis Fawaz Abdulaziz Al Hokair & Co. and its subsidiaries (A Saudi Joint Stock Company) Submitted To: Dr. Mohamed Mostafa Prepared By: Hossam Tarek Karim Tarek 1 Introduction Company Profile • Fawaz Abdulaziz Alhokair Co Fawaz Abdulaziz Al Hokair Co (known as: Al Hokair) is a public Saudi company. • Established in March 1990. • Listed on Saudi Stock Exchange “Tadawul” (TDWL) since December 2006. • Al Hokair operates within the Retailing sector focusing on Apparel Retail. • It has Companies operating across Southern and Central Asia, Northern Africa, Middle East and Southern Europe. • Al Hokair is based in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. 2 Balance Sheet Horizontal Analysis Item 2015 Amount (SAR) 2014 Amount (SAR) Current Assets Comments - Cash and bank balances 279,957,636 101,006,685 178,950,951 177.2% Account receivable 882,333,590 739,364,628 142,968,962 19.3% Amounts due from related parties 281,728,504 137,728,024 144,000,480 104.6% Inventory 2,016,265,250 1,534,192,950 482,072,300 31.4% Total Current Assets 3,460,284,980 2,512,292,287 947,992,693 37.7% Non-Current Assets This increase can be mainly attributed to the large increase in the long term fund taken by the company By looking at the net sales we found an increase of about 25% so an increase in accounts receivable by this amount is normal This very big increase is a good thing because it is mainly attributed to rentals due from newly opened shops Increasing in inventory might indicate attempts of growth by the company by looking at the overall increasing trend of all the assets - Investments 318,467,050 260,091,647 58,375,403 22.4% Fixed Assets 2,046,973,906 1,641,000,670 405,973,236 24.7% Other Assets 943,898,928 602,532,933 341,365,995 56.7% Total Non-Current Assets 3,309,339,884 2,503,625,250 805,714,634 32.2% Total Assets 6,769,624,864 5,015,917,537 1,753,707,327 35.0% Current Liabilities All the assets have experienced an increasing trend and when looking at this and relating it to the fund taken it is apparent that the company is attempting to a growth in its operations This is an indicator the compamy has increased its finances through loans The company has been paying off what is due from the long term fund and thus the amount decreased Short term loan 833,290,230 465,692,323 367,597,907 78.9% current portion of long term fund 195,587,581 307,357,934 (111,770,353) -36.4% Accounts payable 570,495,843 550,155,761 20,340,082 3.7% A small increase in the firm's obligations to others other current liabilities 511,151,946 603,847,059 (92,695,113) -15.4% The firm's short term obligations have decreased Total Current Liabilities 2,110,525,600 1,927,053,077 183,472,523 9.5% Non-Current Liabilities - Long Term Funding 2,163,460,629 565,709,222 1,597,751,407 282.4% End of service indemnities 78,756,624 70,161,999 8,594,625 12.2% Total Non-Current Liabilities 2,242,217,253 635,871,221 1,606,346,032 252.6% Total Liabilities 4,352,742,853 2,562,924,298 1,789,818,555 69.8% Shareholders Equity 3 Increase or (Decrease) during 2015 Amount (SAR) Percent The company has taken a long term fund to finance its growth operations which in turn increased its long term liabiities by a very large amount - Capital & resrves 1,951,725,690 1,378,278,314 573,447,376 41.6% retained earnings 447,720,167 1,047,467,808 (599,747,641) -57.3% Total Shareholder Equity 2,399,445,857 2,425,746,122 (26,300,265) -1.1% minority interest 17,436,154 27,247,117 (9,810,963) -36.0% Total Equity Total Liabilities & Shareholders Equity 2,416,882,011 2,452,993,239 (36,111,228) -1.5% 6,769,624,864 5,015,917,537 1,753,707,327 35.0% Capital increased indicating more investment by the owners The company has decided to reduce its dividends as a strategy for debt reduction due to the short and long term debts the company has undertaken Balance Sheet Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Balance Sheet Cash increase by 177% 300 000 000 250 000 000 200 000 000 150 000 000 Ряд1 100 000 000 50 000 000 0 2015 2014 Years Long Term Funding increase by 282% 2 500 000 000 2 000 000 000 1 500 000 000 Long Term Funding 1 000 000 000 500 000 000 0 2015 4 2014 Balance Sheet Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Balance Sheet Account Receivable 900 000 000 850 000 000 800 000 000 750 000 000 Ряд1 700 000 000 650 000 000 2015 2014 Net Sales 8 000 000 000 7 000 000 000 6 000 000 000 5 000 000 000 4 000 000 000 Ряд1 3 000 000 000 2 000 000 000 1 000 000 000 0 2015 5 2014 Balance Sheet Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Balance Sheet Тысячи Non Current assets Increase 2 500 000 2 000 000 1 500 000 Investments Fixed Assets 1 000 000 Other Assets 500 000 0 2015 2014 Total Liabilities Increase 2 500 000 000 2 000 000 000 1 500 000 000 Short term loan Long Term Funding 1 000 000 000 500 000 000 0 2015 6 2014 Balance Sheet Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Balance Sheet Owner's Equity 2 500 000 000 2 000 000 000 1 500 000 000 Capital & resrves retained earnings 1 000 000 000 500 000 000 0 2015 2014 • The owners increased the investment in the company by increasing capital • Even Though there was a net income. Yet, during the accounting period the company paid about 600m SAR in dividends which in turn reduced retained earnings in 2015 by 57% 7 Balance Sheet Vertical Analysis Item Current Assets 2015 Amount (SAR) Percent 2014 Amount (SAR) Percent Difference Comments Cash and bank balances 279,957,636 4.1% 101,006,685 2.0% Account receivable Amounts due from related parties 882,333,590 13.0% 739,364,628 14.7% The percentage of cash from total asstes has doubled and this can be 2.1% mainly attributed to the long term fund. It is a good thing that accounts receivable (even though they increased) yet -1.7% they decreased as a percantage of total assets 281,728,504 4.2% 137,728,024 2.7% 1.4%This increase is mainly attributed to rentals due from newly opened shops Inventory 2,016,265,250 29.8% 1,534,192,950 30.6% -0.8% Total Current Assets Non-Current Assets 3,460,284,980 51.1% 2,512,292,287 50.1% 1.0% Investments 318,467,050 4.7% 260,091,647 5.2% Fixed Assets 2,046,973,906 30.2% 1,641,000,670 32.7% Other Assets 943,898,928 13.9% 602,532,933 12.0% Total Non-Current Assets 3,309,339,884 48.9% 2,503,625,250 49.9% Total Assets Current Liabilities 6,769,624,864 100% 5,015,917,537 100% Short term loan 833,290,230 12.3% 465,692,323 9.3% current portion of long term fund 195,587,581 2.9% 307,357,934 6.1% Due to loans taken the short term loan as a percentage of Liablities and OE 3.0% has increased All other percentages of short term liabilities as a percentage of Liabilities and OE have decreased but they were mainly replaced by the huge increase -3.2% in the percentage of long term funding Accounts payable 570,495,843 8.4% 550,155,761 11.0% -2.5% other current liabilities 511,151,946 7.6% 603,847,059 12.0% -4.5% Total Current Liabilities Non-Current Liabilities 2,110,525,600 31.2% 1,927,053,077 38.4% -7.2% 0.0% Long Term Funding 2,163,460,629 32.0% 565,709,222 11.3% This long term fund represents the major part of liabilities and OE with a 20.7% huge increase of 20% End of service indemnities 78,756,624 1.2% 70,161,999 1.4% -0.2% Total Non-Current Liabilities 2,242,217,253 33.1% 635,871,221 12.7% 20.4% Total Liabilities Shareholders Equity 4,352,742,853 64.3% 2,562,924,298 51.1% The total liabilities represent the major part of the liabilities and OE in 2015 13.2% mainly due to the long term fund Capital & resrves 1,951,725,690 28.8% 1,378,278,314 27.5% retained earnings 447,720,167 6.6% 1,047,467,808 20.9% Total Shareholder Equity 2,399,445,857 35.4% 2,425,746,122 48.4% minority interest 17,436,154 0.3% 27,247,117 0.5% -0.3% Total Equity Total Liabilities & Shareholders Equity 2,416,882,011 35.7% 2,452,993,239 48.9% -13.2% 5,015,917,537 100% 8 6,769,624,864 100% -0.5% Even though horizontal analysis showed an increasing trend of non current assets it is obvious from vertical analysis that this increase as a percent of -2.5% total assets is more from cash and receivables than from fixed assets and 1.9% investments. The fixed assets and investments as a percentage of total assets experienced a decrease This indicates that in general even though assets are increasing the increase -1.0% in cash and receivables are more than increase in fixed assets. 0.0% 1.4% An overall decrease in owner equity as a percentage and an increase in liabilities as a percentage of liabilities and OE also mainly due to the long -14.3% term fund -12.9% Vertical Balance Sheet Vertical Balance Sheet 2015 Assets as a % of total Assets 2014 Assets as a % of Total Assets 100% 100% 90% 90% Other Assets 80% Other Assets 80% Fixed Assets Fixed Assets 70% 60% Investments 60% Investments 50% Inventory 50% Inventory 70% 40% Amounts due from related parties 30% 40% Amounts due from related parties 30% Account receivable Account receivable 20% 20% Cash and bank balances Cash and bank balances 10% 10% 0% 0% 2014 2015 • Even though horizontal analysis showed an increasing trend of assets it is obvious from vertical analysis that this increase as a percent of total assets is more from cash and receivables than from fixed assets and investments. • The fixed assets and investments as a percentage of total assets experienced a decrease • This indicates that in general even though assets are increasing the increase in cash and receivables are more than increase in fixed assets and investments. 9 Vertical Balance Sheet Vertical Balance Sheet 2014 Liabilities and O.E 2015 Liabilities and O.E 100% 100% 90% 90% 80% 80% 70% 70% 60% 60% Total Equity 50% Total Equity 50% Total Liabilities 40% Total Liabilities 40% 30% 30% 20% 20% 10% 10% 0% 2014 0% 2015 • An overall decrease in owner equity and an increase in liabilities as a percentage of liabilities and OE also mainly due to the loans taken by the company 10 Income Statement Horizontal Analysis Increase or (Decrease) during 2015 Item Year Ended Year Ended 31 March 2015 31 March 2014 Revenues Net Sales Direct Cost Amount (SAR) Percent 6,898,673,324 5,482,386,435 (5,111,496,492) (4,084,411,294) 1,397,975,141 1,416,286,889 25.8% (1,027,085,198) 25.1% Increase in net sales is a good sign for the company As sales increase the cost of goods sold also increases which is a normal sign 389,201,691 27.8% An increase in gross profit which is a good indication Gross Profit Expenses Selling and Marketing expenses 1,787,176,832 (301,366,415) (205,146,809) (96,219,606) 46.9% Administrative expenses (351,048,740) (246,873,655) (104,175,085) 42.2% Depreciation and amortization (288,908,161) (225,756,380) (63,151,781) 28.0% 11 Comments Total Expenses (941,323,316) (677,776,844) (263,546,472) 38.9% Income from operations 845,853,516 720,198,297 125,655,219 17.4% An increase in marketing expenses for example together with a jump in sales indicate that the marketing activities were effective in driving up sales .In general the expenses such as depreciation expenses have increased which can bedirectly attributed to the growth trend of the company and that it is increasing its assets Share in Earnings from associates 31,460,690 13,156,725 18,303,965 139.1% This represents income for other subsidiaries or companies that the firm is investing in and this increase is a good sign that the company is investing well financing charges (100,107,335) (50,421,618) (49,685,717) 98.5% These charges increased as share in earnings increased other income 54,817,844 130,622,937 (75,805,093) -58.0% Income before Taxes 832,024,715 813,556,341 18,468,374 2.3% Income Tax Income Before minority interest (19,707,110) (41,958,330) 22,251,220 -53.0% 812,317,605 771,598,011 40,719,594 5.3% Minority Interest (9,366,055) (244,518) (9,121,537) 3730.4% Net Income for the year 802,951,550 771,353,493 31,598,057 4.1% Net income has increased which is a good sign Income Statement Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Income Statement Cost of Sales Net Sales (6 000 000 000) 8 000 000 000 7 000 000 000 (5 000 000 000) 6 000 000 000 (4 000 000 000) 5 000 000 000 4 000 000 000 Ряд1 (3 000 000 000) Direct Cost 3 000 000 000 (2 000 000 000) 2 000 000 000 1 000 000 000 (1 000 000 000) 0 2015 2015 2014 0 Gross Profit 2 000 000 000 1 800 000 000 1 600 000 000 1 400 000 000 1 200 000 000 1 000 000 000 Gross Profit 800 000 000 600 000 000 400 000 000 200 000 000 0 2015 12 2014 2014 Income Statement Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Income Statement Increase in expenses Fixed Assets (400 000 000) 2 500 000 000 (350 000 000) 2 000 000 000 (300 000 000) (250 000 000) Selling and Marketing expenses (200 000 000) 1 500 000 000 Administrative expenses Fixed Assets Depreciation and amortization 1 000 000 000 (150 000 000) (100 000 000) 500 000 000 (50 000 000) 2015 0 2014 0 2015 2014 • An increase in marketing expenses for example together with a jump in sales indicate that the marketing activities were effective in driving up sales • An increase in depreciation expenses when compared to the increase in fixed assets can be directly attributed to the growth trend of the company and that it is increasing its assets 13 Income Statement Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Income Statement Share in Earnings from associates 35 000 000 Net Income for the year 810 000 000 805 000 000 30 000 000 800 000 000 795 000 000 25 000 000 790 000 000 20 000 000 785 000 000 Share in Earnings from associates 15 000 000 Net Income for the year 780 000 000 775 000 000 10 000 000 770 000 000 765 000 000 5 000 000 760 000 000 755 000 000 0 2015 2014 2015 2014 • The share in earnings from Associates represents income for other subsidiaries or companies that the firm is investing in and this increase is a good sign that the company is investing well. • Net income has increased which is a good sign 14 Income Statement Vertical Analysis Year Ended 31 March 2015 Item Revenues Amount Net Sales 6,898,673,324 Percent 100% Year Ended 31 March 2014 Amount (SAR) Percent Difference in % 5,482,386,435 100.0% 0.0% Direct Cost (5,111,496,492) 74.1% (4,084,411,294) 74.5% Decreasing the cost of goods as a percentage of -0.4% sales is a good sign Gross Profit Expenses 1,787,176,832 25.9% 25.5% 0.4% Increase of gross profit as a sales percentage is good 3.7% Increase in expenses with respect to sales is 0.6% consistent with the previous conclusion of a growth and investment trend of the company 1,397,975,141 Selling and Marketing expenses (301,366,415) 4.4% Administrative expenses (351,048,740) 5.1% (246,873,655) 4.5% 0.6% Depreciation and amortization (288,908,161) 4.2% (225,756,380) 4.1% 0.1% (205,146,809) Total Expenses (941,323,316) 13.6% (677,776,844) 12.4% 1.3% Income from operations Share in Earnings from associates financing charges other income Income before Taxes Income Tax Income Before minority interest Minority Interest 845,853,516 12.3% 720,198,297 13.1% -0.9% 31,460,690 (100,107,335) 54,817,844 832,024,715 (19,707,110) 0.5% 1.5% 0.8% 12.1% 0.3% 13,156,725 (50,421,618) 130,622,937 813,556,341 (41,958,330) 0.2% 0.9% 2.4% 14.8% 0.8% 0.2% 0.5% -1.6% -2.8% -0.5% 812,317,605 (9,366,055) 11.8% 0.1% 771,598,011 (244,518) 14.1% 0.0% -2.3% 0.1% 14.1% Even though the dollar amount of income with respect to sales has increased yet the percentage of net income to sales has decreased which can be attributed to the overall increase in expenses due to -2.4% growth operations Net Income for the year 15 Comments 802,951,550 11.6% 771,353,493 Income Statement Vertical Analysis Vertical Income Statement Direct Cost as a percentage of net sales Direct Cost as a percentage of net sales 100% 100% 90% 90% 80% 80% 70% 70% 60% 60% Net Sales 50% Net Sales 50% Direct Cost Direct Cost 40% 40% 30% 30% 20% 20% 10% 10% 0% 0% 2015 2014 • Decreasing the cost of goods as a percentage of sales is a good sign 16 Income Statement Vertical Analysis Vertical Income Statement 100% Vertical Analysis 100% Vertical Analysis 90% 90% 80% 80% Net Income for the year Net Income for the year 70% 70% Minority Interest Minority Interest 60% Income Tax Income Tax 60% other income other income 50% 50% financing charges financing charges 40% Share in Earnings from associates 30% 40% Share in Earnings from associates 30% Depreciation and amortization Depreciation and amortization Administrative expenses Administrative expenses 20% Selling and Marketing expenses 10% 20% Selling and Marketing expenses 10% 0% 0% 2014 2015 -10% • Increase in expenses with respect to sales is consistent with the previous conclusion of a growth and investment trend of the company • Even though the dollar amount of income has increased yet the percentage of net income with respect to sales has decreased which can be attributed to the overall increase in expenses due to growth operations 17 Ratio Analysis Ratio analysis has been done using 4 main Tests: Test of Profitability: To view the overall profitability of the firm which ensures a reasonable return to its owners and optimum utilization of its assets. It is a primary measure of the overall success of a company. Test of Liquidity: Helps in determining the liquidity position of the firm. A firm can be said to have the ability to meet its current obligations when they become due, which is measured by the help of liquidity ratios. Test of Solvency: Helps in assessing the long term financial viability of a firm, and ability to meet its obligations. Market Test: Relate the current market price of a share of stock to an indicator of the return that might accrue to the investor. 18 Ratio Analysis – Test of Profitability Nr. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 19 Ratios Particulars (2015) Net Income Return on Equity = Net = 802,951,550 Income / Average Average Stockholders' Equity Stockholders' Equity = (2,399,445,857 + 2,425,746,122)/2 Net Income = 802,951,550 Return on Assets = (Net Interest Expense (net of tax) Income + Interest Expense =0 (net of tax)) / Average Total Assests Average Total Assets = (6,769,624,864 + 5,015,917,537)/2 Return on Equity Financial Leverage = 33.3% Percentage = Return on Return on Assets Equity – Return on Assets = 13.8 % Earnings per Share (EPS) = Net Income /Average Number of Shares Outstanding for the Period Net Income = 802,951,550 Average Number of Shares Outstanding for the Period = 210,000,000 Cash Flow from Operating Quality of Income = Cash Activities Flow from Operating = 238,584,557 Activities / Net Income Net Income = 802,951,550 Net Income Profit Margin = Net Income = 802,951,550 / Net sales Net Sales = 6,898,673,324 Net Sales Revenue Fixed Asset Turnover = Net = 6,898,673,324 Sales Revenue / Average Average Net Fixed Assets Net Fixed Assets = (3,309,339,884 + 2,503,625,250)/2 Purpose This measure indicates how much income was earned for every dollar invested by the owners Many analysts consider this ratio as the best overall measure of a company’s profitability Financial leverage is the advantage or disadvantage that occurs as the result of earning a return on equity that is different from the return on assets Earnings per share is probably the single most widely watched financial ratio A ratio higher than 1 indicates high-quality earnings This ratio tells us the percentage of each sales dollar that is income This ratio measures a company’s ability to generate sales given an investment in fixed assets Values (2015) Values (2014) 33.3% 13.6% 34.7% 17.0% Al Othaim Markets Co - Values (2015) Remarks 22.5% The % is very good as an indication of a profitable business, even compared to Al Othaim 8.5% The % decreased from 2014 to 2015 due to the increase in total assets. Still a good indication of profitability even compared to Al Othaim 19.7% 17.7% 14.0% SAR 3.82 SAR 3.67 SAR 2.57 0.30 0.96 0.94 11.6% 2.37 14.1% 2.19 The % is high in 2015 but close to that of 2014, and higher than that of Al Othaim, which indicates that AlHokair depend on loans to fund their assets, that is risky The EPS increased a bit from 2014 to 2015 due to having same Nr. Of shares and slightly increased net income. It is better than that of Al Othaim by SAR 1.25 per share 2015 value is very low compared to 2014 and AlOthaim which is a very bad indication about the net income for 2015 3.8% The % was lower than that of 2014 but much better than Al Othaim 5.77 The value is not good compared to Al Othaim, whose value is more than double that of Al Hokair Ratio Analysis – Test of Liquidity Nr. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 20 Ratios Cash Ratio = Cash + Cash Equivalents / Current Liabilities Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities Particulars (2015) Purpose Cash & Cash Equivalents = 279,957,636 Current Liabilities = 2,110,525,600 This ratio measures the adequacy of available cash Current Assets = 3,460,284,980 Current Liabilities = 2,110,525,600 This ratio measures the ability of the company to pay current debts as they become due Quick Assets Quick Ratio = Quick Assets / = 1,435,157,408 Current Liabilities Current Liabilities = 2,110,525,600 Net Credit Sales Receivable Turnover = Net = 6,898,673,324 Credit Sales / Average Net Average Net Receivables Receivables = (882,333,590 + 739,364,628)/2 Days in Year Average Age of Receivables = 365 = Days in Year / Receivable Receivable Turnover Turnover = 8.51 Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Turnover = Cost of = 5,111,496,492 Goods Sold / Average Average Inventory Inventory = (2,016,265,250 + 1,534,192,950)/2 Days in Year Average Days’ Supply in = 365 Inventory = Days in Year / Inventory Turnover Inventory Turnover = 2.88 Cost of Goods Sold Accounts Payable Turnover = 5,111,496,492 = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Accounts Payable Average Accounts Payable = (570,495,843 + 550,155,761)/2 Days in Year Average Age of Payables = = 365 Days in Year / Accounts Accounts Payable Turnover Payable Turnover = 9.12 This ratio is like the current ratio but measures the company’s immediate ability to pay debts This ratio measures how quickly a company collects its accounts receivable This ratio measures the average number of days it takes to collect receivables. This ratio measures how quickly the company sells its inventory This ratio measures the average number of days it takes to sell the inventory This ratio measures how quickly the company pays its accounts payable This ratio measures the average number of days it takes to pay its suppliers Values (2015) Values (2014) 0.13 1.64 0.68 8.51 42.90 2.88 126.76 9.12 40.01 0.05 1.30 0.12 7.41 49.22 2.66 137.10 7.42 49.16 Al Othaim Markets Co - Values (2015) Remarks 0.23 The ratio is 0.13 to 1 which means that the cash in hand is not safe to pay for the current liabilities 0.82 The ratio is 1.64 to 1, which is considered safe that the company has good liquidity for the short term 0.25 The ratio is 0.68 to 1, which explains that AlHokair's immediate ability to pay debts is not safe, but better than 2014 and AlOthaim 214.07 8.51 Times, which is not good, considering that AlOthaim's turnover is much better 1.71 42.9 Days, which seems high even compared to that of AlOthaim 9.40 2.88 Times, which is not good being low even compared to that of AlOthaim 38.83 126.76 days,which is not good being high even compared to that of AlOthaim 5.43 9.12 Times, which is acceptable and higher than that of 2014 and AlOthaim 67.17 40.01 Days, which is acceptable being better than 2014 and AlOthaim Ratio Analysis – Test of Solvency and Market Test Nr. Ratios Particulars (2015) Purpose This ratio measures Total Liabilities Debt-to-Equity Ratio = the amount of = 4,352,742,853 1 Total Liabilities / liabilities that exists Stockholders’ Equity Stockholders’ Equity for each $1 invested = 2,399,445,857 by the owners Price/Earnings (P/E) Ratio = Current 2 Market Price Per Share / Earnings Per Share 21 Current Market Price Per Share = 101 Earnings Per Share = 3.82 This ratio measures the relationship between the current market price of the stock and its earnings per share Values (2015) 1.81 26.44 Values (2014) 1.06 25.89 Al Othaim Markets Co Values (2015) Remarks 1.80 The value is very high in 2015, even compared to 2014 which is not safe. However almost same value was noted for Al Othaim 20.86 The P/E ratio in 2015 suggests that the stock price is relatively high compared to earnings Conclusion Al Hokair seems well performing on the profitability level, where compared to its competitor “AlOthaim”, it has higher ratio % for Return on Equity and Return on Assets. It’s EPS is also good exceeding AlOthaim by SAR 1.25. These indications would attract investors to invest their monies in AlHokair’s stock. The draw backs in profitability would be the Financial leverage ratio that is high indicating that their earnings are volatile, also their Quality of income in 2015 was very low which was highly affected by the big reduction in Cash flow from Operating Activities. On the liquidity level, AlHokair’s current ratio indicates that they are good to pay their debts in the short period, but the cash ratio and quick ratio indicate that they cannot provide immediate payments for their debts. This means that AlHokair has sufficient assets to cover short-term debt obligations which indicates less risk for creditors. However, a lower liquidity ratio is generally preferred by shareholders because it indicates that assets are being used to fund and expand a company’s operations. 22 Conclusion Al Hokair’s Receivable Turnover and Average age of Receivables are relatively not good compared to AlOthaim, which indicates trouble with the company’s credit and collection policies. Al Hokair’s Inventory Turnover and Average Days’ Supply in Inventory are relatively not good compared to AlOthaim, which may cause problems since the longer inventory remains in a company’s warehouse, the more likely it will be outdated and subject to being obsolete. Al Hokair’s Accounts Payable Turnover and Average Age of Payables are relatively good compared with AlOthaim, which may put AlHokair in a better position regarding dealing with suppliers whom may favor AlHokair due to their better payment policies. 23 Conclusion Al Hokair’s Debt to Equity Ratio is very high being 1.81 which means that more assets are financed by debt than those financed by money of shareholders‘. The ratio increased from 2014 to 2015 by more than 70% which is alarming because it means that the percentage of assets that are financed by the debts is increasing. Al Hokair’s P/E ratio is higher than that of AlOthaim which means that the market values AlHokair’s earnings at a higher level. The relatively high P/E ratio in 2015 shows that investors may be willing to pay a higher share price because of growth expectations in the future. The high P/E ratio suggests that the stock price is relatively high compared to earnings, which may indicate that AlHokair’s shares are overvalued, but it could also mean that AlHokair deserves a premium on the value of its earnings due to superior management. Overall, Al Hokair had constant performance during 2014 and 2015 with high profitability and high net income, which may be tempting for investors, however their quality of income and the huge loan they acquired in 2015 are high risks that are important to be considered by investors. 24 Graphs Interpretations Thank You 25