Current and Charge: Electrical Conduction Basics
advertisement

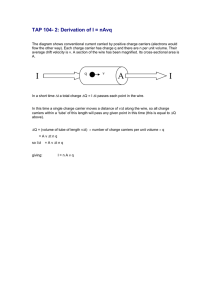
4.1 Current and charge Electrical conduction Electrical conduction: * is the movement of charge carriers, eg electrons * the rate of flow of charge is called the current and is measured in amperes or amps I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C 4.1 Current and charge Electrical conduction Electrical conduction: * is the movement of charge carriers, eg electrons * the rate of flow of charge is called the current and is measured in amperes or amps I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C 4.1 Current and charge Electrical conduction Electrical conduction: * is the movement of charge carriers, eg electrons * the rate of flow of charge is called the current and is measured in amperes or amps I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C 4.1 Current and charge Electrical conduction Electrical conduction: * is the movement of charge carriers, eg electrons * the rate of flow of charge is called the current and is measured in amperes or amps I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C 4.1 Current and charge Electrical conduction Electrical conduction: * is the movement of charge carriers, eg electrons * the rate of flow of charge is called the current and is measured in amperes or amps I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C 4.1 Current and charge Electrical conduction Electrical conduction: * is the movement of charge carriers, eg electrons * the rate of flow of charge is called the current and is measured in amperes or amps I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C Charge carriers: 1 Metals When a voltage is applied across a conductor delocalised electrons are attracted to the positive terminal 2. Insulators Electrons are firmly attached to atoms and can not be moved through the conductor 3. Semiconductors The number of Charge carriers available for conduction increases with temperature . Resistance decreases with temperature 4. Ions in solution can also be charge carriers Charge carriers: 1 Metals When a voltage is applied across a conductor delocalised electrons are attracted to the positive terminal 2. Insulators Electrons are firmly attached to atoms and can not be moved through the conductor 3. Semiconductors The number of Charge carriers available for conduction increases with temperature . Resistance decreases with temperature 4. Ions in solution can also be charge carriers Charge carriers: 1 Metals When a voltage is applied across a conductor delocalised electrons are attracted to the positive terminal 2. Insulators Electrons are firmly attached to atoms and can not be moved through the conductor 3. Semiconductors The number of Charge carriers available for conduction increases with temperature . Resistance decreases with temperature 4. Ions in solution can also be charge carriers Charge carriers: 1 Metals When a voltage is applied across a conductor delocalised electrons are attracted to the positive terminal 2. Insulators Electrons are firmly attached to atoms and can not be moved through the conductor 3. Semiconductors The number of Charge carriers available for conduction increases with temperature . Resistance decreases with temperature 4. Ions in solution can also be charge carriers Charge carriers: 1 Metals When a voltage is applied across a conductor delocalised electrons are attracted to the positive terminal 2. Insulators Electrons are firmly attached to atoms and can not be moved through the conductor 3. Semiconductors The number of Charge carriers available for conduction increases with temperature . Resistance decreases with temperature 4. Ions in solution can also be charge carriers 4.1 Current and charge Problem: A wire carries a current of 5mA for 15 mins. i) calculate the charge passing through the wire in this time, Ii) calculate the number of electrons passing through the wire each second I (Amp) Q Total charge = = Q t (coulomb) (second) Ne charge on an electron 1.6 x 10 Number of charge carriers -19 C Problem: A wire carries a current of 5mA for 15 mins. i) calculate the charge passing through the wire in this time, Ii) calculate the number of electrons passing through the wire each second Problem: A wire carries a current of 5mA for 15 mins. i) calculate the charge passing through the wire in this time, Ii) calculate the number of electrons passing through the wire each second Problem: A wire carries a current of 5mA for 15 mins. i) calculate the charge passing through the wire in this time, Ii) calculate the number of electrons passing through the wire each second Problem: A wire carries a current of 5mA for 15 mins. i) calculate the charge passing through the wire in this time, Ii) calculate the number of electrons passing through the wire each second Problem: A wire carries a current of 5mA for 15 mins. i) calculate the charge passing through the wire in this time, Ii) calculate the number of electrons passing through the wire each second