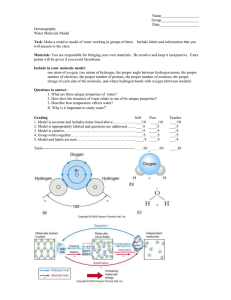
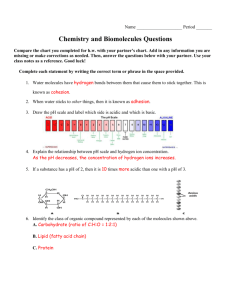
Biochemistry Do Now: Try to organize the following terms next to their correct definition: Ion, Electron, Neutron, Atom, Molecule, Element, Proton. _____________: The smallest bit of ordinary matter. Cannot be broken into smaller pieces. _____________: A group of atoms held together by chemical bonds. The smallest unit that can take part in a chemical reaction. _____________: A subatomic particle found in the nucleus of atoms. Positive (+) charge. _____________: A subatomic particle found in the nucleus of atoms. Neutral (=) charge. _____________: A subatomic particle around the nucleus of an atom. Negative (-) charge. _____________: A substance made entirely of one type of atom on the Periodic Table. _____________: A type of molecule with a net (total) electrical charge, in other words an unequal number of protons and electrons. Organic molecules always contain Carbon (and hydrogen) molecules, whole inorganic molecules usually do not. The most common elements (atoms) found in organisms are: Sulfur, Phosphorus, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon, and Hydrogen. (S.P.O.N.C.H.) How to write a Molecular Formula (Fill in top boxes from notes) Structural formula Molecular formula C2O2H4 Molecules can be written this way to communicate the type and number of atoms and how they are connected. Molecules can be written this way to simply communicate the number and type of atoms. (The examples above are the same molecule) From the structural formulas below, write in the molecular formula and whether it is organic or inorganic. Structural Formula Molecular Formula H2O CH3Cl Organic or Inorganic NH3 CO2 C2H6 NO3 C6H6 C6H12O6 Basic Organic Molecules Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The hydrogen to oxygen ratio is ~2:1. Example: Glucose is a simple carb. (C6H12O6). Carbs are basically a bunch of simple sugars (like glucose) strung together to form a large macromolecule (like starch). This is why carbs make you fat! Monosaccharide = Small, single sugar molecule Polysaccharide = Chains of complex sugars Carbohydrates always end in the suffix -ose. Ex: Glucose, sucrose, fructose. Carbs are used as a short term energy source. Honey, fruit, seeds, bread, pasta, or anything with sugar is made of carbs. Lipids Lipids are also made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, but the ratio is hydrogen to oxygen is greater than 2:1. Lipids are mostly found in fats, waxes, oils, and steroids. They provide long term energy storage and insulation. (I.E. FAT) Lipids are made of long chains of hydrocarbons, with a carboxyl head. They are also hydrophobic, which is why oil and water don’t mix. Phospholipids are especially important as they make up all cell membranes. Phospholipids lined up in a lipid bilayer. While the ‘tail’ is hydrophobic, the ‘head’ is hydrophilic. Together it can block almost any molecule. Proteins Proteins are what muscles (meat) and many other body structures are made of. Fun fact: They cannot be turned into fat! Proteins are long chains made up of amino acids. They can be combined in almost endless ways to make a variety of structures. (Also known as polypeptides for the peptide bonds connecting them.) Amino acids are made up of an amino group (H2N), a carboxyl group (CHO2), and a side chain (Labeled R). Some examples of common proteins: Hormones, body structures, and enzymes. (Regulates chemical reactions) Nucleic Acids Nucleotides are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Nucleic acids form long strings of DNA or RNA, usually found in the cell nucleus. This string of nucleic acid forms genetic material, which carries all the instructions for building life.