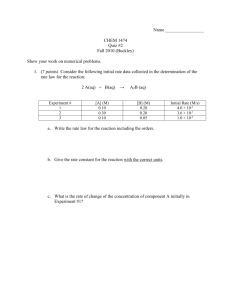
Reaction Rate Reaction Rate In chemistry we can have Slow and Fast reactions… Reaction Rate Example of slow reactions… Example of fast reactions… Zinc + Hydrochloric Acid Concrete setting Rust forming Burning Reaction Rate But is not always enough to know just how fast or slow a reaction is…. Examples? Sometimes we need to know exactly how fast a reaction goes, and how long it will take to be finished Reaction Rate! Reaction Rate Measure of the change that happens in a single unit of time The rate of reaction is found by measuring the amount of a reactant used up per unit of time, or the amount of a product produced per unit of time. Let`s get Practical!!!!! Reaction Rate Reactant Concentration Factors affecting the rate of reaction Temperature Catalyst Surface area Reaction Rate – changing the rate Changing the reactant concentration Lets make a graph Reaction Rate – changing the rate A reaction goes faster when the concentration of a reactant is increased Reaction Rate – changing the rate Changing the temperature Why do we use the fridge? A reaction goes faster when the temperature is raised Oh dear! The Oven was too hot… Reaction Rate – changing the rate Lets make a graph Reaction Rate – changing the rate A rate of reaction increases when the surface area of a solid reactant is increased Reaction Rate – changing the rate What is a catalyst? Substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction, but remains chemically unchanged itself Reaction Rate – changing the rate Manganese (IV) oxide acts as a catalyst for the reaction. Why is that “Raw liver” acts as a catalyst to? ENZYMES!!!!! Reaction Rate – changing the rate Reaction Rate – collision theory Do not Forget to relate the reaction rate with the particle collision theory… • The particles collide with each other • The collision must have enough energy to be successful. In other words, enough energy to break bonds to allow reaction to occur. COLLISION THEORY The rate of reaction depends on how many successful collisions there are in a given unit of time. Reaction Rate – explained by collision theory Changing the reactant concentration Reaction Rate – changing the rate Changing the temperature Reaction Rate – changing the rate Reaction Rate – changing the rate Reaction Rate – changing the rate Reaction Rate – changing the rate