Tesla Company Analysis: History, Market, and Future Growth
advertisement

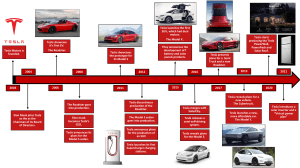
Tesla Graham MacWilliams and Aloke Desai History Founded in 2003 by Elon Musk, Martin Eberhard, and Marc Tarpenning March 2008- Tesla begins production of Roadster. Eventually sells 2,150 of Roadsters. June 2008- Announce Model S Jan 2010- Tesla registers for an IPO May 2010- Tesla buys former GM factory in Fremont, CA and Toyota signs deal to cooperate in EV development The Macro Outlook Electric car sales have increased 228% in last year alone 17,000 in 2011 compared to $38,000 in 2012 Tesla essentially started the electric car market in the United States (Volt and Leaf didn’t exist before) EV market has been trailing off $10,000 tax rebate for EV cars this next year under the Obama administration Makes EV cars more competitive Why Tesla? Biggest opportunity for growth Elon Musk’s proven leadership (PayPal and SpaceX) Appleizing the car industry New form of selling cars with no dealerships Prove to transform the market, first to produce electric cars relatively cheaply Model S Announced in 2008 Released this past summer The specs of a sports car while still being completely electric Competitively price—starts at $49,000 Equipped with some of most the advanced technology— 17’’ screen Voted car of the year by Autmobile.com Room for Growth Stock is so low because Tesla lost $1 billion on the Roadster Most don’t know it was planned Competitive price can allow for unlimited growth, especially in countries like China EV market is constantly expanding, Tesla leads the market with very few legitimate competitors Tesla plans to release Model X (cheaper, mini-SUV) where they start making profits Valuation Measures Historical Information Comparison with Market Competitors Main competitor is Fisker Karma starts at $96,000 Repeated troubles safety-wise Chevy and Nissan both have Evs, but neither are sports cars Sales of both are down Main Concerns Lost money on the Roadster Analysts limit value of EV market Production capacity Questions ?