ANALYZING INDUSTRY COMPETITION Porter's Five Forces Model
advertisement
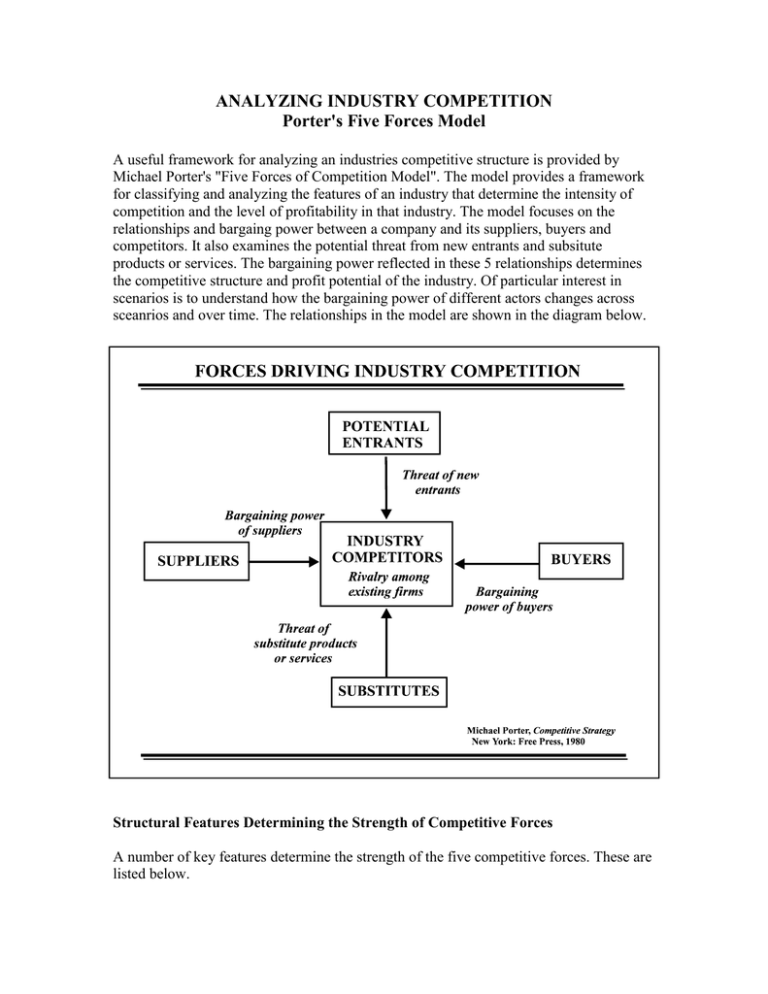
ANALYZING INDUSTRY COMPETITION Porter's Five Forces Model A useful framework for analyzing an industries competitive structure is provided by Michael Porter's "Five Forces of Competition Model". The model provides a framework for classifying and analyzing the features of an industry that determine the intensity of competition and the level of profitability in that industry. The model focuses on the relationships and bargaing power between a company and its suppliers, buyers and competitors. It also examines the potential threat from new entrants and subsitute products or services. The bargaining power reflected in these 5 relationships determines the competitive structure and profit potential of the industry. Of particular interest in scenarios is to understand how the bargaining power of different actors changes across sceanrios and over time. The relationships in the model are shown in the diagram below. Structural Features Determining the Strength of Competitive Forces A number of key features determine the strength of the five competitive forces. These are listed below. Threat of Entry (Barriers to Entry & Reaction of Existing Competitors) Economies of scale and economies of experience Absolute cost advantage Capital requirements Product / service differentiation Switching costs for customers to change supplier Access to distribution channels Government, legal or regulatory barriers Degree of expected retaliation from existing competitors Threat of Substitutes (Products and Services) Buyer propensity to buy substitute products or services Relative price performance of substitutes Quality of subsitute product or service Switching costs Bargaining Power of Buyers Or Suppliers (same factors) Percentage of total buyer companies costs (how important is product in buyers cost structure?) Product / service differentiation (more buyer power for commodities or standard services) Competition between buyers for resource (buyer has less power for scarce resource) Size and concentration of buyer group vs supplier group Buyers switching costs Buyers information (greater buyer power with full demand & price information) Threat of backward integration by buyer or forward integration by supplier Intensity of Rivalry Among Existing Firms Diversity of competitors Concentration (dominance by a few firms usually results in less intensive rivalry) Industry growth (slow growth increases rivalry) Fixed costs (high fixed costs increases competition for market share) Product / service differentiation (high rivalry for commodities or standard services) Strategic stakes (long term commitment to industry) Exit barriers (high exit barriers discourage excess capacity from leaving)