two or more cells connected together
advertisement
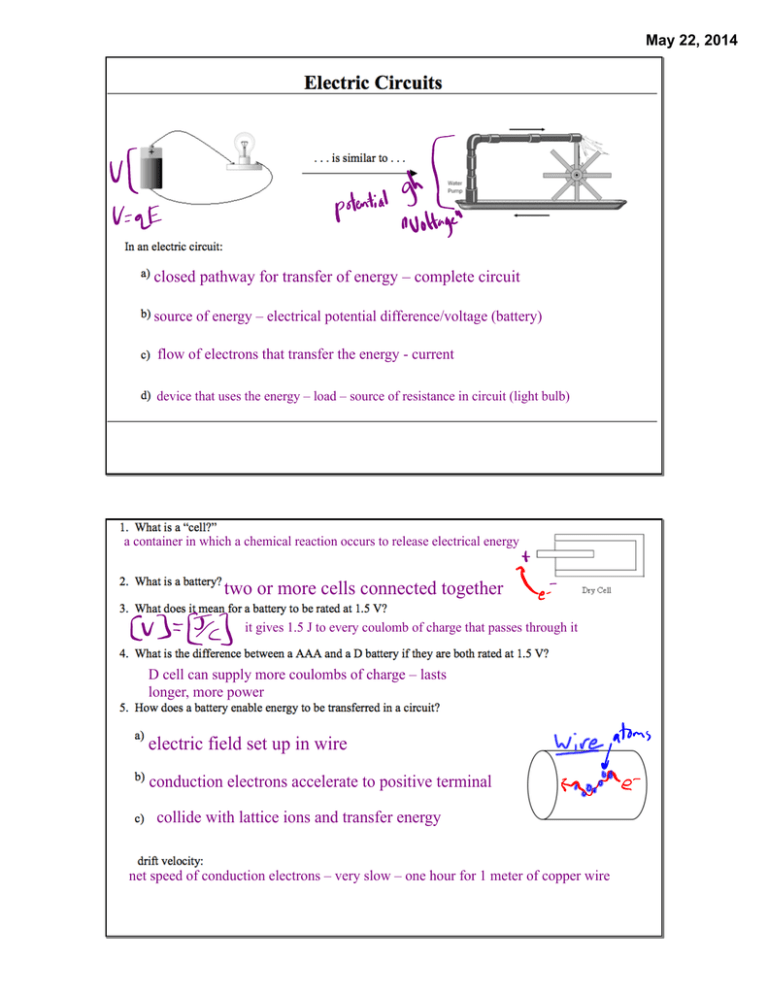
May 22, 2014 closed pathway for transfer of energy – complete circuit source of energy – electrical potential difference/voltage (battery) flow of electrons that transfer the energy - current device that uses the energy – load – source of resistance in circuit (light bulb) a container in which a chemical reaction occurs to release electrical energy two or more cells connected together it gives 1.5 J to every coulomb of charge that passes through it D cell can supply more coulombs of charge – lasts longer, more power electric field set up in wire conduction electrons accelerate to positive terminal collide with lattice ions and transfer energy net speed of conduction electrons – very slow – one hour for 1 meter of copper wire May 22, 2014 rate of flow of electric charge May 22, 2014 ratio of applied potential difference to current For a conductor at constant temperature, potential difference is proportional to current over a wide range of potential differences the resistance of these materials is constant over a wide range of applied voltages device whose resistance remains constant – obeys Ohm’s law device whose resistance changes – doesn’t follow Ohm’s law