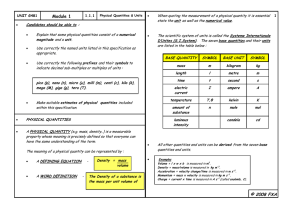
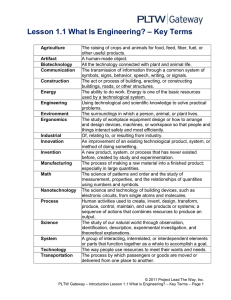
AS Physics : Base and derived units Physics is the science of the material world, and one of its main components is the measurement of aspects of that world. Every measurement involves the usage of a unit; it is this part of the measurement that defines what the numbers refer to. All units may be simplified down so that they are made up of one or several base units. The quantities that these units describe are the fundamental quantities of physics – all quantities can be defined in terms of these seven units. In the case of each base unit, there are alternative scales that may be used (e.g. Celsius or Fahrenheit as opposed to Kelvin for temperature), but uses of these alternatives are limited. The names and symbols described below are known as SI units – they are recognised and standardised around the world. Base and Derived Units Base Derived Metres - m Coulomb - C Amperes - A Volt - V Kelvin – K Newton - N Kilogram - kg Pascal - Pa Second – s Watt - W Candela – cd Ohm - Ω Mole - mol Joule - J Unit Prefixes Power 109 106 103 10-3 10-6 10-9 10-12 Prefix giga Mega Kilo milli micro nano pico Symbol G M k m μ n p The unit for a particular measurement can easily be substantiated from the equation. The equation can be arranged, then simplified, before substituting in the units for their corresponding symbols left in the simplified equation. Work out the base units for the derived units given in the table above. GJ2008.