Contract law
advertisement

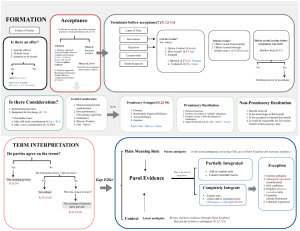
Formation, Content, Execution, Breach of Contract According to the principle of freedom of contract, parties can also make contracts that are not included in those specifically regulated by the law (so called atypical contracts) if such contracts are directed to the realization of interests worthy of protection according to the legal order. Thus scholars use to say that private autonomy is a source of law. The existence of agreement is determined objectively on the basis of the parties’ words and actions. The objective evidence of agreement is traditionally the existence of an offer and of corresponding acceptance (art. 1326). Offer An offer is an expression of willingness to contract without further negotiation. Offer needs to be comunicated to the other party. Offer and invitation to treat. Invitation to treat is not an offer. It’s just a manner to stimulate interest , to achieve more information and to go on with negotiation. Invitation to treat and advertising Generally speaking advertisement, brochures ecc. are invitations to treat. Acceptance Acceptance is the answer to a specific offer, made with the intention to be bound. Acceptance needs to be comunicated to the other party. Acceptance needs to be conform to the offer. Acceptance and Counter Offer An acceptance must be unconditional and compliant with the exact terms proposed by the offeror. When the offeree alters the terms contained in the offer or adds a new term, that response is not an acceptance. It constitutes a counter offer. Cases of termination of offers: - Lapse of time. Usually offers have a determined duration - Death of the offerer - Revocation. An offer may be expressly termined by offeror. It’s for the parties to make their agreement and ensure that the terms are sufficiently certain to be enforced. Courts will generally refuse to fill any gap. Therefore courts, in practice, fill the gaps if some evidence is available. In particular courts can take in to account commercial practice and previous performance. As general principle when an essential term is missing the agreement will be too uncertain to be enforceable. When the law states that a contract is enforceable only if recorded in a particular way, the rule is described as a requirement of form. The general rule is that there is no requirement that contracts be made in writing and parties may decide wheter written evidence is necessary. In commercial dealing written evidence is almost inevitably available taking into account the complexity and the value of obligations. Contracts need to be complaint with imperatives norms. In some case there could be also a controll of the substantive content of contract. Controll of unfair clauses Exemption clauses(such as clauses which exclude or limit liability for breach of contract) are generally considered to be unfair. Parties are bound by the terms of their contract (art. 1372). A contract is legally enforceable if there’re mechanisms of enforceament of contractual obligations. It is important to identify the standard of performance required in relation to each contractual obligation since a failure to perform to the required standard constitutes a breach. Every breach of contract will give rise to a right to claim damages (art. 1218). A breach of contract will occur where, without lawful excuse, a party either fails or refuses to perform a contractual obligation- The Italian civil code recognizes the dissolution of the contract” due to nonperformance (art. 1453), impossibility (art. 1463)and, finally, excessive onerousness (art. 1467). A contract is discharged by the perfect performance by both parties. A contract could be also discharged by agreement between parties.