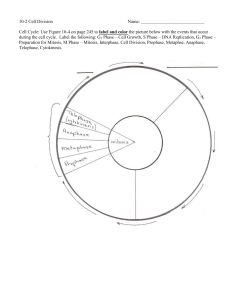
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Directions: Read the paragraph below about cell cycle and answer questions #1-7. the THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates itself. These events can be divided into two main parts: interphase and the mitotic phase. Interphase occurs between cell division phases and includes G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase. During interphase the cell is forming and carries on with its normal metabolic functions. During the mitotic phase (also called M phase for mitosis), the cell is replicating itself. The cell cycle is an essential process by which a singlecell fertilized egg develops into a mature organism and the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are formed. 1. What is meant by the cell cycle? 2. In what type of cells --- prokaryotes or eukaryotes --- does the cell cycle occur? 3. Name the 2 main PHASES of the cell cycle. 1) 4. __________ is in between the times when a cell is dividing. 5. What is occurring in a cell during interphase? 6. What is occurring during the mitosis phase (M Phase)? 7. Name three things that form as a result of the cell cycle. 1. 2. 3. 1 2) Directions: Read the paragraphs below about interphase and answer questions #8-17. INTERPHASE Interphase is a phase of the cell cycle during which cell division is NOT occurring. During interphase, the cell obtains nutrients and duplicates (copies) its chromatids (genetic material). The genetic material or chromatids are located in the nucleus of the cell and are made of the molecule DNA. 8. What process NEVER occurs in interphase? 9. Cells obtain ______________ and duplicate or copy their ___________ or genetic material during interphase. Most eukaryotic cells spend the majority of their lifetime in interphase. For example, human skin cells, which divide about once a day, spend roughly 22 hours in interphase. About 90 percent of cells are in interphase. Some cells, such as nerve cells, can stay in interphase for decades. There are 3 parts of interphase: G1 (growth 1 in which the cell creates organelles and begins metabolism), S phase (DNA synthesis in which the chromosomes of the cell are copied), and G2 (growth 2 in which the cell grows in preparation for cell division). 10. In what PHASE do most cells spend the majority of their lifetime? 11. How often do human skin cells divide each day? 12. How many hours per day is a human skin cell in interphase? 13. What type of cell may spend decades in interphase instead of dividing? 14. Name the 3 stages in interphase. 1) 2) 15.What does G1 stand for and what occurs in this stage? 16.What does S stand for and what occurs in this stage? 17.What does G2 stand for and what occurs in this stage? 2 3) Directions: Read the paragraphs below about mitosis and cytokinesis and answer questions #18-26. MITOSIS & CYTOKINESIS After the G2 phase of interphase, the cell is ready to start dividing. The nucleus and nuclear material (chromosomes made of DNA) divide first during the stage of the cell cycle known as MITOSIS. Mitosis is the process in which a eukaryotic cell (cell containing a nucleus) separates its nucleus. 18. What follows the G2 phase? 19. What part of the cell is actually dividing in mitosis? Mitosis is generally followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm and cell membrane. This results in two identical cells (both have an identical set of chromosomes) with an equal distribution of organelles and other cellular components. These two identical cells are called daughter cells. The mitotic (M) phase and cytokinesis (C phase) together are called cell division. 20. What process follows mitosis? 21. The nucleus is divided during _____________, while cytoplasm of the cell is divided during _____________. 22. How do the two new cells compare with each other? 23. The two new cells are called _____________ cells. The process of mitosis (division of the nucleus) is divided into four stages (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase). Immediately following mitosis, the cell membrane must also divide. This division of the cell membrane and cytoplasm is cytokinesis. Animal cells divide the cytoplasm by constricting the cell membrane in the middle to form a cleavage furrow. Plant cells form a cell plate in the center to divide the cytoplasm. There is only one cell at interphase, but there are two identical cells after cytokinesis. 24. Name the 4 mitotic stages. 1) 2) 3) 25. How does cytokinesis occur in an animal cell? 26. How does cytokinesis occur in a plant cell? 3 4) Directions: Read the paragraphs below about the stages of mitosis and answer questions #27-35. The Stages of Mitosis Prior to mitosis (during interphase), the genetic material is called chromatin and can NOT be clearly seen because it isn’t tightly coiled. When prophase (the first stage of mitosis) begins, the DNA molecules are progressively shortened and condensed by coiling, to form visible chromosomes. Also during prophase, enzymes break down the nuclear membrane and nucleolus so they are no longer visible, and spindle fibers form which will attach to the chromosomes. At metaphase, the spindle fibers attach themselves to the centromeres of the chromosomes; the centromeres hold together the chromosome pairs. The spindle fibers align the chromosomes at the equator (middle of the cell). Anaphase is the next stage. The spindle fibers shorten and the centromere splits separating the two sister chromatids. During telophase, the chromosome pairs (chromatids) are pulled to opposite poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope and nucleolus reform before the chromosomes uncoil. The spindle fibers disintegrate. 27. Genetic material is called ______________ during interphase and IS / IS NOT clearly visible. 28. What makes the chromosomes become visible during prophase? 29. What is used to help break down the nuclear membrane? 30. Besides the nuclear membrane, what else is broken down during prophase? 31. What forms during prophase to LATER attach and move chromosomes? 32. Doubled chromosomes are held together by the _____________. 33. Where do chromosomes line up during metaphase? 34. During what stage are sister chromatids separated and moved to opposite ends of the cell? 4 35. Name 4 things that happen during telophase. a. b. c. d. Directions: **Use page 285 in your textbook for reference**The picture below represents plant cells in different stages of the cell cycle. In the table at the bottom of the page, identify the stage of the cell cycle for each numbered plant cell. #1 has been completed for you as an example. Answer choices include the following: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, or telophase. Remember you may use metaphase more than once. Look around…do you see any others that look like #1?? 1. Metaphase 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Go to next page….one more thing to do to complete this assignment!!! 5 Directions: In the blank space below, draw, color, and label the cell cycle for an animal cell. Be sure to include the name of each stage, as well as a description of what is happening in each stage. Use the diagram in your Biology book on page 285. Your cell pictures should look like the animated pictures, not the microscope pictures. Color it just as you see it in the textbook (ex: red and yellow chromosomes, green spindle fibers, etc.) Example: This is what anaphase looks like on pg. 285 of your textbook. When you draw anaphase, your picture should look like this (the animated picture), NOT like this (the microscope picture). 6