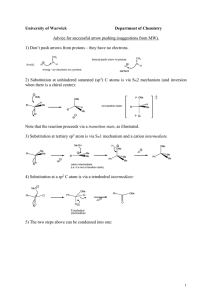
BIOAVAILABILITY AND METABOLISM STUDY OF POLYMETHOXYFLAVONOIDS 230th ACS National Meeting Natural Occurrence of PMFs • PMF: rich in citrus genus Particularly in the peel oil of orange and mandarin More than 20 PMFs isolated from different tissues of citrus plants www.fas.usda.gov/htp/horticulture/citrus.html PMF: Anti-inflammatory Agent • Scavenger of free radical species HO•, O2-, NO, etc. • Inhibitor of some enzymes Matrix MetalloProteinases: MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9 Other enzymes: PGE2, COX-2 and iNOS etc. PMF: Anti-inflammatory Activity • Activation of some transcription factors being down-regulated • Over expression of some protein mediators also being down-regulated Enzymes: COX, LOX, iNOS, myeloperoxidase etc. Cytokines: Interleukins (IL-1 and IL-6) and TNF- etc. PMF: Anti-cancer Property • Inhibition of NO and O2- generation and tumor promotion • Inhibition of tumor cell proliferation • • • • Human prostate, skin, mammary and colon carcinoma cell lines Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects on gastric cancer cells Disruptive effects on cell-cycle progression Human umbilical endothelial cell migration and proliferation • Inhibition of MMP production • Suppression of PGE2 production and COX-2 protein expression PMF: Anti-atherogenic Property • Reducing hepatic production of cholesterol • • Reduction of circulating LDL and VLDL Reduction of cardiovascular disease occurrence • Preventing atherosclerosis • inhibiting macrophage derived foam cell formation at the lesion site within a vessel wall Isolated PMFs from Sweet Orange Peel (H, OMe) OMe R8 O MeO MeO R3' (H, OMe) R3 (H, OH, OMe) R5 O (OH, OMe) Flavone examples: 5,6,7,4’-Tetramethoxyflavone, Sinensetin, Tangeretin, Nobiletin, 3methoxysinensetin, 3-methoxynobiletin and possibly dimethylmikanin Bioavailability of Polymethoxyflavones Nobiletin Bioavailability in Mouse Free Nobiletin in Mouse Plasma 450 Concentration (ng/ml) 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 -50 0 50 100 150 200 250 Time (min) 300 350 400 450 PMF Bioavailability in Horse PMF in Horse Plasma Concentration (ng/ml) 600 500 400 Nobiletin 300 Tangeretin 200 100 0 -100 0 10 20 Time (h) 30 40 ABSORPTION Solubility and Permeability • LYSA: LYophilisation Solubility Assay HT-solubility measurement included in the MDO system Different from classical shake-flask solubilty (THESA) method LYSA powders in amorphous form – higher values of solubility • PAMPA: Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeation Assay Transcellulare permeation based on passive diffusion, driven by a concentration gradient between donor and acceptor The small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum) is the major absorption site with the largest absorption area. PAMPA assay mimics these absorption conditions using an artificial phospholipid membrane PMF: Solubility and Permeability OMe MeO O LASA (g/ml) PAMPA (cm/s X 10-6) 1.02 OMe H OMe MeO O OH LASA (g/ml) PAMPA (cm/s X 10-6) 6 0.98 M 29 1.05 H 22 1.14 H 53 0.98 M 37 0.55 M MeO MeO OMe O OMe O OMe OMe MeO 19 O OMe OMe 1.62 H MeO MeO O OH MeO OMe O OMe O OMe OMe MeO O OMe 285 1.38 OH OMe H MeO MeO O OMe MeO OMe O OMe O OMe OMe OMe MeO O OMe 14 OH OMe 0.75 M MeO MeO O OH MeO OMe O OMe O OMe OMe MeO O MeO OMe 8 OMe OMe 0.93 M OMe MeO O MeO OMe O OH OMe O OMe OMe OMe MeO O OMe OMe OMe 0.9 M MeO O MeO MeO OH O OMe OH O OMe 32 Caco-2 of Some PMFs OMe MeO O OH OMe OMe MeO MeO O MeO O OMe MeO OH OMe O OMe O LASA (g/ml) 6 8 37 PAMPA M M M A to B 558 802 1700 B to A 507 535 1000 0.9 0.7 0.6 Caco-2 Papp Ratio: B to A A to B Note: 1) Papp > 100 (10-7 cm/s) high permeability 2) Ratio of B to A A to B OMe OMe OMe O MeO OMe OMe > 3: efflux liability Metabolism Study of Nobiletin Significance in Characterizing Metabolites Understanding metabolic pathway Identification of health beneficial entities Mechanism-based drug design Disease prevention and treatment Biotransformation Study of Tangeretin OMe OMe MeO rat liver MeO microsomes MeO O MeO HO OH O OH OMe MeO OMe O OMe OMe O MeO MeO O OMe O OMe O OMe OH OMe OH MeO O HO OMe O Major metabolites OH O Biotransformation Study of Nobiletin OMe OMe MeO O OMe MeO ver i l rat es m o crs mi ra t in OMe OMe MeO OMe O O OH viv ur ine o OH OMe MeO O OMe MeO MeO OMe O Major Metabolite OMe O Major Metabolite Synthesis of 3′-Demethylnobiletin Orange Peel Extracts Isolation R1 OMe MeO R1 R2 R2 OMe O R3 MeI, Acetone MeO MeO K2CO3 OH O O R3 OMe NaOH(aqu), EtOH MeO MeO reflux,16 h MeO OH OMe O OMe O Gardenin O H OBn OMe 50% NaOH (aqu) 25 oC, 16 h OMe MeO OH OMe OBn MeO OMe O OMe OMe H3PO4, EtOH MeO 90 oC, 72 h O MeO OMe O OBn Syntheses of Potential Metabolites OMe OMe MeO O OBn MeO OMe OMe MeO i) DDQ, Dioxane,reflux ii) H2, Pd-C, EtOAc O MeO OMe O OMe O 3'-demethylnobiletin Also synthesized: OH OMe MeO O OMe OH OMe MeO O OH MeO MeO OMe O 4'-demethylnobiletin OMe O 3',4'-didemethylnobiletin OH Nobiletin Metabolites in Mouse Plasma Minimum four metabolites: • • Minimum three mono-demethylnobiletins Di-demethylnobiletin as a minor metabolite 1 2 3 4 5 (Nobiletin) Retention Time (min) Peak Time MW 1 0.86 374 2 1.05 388 3 1.13 388 4 1.26 388 5 1.71 402 Nobiletin Metabolites in Mouse Urine Minimum five metabolites: • • • 3′ or 4′-demethylnobiletin or both (major) Minimum three other mono-demethylnobiletins Di-demethylnobiletin metabolite (Nobiletin) 1. 374 2. 388 3. 388 4. 388 5. 388 6. 402 Nobiletin: Biotransformation in Mice • Nobiletin metabolization in mice Minimum 4 metabolites in plasma Minimum 5 metabolites in urine • Major metabolite in urine 3’-demethylnobiletin • Minor metabolites 4’-demethylnobiletin in urine 3’ and 4’-demethylnobiletin in plasma Other mono- and di-demethylated nobiletin Thank you for your attention!