Electricity – Practice B
advertisement

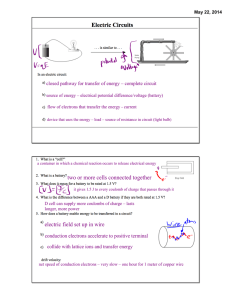
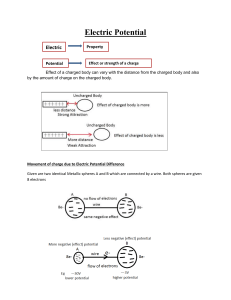
Electricity – Practice B Name ______________________________________________________ Reagan IB Physics Mr. Putnam Period _______ Date _____________________________________ This assignment goes along with Tsokos Chapter 5.4. Answer questions 1-­‐14 while reading the chapter. Attach a separate sheet of paper with the chapter review questions listed at the end of the page. 1. For electric current, write: a. a definition b. an equation c. the units (along with the abbreviation used) 2. If 8.5 x 1019 electrons move through a certain point in a wire each second, determine the current passing through the wire. 3. If the electrons in a conductor, such as copper, move freely like gas molecules in a container, explain why this random motion does not result in electric current. 4. The presence of an electric field inside a conductor accelerates the free electrons in the conductor. At a molecular scale, explain why electric current causes an increase in temperature of the conductor. 5. Define drift velocity. 6. Assume that for a typical metal, there are approximately 1028 free electrons per cubic meter and for a typical 100 W bulb circuit, the electric current measures 1 A. If the wire has a cross-­‐sectional area of 10-­‐6 m2 (a typical wire), we can calculate the velocity of the electrons making up the current as v = 0.0006 ms-­‐1. Explain why electrical current seems much faster in our experience with light switches. 7. What are the similarities and differences between thermionic emission and the photoelectric effect? 8. For electric resistance, write: a. a definition b. an equation c. the units (along with the abbreviation used) 9. Describe Ohm’s law in words, and show a graph (including labeled axes) that represents a ohmic material (a material that obeys Ohm’s law). 10. Does the filament in an incandescent light bulb obey Ohm’s Law? Explain your answer and under what circumstances the filament could be considered ohmic. 11. Explain which factors affect the resistance of a wire, along with a description of the relationship between each factor and resistance. 12. Explain what is meant by potential difference across a resistor. 13. Determine the current through the 40 Ω resistor in the circuit shown. 4 A 25 Ω 40 Ω 14. For electric power, write: a. a definition b. two different equations c. the units (along with the abbreviation used) Chapter Review Questions: Tsokos Chapter 5.4 problems 2, 4, 5, 8 -­‐ 13, 15 – 17, 19