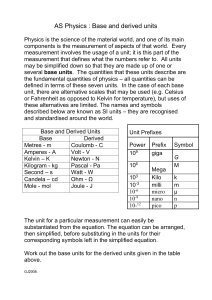
Measurement in everyday life Measurement of mass Measurement of volume Measurement in everyday life Measurement of length Measurement of temperature Need for measurement in physics To understand any phenomenon in physics we have to perform experiments. Experiments require measurements, and we measure several physical properties like length, mass, time, pressure etc. temperature, Experimental verification of laws & theories also needs measurement of physical properties. Physical Quantity A physical property that can be measured and described by a number is called physical quantity. Examples: • Mass of a person is 65 kg. • Length of a table is 3 m. • Area of a hall is 100 m2. • Temperature of a room is 300 K Types of Physical Quantities 1. Fundamental quantities: The physical quantities which do not depend on any other physical quantities for their measurements are known as fundamental quantities. Examples: • Mass • Length • • Time Temperature Types of Physical Quantities 2. Derived quantities: The physical quantities which depend on one or more fundamental quantities for their measurements are known as derived quantities. Examples: • • Area Volume • • Speed Force Units for measurement The standard used for the measurement of a physical quantity is called a unit. Examples: • metre, foot, inch for length • kilogram, pound for mass • second, minute, hour for time • fahrenheit, kelvin for temperature Characteristics of units Well – defined Suitable size Reproducible Invariable Indestructible Internationally acceptable CGS system of units This system was first introduced in France. It is also known as Gaussian system of units. It is based on centimeter, gram and second as the fundamental units of length, mass and time. MKS system of units This system was also introduced in France. It is also known as French system of units. It is based on meter, kilogram and second as the fundamental units of length, mass and time. FPS system of units This system was introduced in Britain. It is also known as British system of units. It is based on foot, pound and second as the fundamental units of length, mass and time. International System of units (SI) In 1971, General Conference on Weight and Measures held its meeting and decided a system of units for international usage. This system is called international system of units and abbreviated as SI from its French name. The SI unit consists of seven fundamental units and two supplementary units. Seven fundamental units Definition of metre The metre is the length of the path travelled by light in a vacuum during a time interval of 1/29,97,92,458 of a second. Definition of kilogram The kilogram is the mass of prototype cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy preserved at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, at Sevres, near Paris. Prototype cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy Definition of second One second is the time taken by 9,19,26,31,770 oscillations of the light emitted by a cesium–133 atom. Two supplementary units 1. Radian: It is used to measure plane angle θ = 1 radian Two supplementary units 2. Steradian: It is used to measure solid angle Ω = 1 steradian Rules for writing SI units 1 Full name of unit always starts with small letter even if named after a person. • newton • ampere • coulomb not • Newton • Ampere • Coulomb Rules for writing SI units 2 Symbol for unit named after a scientist should be in capital letter. • N for newton • A for ampere • K for kelvin • C for coulomb Rules for writing SI units 3 Symbols for all other units are written in small letters. • m for meter • kg for kilogram • s for second • cd for candela Rules for writing SI units 4 One space is left between the last digit of numeral and the symbol of a unit. • 10 kg • 5N • 15 m not • 10kg • 5N • 15m Rules for writing SI units 5 The units do not have plural forms. • 6 metre • 14 kg • 20 second • 18 kelvin not • 6 metres • 14 kgs • 20 seconds • 18 kelvins Rules for writing SI units 6 Full stop should not be used after the units. • 7 metre • 12 N • 25 kg not • 7 metre. • 12 N. • 25 kg. Rules for writing SI units 7 No space is used between the symbols for units. • 4 Js • 19 Nm • 25 VA not • 4Js • 19 N m. • 25 V A. SI prefixes Factor Name Symbol Factor Name Symbo l 1024 1021 yotta zetta exa peta tera giga Y Z E P T G 106 103 mega M kilo k 102 101 hecto h deka da 1018 1015 1012 109 10−1 10−2 deci centi milli micro nano pico d c m μ n p 10−15 10−18 femto f atto a 10−21 10−24 zepto z yocto y 10−3 10−6 10−9 10−12 Use of SI prefixes • 3 milliampere = 3 mA = 3 x 10−3 A • 5 microvolt = 5 μV = 5 x 10−6 V • 8 nanosecond = 8 ns = 8 x 10−9 s • 6 picometre = 6 pm = 6 x 10−12 m • 5 kilometre = 5 km = 5 x 103 m • 7 megawatt = 7 MW = 7 x 106 W Some practical units for measuring length 1 micron = 10−6 m Bacterias 1 nanometer = 10−9 m Molecules Some practical units for measuring length 1 angstrom = 10−10 m Atoms 1 fermi = 10−15 m Nucleus Some practical units for measuring length Astronomical unit = It is defined as the mean distance of the earth from the sun. 1 astronomical unit = 1.5 x 1011 m Distance of planets Some practical units for measuring length Light year = It is the distance travelled by light in vacuum in one year. 1 light year = 9.5 x 1015 m Distance of stars Some practical units for measuring area • Acre = It is used to measure large areas in British system of units. 1 acre = 208’ 8.5” x 208’ 8.5” = 4046.8 m2 • Hectare = It is used to measure large areas in French system of units. 1 hectare = 100 m x 100 m = 10000 m2 • Barn = It is used to measure very small areas, such as nuclear cross sections. 1 barn = 10−28 m2 Some practical units for measuring mass 1 metric ton = 1000 kg Steel bars 1 quintal = 100 kg Grains Some practical units for measuring mass 1 pound = 0.454 kg 1 slug = 14.59 kg Newborn babies Crops Some practical units for measuring mass • 1 Chandrasekhar limit = 1.4 x mass of sun = 2.785 x 1030 kg • It is the biggest practical unit for measuring mass. Massive black holes Some practical units for measuring mass • 1 atomic mass unit = 1 12 x mass of single C atom • 1 atomic mass unit = 1.66 x 10−27 kg • It is the smallest practical unit for measuring mass. • It is used to single atoms, proton and measure neutron. mass of Some practical units for measuring time • 1 Solar day = 24 h • 1 Sidereal day = 23 h & 56 min • 1 Solar year = 365 solar day = 366 sidereal day • 1 Lunar month = 27.3 Solar day • 1 shake = 10−8 s Seven dimensions of the world Fundamental Quantities Dimensions Length L Mass M Time T Temperature K Current A Amount of substance N Luminous intensity J THANK YOU