carbo

Monosaccharides and
Disaccharides
The elements which make up carbohydrates are:
•Carbon
•Hydrogen
•Oxygen
(C)
(H)
(O)
Monosaccharides
-Single Sugar-
Monosaccharides are:
•Sweet tasting
•Soluble in water
•Reducing sugars
These are the basic building blocks of other carbohydrates of which are the reducing sugars:
•Glucose
•Fructose
The Formula for glucose is
C
6
H
12
O
6
Disaccharides
-Double Sugars-
•May be non-reducing
•Sweet tasting
•Water soluble
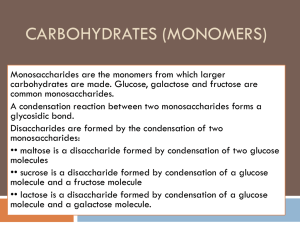
Disaccharides are formed by CONDENSATION REACTION of 2
Monosaccharides, the bond is called a glycosidic bond.
•Sucrose
•Maltose
Condensation Reactions
The chemical reaction that links monosaccharides together to produce polymers (disaccharides etc) is called a
CONDENSATION REACTION .
Examples include:
• 2 glucose molecules to form maltose
• A glucose and a fructose to form sucrose
2 Glucose to form Maltose
+
Condensation H
2
O
Hydrolysis
A Glucose and a Fructose to form
Sucrose
+
Condensation H
2
O Hydrolysis
Summary
So…
CLASSIFICATION: The basic sugar unit = the saccharide
•1 sugar unit = Monosaccaride
•2 sugar units = Disaccharide
Examples of Monosaccharides: Glucose, Fructose
Examples of Disaccharides: Maltose, Sucrose
These are formed by CONDENSATION REACTIONS
To reverse the reaction it is called HYDROLYSIS