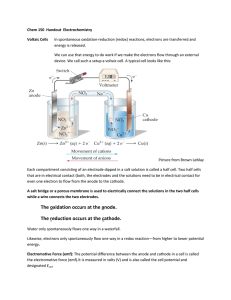
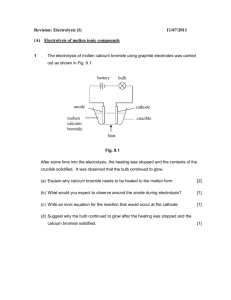
TAREK S. ELHAGE Electrolysis-Past papers questions IGCSE - CHEMISTRY Electrolysis questions + past papers questions www.chem-exptc.com 2010 UAE – ABU DHABI www.chem-exptc.com Electrolysis-Past papers questions 1. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN salt (compound) the product at the CATHODE is: A. B. C. D. Non – metal Metal Sodium Chlorine 2. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN salt (compound) the product at the ANODE is: A. B. C. D. Non – metal Metal Sodium Chlorine 3. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN sodium chloride ( NaCl ) the product at the anode and the cathode are: A. B. C. D. Anode Cathode Sodium Sodium Chlorine chloride Chloride chlorine Sodium sodium 4. During the electrolysis of a MOLTEN lead iodide ( PbI 2 ) the product at the anode and the cathode are: A. B. C. D. Anode Cathode hydrogen iodine lead lead iodine lead iodide iodine 5. Circle the correct answer concerning the properties of halogens Chlorine Bromine Iodine A. B. Green, solid Green, gas Green, solid Red brown, gas Red brown, solid Pale pink, liquid C. Green, liquid Red brown, liquid Pale pink, liquid D. Green, gas Red brown, liquid Pale pink, solid Electrolysis-Past papers questions 6. During the electrolysis of a CONCENTRATED CuSO4 (aq ) the product at the CATHODE is: A. H 2( g ) B. O2 ( g ) C. SO2( g ) D. Red brown deposit (Cu (s ) ) 7. During the electrolysis of a DILUTE CuSO4(aq ) the products at the CATHODE and the ANODE are: cathode anode A. O2 ( g ) Cu (s ) B. H 2( g ) O2 ( g ) C. Cu (s ) O2 ( g ) D. Cu (s ) SO2( g ) 8. The colour of the universal indicator in a neutral medium is . A. B. C. D. Blue Red Green Violet 9. When a few drops of the universal indicator are added to the acid HCl (aq ) , the expected colour is A. Blue B. Red C. Green D. Violet 10. An acid reacts with metal to produce A. B. C. D. Salt + water Salt + base Salt + hydrogen Water + carbon dioxide Electrolysis-Past papers questions 11. Name the products of the electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid (i) At cathode: ……………………………………. (ii) At anode: ……………………………………… 12. Which of the following does NOT contain ions? (a) (b) (c) (d) Aqueous hydrogen chloride Gaseous hydrogen chloride Solid potassium nitrate Molten potassium chloride 13. Which of the following does NOT contain free ions? (a) (b) (c) (d) Aqueous hydrogen chloride Aqueous ammonia Solid potassium nitrate Molten potassium chloride 14. When aqueous H 2 SO 4(aq) solution is electrolysed using inert carbon electrodes, the substance formed at anode is (a) hydrogen gas (b) Oxygen gas (c) Copper (II) ion (d) Copper deposit 15. When aqueous H 2 SO 4(aq) solution is electrolysed using inert carbon electrodes, the substance formed at cathode is: (a) hydrogen gas (b) Oxygen gas (c) Copper (II) ion (d) Copper deposit 16. When aqueous H 2 SO 4(aq) solution is electrolysed using inert carbon electrodes, the substance formed at anode is a: (a) Gas that burns with pop sound (b) Gas that relights a glowing splint (c) Brown gas (d) Pink solid Electrolysis-Past papers questions 17. The diagram shows the electrolysis of a molten compound X. What is compound X? A. Copper (II) Chloride + − B. Lead(II) bromide C. Sodium chloride Carbon electrode Carbon electrode D. Sodium bromide bubbles of brown gas Molten compound X Molten Silvery metal heat 18. The diagram shows the electrolysis to electroplate nickel with different metals + − 1 Ni 2 Ni 3 Ni Aqueous Copper (II) sulphate Which nickel electrodes are plated with a metal? A- 1 only B- 1 and 3 only C- 2 only D- 2 and 4 only 4 Ni Aqueous sodium Chloride Electrolysis-Past papers questions 19. Metal X is low in the reactivity series and it is liberated by electrolysis of its bromide. Metal X is ……1…… and the bromide is ……2…… . Which words correctly complete gaps 1 and 2? 1 2 Lead In solution Lead molten C. Sodium In solution D. Sodium molten A. B. 20. Copper and hydrogen can each be formed by electrolysis. At which electrodes are these elements formed? copper hydrogen anode anode anode cathode C. cathode anode D. cathode cathode A. B. 21. Two elements X and Y form ionic compounds, XBr2 and Y2O3. The compounds are separately melted and electricity is passed through the liquids. What are the products at the cathodes? A. bromine and oxygen B. bromine and Y C. oxygen and X D. X and Y Electrolysis-Past papers questions 22. Which change can take place during electrolysis? A. lead(IV) oxide → lead(II) oxide + oxygen B. concentrated hydrochloric acid → hydrogen + chlorine C. sodium hydroxide + nitric acid → sodium nitrate + water D. lead(II) nitrate + sulphuric acid → lead(II) sulphate + nitric acid 23. What is the charge on an anode and the type of element formed at such an electrode? charge on anode type of element formed A. negative metal B. negative non-metal C. positive metal D. positive non-metal 24. The diagram shows how to cause a chemical change in a molten compound. + - electrodes molten compound What is this process used for? A. removal of oxides from metals B. extraction of metal from its ore C. neutralisation of industrial waste D. production of fertilisers heat Electrolysis-Past papers questions 25. A molten compound is electrolysed. Two atoms of X are deposited at the negative electrode at the same time as three atoms of Y are deposited at the positive electrode. These results show that: • X is a …..1..…; • Y is a …..2..…; • the formula of the compound is …3… . How are gaps 1, 2 and 3 correctly completed? 1 2 3 A. metal non-metal X3Y2 B. metal non-metal X2Y3 C. non-metal metal X3Y2 D. non-metal metal X2Y3 26. In which electrolysis are chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide all produced? aqueous sodium chloride molten sodium chloride A. B. C. D. 27. Metallic and non-metallic elements can both be extracted by electrolysis. Which element is produced at the negative electrode (cathode)? A. bromine B. chlorine C. oxygen D. hydrogen Electrolysis-Past papers questions 28. The electrolysis of concentrated aqueous sodium chloride makes three products. Which products are shown at the correct electrodes? anode (+ve) cathode (–ve) A. chlorine sodium hydroxide B. sodium hydroxide chlorine C. hydrogen sodium D. chlorine hydrogen 29. The diagram shows that two gases are formed when concentrated hydrochloric acid is electrolysed between inert electrodes. +ve - ve concentrated hydrochloric acid Which line correctly describes the colours of the gases at the electrodes? anode (+ve) cathode (–ve) A. colourless colourless B. colourless yellow-green C. yellow-green colourless D. yellow-green yellow-green Electrolysis-Past papers questions 30. The diagram shows the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide. electrode X + − electrode Y molten lead ( II) bromide heat What is seen at each electrode? electrode X electrode Y A. brown gas silvery metal B. brown metal green gas C. green gas brown metal D. silvery metal brown gas 31. The following electrolysis circuit is set up, using inert electrodes P, Q, R and S. + P − + Q R − S Molten Lead (II) bromide Concentrated hydrochloric acid At which of the electrodes is a Group VII element produced? A. P only B. P and R C. Q only D. Q and S Electrolysis-Past papers questions 32. The following electrolysis circuit is set up, using inert electrodes At which electrode is a metal deposited? + A + C − B − D Molten Lead (II) bromide Concentrated aqueous sodium chloride 33. The diagram shown is not complete. X concentrated hydrochlor ic acid What should be shown at X when the solution has been electrolysed for some time? A Cl 2 B H2 Cl 2 C H2 H2 O2 D H2 Cl 2 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 34. Which product is manufactured by electrolysis? A. aluminium B. copper(II) sulphate C. steel D. sodium chloride 35. The diagram represents the electrolysis of brine (aqueous sodium chloride). brine X chlorine Y + positive electrode negative electrode porous wall What are products X and Y? X Y A. hydrogen aqueous sodium hydroxide B. hydrogen hydrochloric acid C. oxygen aqueous sodium hydroxide D. oxygen hydrochloric acid Electrolysis-Past papers questions 36. Define (a)Electrolysis ………………………………………….…………………..……………………… (b) Electrolyte (liquid) ………………………………………….…………………..…………………… (c)Conductor (metal) ………………………………………….…………………..……………………… (d) Anode ………………………………………….……………………..…………………… (e)Inert electrode ………………………………………….…………………..……………………… 37. In electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride MgCl2 using graphite electrodes (a) Give the formula of the ions present ……………………………………………………………………………………… (b) What is observed at Anode ……………………………, cathode ……………..…………………… (c) Name the product at Anode …………………..…………, cathode …………………………..….… (d) Write the ionic equation to show changes at Anode: ……………………………… → …………………………………… Cathode: …………………………… → ………..…….…………..……..… (e) Draw a labeled dia gram and indicat e the direction of electron flow (f) How are e − removed from outer circuit and where? ……………………………….…………………..………………………………… Electrolysis-Past papers questions 38. Name the products at electrodes, during the electrolysis ( using inert electrodes) of (a) dilute sulphuric acid solution H 2 SO4 ( aq ) i. at anode ……………………… , ii. at cathode ………………………… (b) dilute potassium nitrate solution KNO3( aq ) (i) at anode ……………………, (ii). at cathode ………………….…… (c) Copper (II) sulphate solution CuSO4 ( aq ) i. at anode…………………….…, ii. at cathode ………….……………… (d) concentrated HCl ( aq ) at anode …………………………… , ii. at cathode……………….…… (e) Concentrated NaCl( aq ) i. at anode…………………………………………………, ii. at cathode ………………………………………………… 39. In the electrolysis of molten lead(II) bromide PbBr2(l ) using Graphite electrodes (i) What is observed at anode? ……………………………………………………………………… (ii) Name the product at anode? ……………………………………………………………………… (iii) Write the ionic equation that takes place at anode. …………………………………………………………………. → ……………………………………… (i) What is observed at cathode? …………………………………………………………………… (ii) Name the product at cathode? …………………………………………………………………… (iii) Write the ionic equation that takes place at cathode. …………………………………………………………………. → ……………………………………… Electrolysis-Past papers questions (a) What happens to the ammeter reading if heat is removed? Why? ……………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………. (b) How are electrons removed from the outer circuit? and why? ……………………………………………………………………………………… 40. In the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride ( M gBr 2 ) , using inert electrodes (a) Give the formulae of the ions present: ………………..……….……….. (b) what is observed at each electrode at anode ………………..………….. At cathode………………..……..….. (c) what are the products at the electrodes at anode ………………..………….. At cathode………………..……..….. (d) Write the ionic equation which takes place at - At Anode: …………..………... → ………………..………... - At Cathode: …………..…….… → ………………..………... 41. In the electrolysis of sulphuric acid ( H 2 SO 4(aq) ) , using inert electrodes (a) Give the formulae of the ions present: ……………….……...……….. (b) Which ions move to the positive electrode (anode): ………………………….. (c) Which ions move to the negative electrode (cathode): ……………….……….. (d) Name the product at anode: ..……………………………..……….. (e) Write the ionic equation which takes place at - At Anode: ……..……….…..... → ……….………..………... (f) Name the product at cathode: ..………………………….……….. (g) Write the ionic equation which takes place at cathode At Cathode: …………………..… → …………..……..………... Electrolysis-Past papers questions 42. The following diagram shows electroplating of a an iron spoon with copper (a) The metal of which X is m ade is………………..………….. (b) Is X made anode or cathode ? ……………………….…..... (c) Is the spoon anode or cathode ? ………………………...… (d) A suitable electrolyte is ……………………….………………… (e) In case we need to electroplate the spoon with silver , suggest a suitable (i) Anode …………………..…….. (ii) Electrol yte …………………….. Spoon X electrolyte 43. In purification of copper (a) Impure copper is made ………………..…………………….……….. (b) Pure copper is made cathode ……………………………….……….. (c) The used electrol yte is ………………..………………………..…….. (d) The formed slime (sludge) has economic importance because …..……………………..………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………..…….. Electrolysis-Past papers questions 4 4 . The diagram shows a method for obtaining pure copper from impure copper. positive Electrode ( Anode ) negative Electrode ( cathode ) A B C 1- D electrolyte Name each of the following substances a) Substance A ……………………………………………….. b) Substance B …………………………………………………… c) Substance C ………………………………………….……… d) Substance D ………………………………………….……… Electrolysis-Past papers questions 45. Extraction of Aluminum + A − B C Molten Aluminum collecting on the bottom D (a) Label the letters A to D (b) Give the name of the main aluminum ore. ………………………………………… (c) Why should aluminum ore be treated with sodium hydroxide before electrolysis? ………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………..……… (d) Name the substance in which aluminum oxide is dissolved in the above electrolysis process. ……………………………………………………………………………………… (e) Explain why the substance in part (4) is added to aluminum oxide. ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… (f) Write the balanced ionic equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode. ………………………………….……………………………………………………… Electrolysis-Past papers questions (g) Which electrode has to be frequently replaced during the process? Explain your answer. ……………………………………….…………………………………………… …….……………………………………………………………………………… 46. Zinc is extracted from its ore, zinc blende ,by reduction with carbon after being roasted with air a) Complete the following two equations for the reactions involved in this process ….. ZnS ZnO + ……..…. + ……..…. → ….. ZnO + ……. SO 2 + ……. CO 2 → Zn b) Give one use of Zinc. …………………………………………………… 47. (a)Name the 3 products obtained by electrolysis of KBr ( aq ) using inert electrodes …………………………………………………………………………..…………………………… (a) How is Br 2 obtained from KBr ( aq ) ? ……………………………………………………..…………….……………………..…………… ……………………………………………………..…………..…………..…………..…………… (b) How is I 2 obtained from NaI ( aq ) ? ……...………..……………………………………………………………………………………….… Electrolysis-Past papers questions 48. In the electrolysis cell of concentrated NaCl (aq ) (Brine) Conc. NaCl (aq) + Porous Wall Anode (a) Name the products at − Cathode Anode ……..……………..…., cathode ……….……..…………. (b) Name the solution flows out of the cell. …………………………………………………………………………… (c)How is sodium hydroxide obtained from concentrated NaCl (aq ) ? ………………………………………………………….……………………………… …………………………………………………………..…… …………………………………………………………………………..……………… ………….…………………………………………………… (d) How is chlorine gas obtained from NaCl (aq ) solution? …………………………………………………………………………..……………… …………………………………………………………………………..……………… (e)(a) Name the 3 products of the electrolysis of concentrated KBr(aq ) . …………………………………..…..……, ………………………………....…..………., ………………………….………………… (f) Write the ionic equations taking place at (i) anode:……………………..…… → (ii) Cathode: ……………..…..…… …………………………..…… → ………………………..…..…… Electrolysis-Past papers questions 49. Like Copper, nickel can be refined by electrolysis. Label the diagram to show the purification of nickel in the laboratory − + 50. The diagram below shows an apparatus in which the electrolysis of aqueous sodium sulphate containing litmus solution was carried out. Gas A Gas B Platinium Electrodes Direct Current When the current was passed through the solution, the solution around the anode turned red and the solution around the cathode turned blue. Gas A was found to relight a glowing splint and gas B, when ignited, burned with “pop”. (a) Give the formula of the four ions in aqueous sodium sulphate ……………………………………………………….…………………………… ……………………………………………………………….………………… [2] (b) Which ion caused the litmus to turn red? ……………………………………………………………..…………………… [1] (c) Which ion caused the litmus to turn blue? ……………………………………………………………….………………… [1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (d) (i) Complete the table below Name of gas Name of electrode at which gas is produced Gas A Gas B (ii) Write an equation to show the formation of gas B. ……………………………………………………….…………………………… ……………………………………………………………….…………………… (iii) At which electrode has oxidation taken place? ……………………………………………………….…………………………… ……………………………………………………………..………………… [4] (e) If the experiment is repeated using deionised water without sodium sulphate dissolved in it, no reaction occurs. (i) Explain why there is no reaction? ……………………………………………………….…………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) Explain why the addition of sodium sulphate to deionised water allows a reaction to take place. ……………………………………………………….…………………………… ………………………………………………………………………….………… ……………………………………………………….…………………………… ……………………………………………………………………….………… [2] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 51. Calcium may be prepared by the electrolysis of molten calcium chloride CaCl2 . Steel Cathode Graphite anode + + Graphite anode − Molten Calcium Chloride Graphite (i) How would you convert lime (calcium oxide) into anhydrous calcium chloride? ………………………………………….……………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) What element are the anodes made from? ………………………………………………………………………………………… (iii) At which electrode is the calcium obtained? ………………………………………………………………………………………… (iv) Name the other substance produced during this electrolysis. ……………………………………………………….………………………………… Electrolysis-Past papers questions 52. Lithium is extracted by the electrolysis of its molten chloride. A − + Part of circuit A to B Carbon Electrodes B Part of circuit C to D D C Molten Lithium chloride heat (i) Lithium chloride is an ionic compound. Explain why it conducts electricity in molten state but not in the solid state. ….…………………………………………………………………………….…… [2] (ii) How is electricity conducted in the part of the circuit labeled A to B ……………………………………………………………………………… C to D ……………………………………………………………..………………. [2] (iii) What would be the products of the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous lithium chloride? ……………………………………………………………….………………… [3] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 53. Chemistry is concerned with the transfer of electrons and energy. (a) During electrolysis, electrical energy is supplied, electrons move in the external circuit and ions move in the electrolyte. The diagram Power supply shows the electrolysis of molten − + potassium bromide. External Circuit Electrodes Molten potassium bromide heat (i) Draw an arrow on the diagram to show the direction of the electrons in the external circuit. (ii) [1] Is the following reaction exothermic or endothermic? Give a reason for your choice. 2KBr → 2K + Br2 ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………[2] (iii) Electrons are removed from the external circuit. Howe and where is this done? ………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………[1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (iv) The results of experiments on electrolysis are shown in the following table. Complete the table; the first has been completed as an example. Electrolyte Electrodes Change at cathode Molten Carbon Potassium Bromine metal formed formed potassium bromide Aqueous Change at anode Change to electrolyte Used up Copper Stays the same copper (II) sulphate Carbon hydrogen gas evolved Chlorine formed Potassium hydroxide formed [4] 54. The diagram shows the electrolysis of Lead (II) bromide, PbBr2 − + Brown fumes Silvery metal Molten Lead (II) bromide Heat (a) Explain why solid lead (II) bromide does not conduct electricity. …………………………………………………..………………………………… (b) Balance the equations for the reactions that take place at each electrode. (i) ………... Br − (ii) Pb 2+ + → ……. e − → Br2 + ……… e − Pb (c) Identify the brown fumes shown in the above diagram …………………………………………………..………………………………… (d) Define reduction in terms of electrons …………………………………………………..……………………………… Electrolysis-Past papers questions 55. A metallic cup can be coated in silver by electrolysis. The process is called electroplating Cup Metal electrode electrolyte (a) Identify the metal from which the used electrode is made.………………… (b) Suggest a suitable electrolyte that could be used. ..……………………….. (c) Should the cup be made anode or cathode? ………………………………... 56. The diagram shows the apparatus used to electrolyse lead(II) bromide. (a) The wires connected to the electrodes are made of copper. Explain why copper conducts electricity. .................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................. (b) Explain why electrolysis does not occur unless the lead(II) bromide is molten. ................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................... (c) The reactions occurring at the electrodes can be represented by the equations shown in the table. Complete the table to show the electrode (A or B) at which each reaction occurs, and the type of reaction occurring (oxidation or reduction). Electrolysis-Past papers questions Paper3 57. The electrolysis of concentrated aqueous sodium chloride produces three commercially important chemicals; hydrogen, chlorine and sodium hydroxide. (a)The ions present are Na+(aq), H+(aq) ,Cl –(aq) and OH–(aq). (i)Complete the ionic equation for the reaction at the negative electrode (cathode). ………………. + ………………. → [1] (ii)Complete the ionic equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode). ………………. - ………………. → [1] (iii)Explain why the solution changes from sodium chloride to sodium hydroxide. ……………………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] (b) (i) Why does the water supply industry use chlorine? ……………………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] (ii)Name an important chemical that is made from hydrogen. ……………………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] (iii)Sodium hydroxide reacts with fats to make soap and glycerine What type of compound are fats? ……………………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] Nov-2008 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 1. Copper is purified by electrolysis. (a) Complete the following. The positive electrode (anode) is made from………………………………. The negative electrode (cathode) is made from …………………………… The electrolyte is aqueous …………………………………………………[3] (b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode). ……………………..……………………………………………………..………. [2] (c) (i) Give two reasons why copper is used, in electric wiring, …………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………..………. [2] in cooking utensils., …………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………..………. [2] (ii) Give another use of copper. ……………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] [Total: 10] May-2008 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 1. Zinc is extracted from zinc blende, ZnS. Zinc blende is heated in air to give zinc oxide . part of the zinc oxide reacts with sulphuric acid to give aqueous zinc sulphate. This is electrolysed with inert electrodes (the electrolysis is the same as that of copper (II) sulphate with inert electrodes). ions present: Zn2+(aq) SO 24− (aq) H+(aq) OH-(aq) (i) Zinc forms at the negative electrode (cathode). Write the equation for this reaction. ………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] (ii) Write the equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode). ………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] (iii) The electrolyte changes from aqueous zinc sulphate to ………………………………………………………………………..………. [1] (a) Give two uses of zinc. 1……………...………………………………………………………..………. 2. ………………………….……………………………………..………. [2] Nov-2007 Electrolysis-Past papers questions (a) Cell reactions are both exothermic and redox. They produce electrical energy as well as heat energy. (i) The diagram shows a simple cell. voltmeter V zinc electrode becomes thinner iron electrode bubbles of hydrogen form dilute sulphuric acid Which substance in this cell is the reductant and which ion is the oxidant? reductant ………zinc……………………………………………………… oxidant ………hydrogen ions…………………………………………… (ii) [2] How could the voltage of this cell be increased? magnesium instead of zinc or increase concentration of acid or copper instead of iron ( increase the reactivity difference) ………………………………………………………………………………..………………[1] (ii) What is the important large scale use, relating to iron and steel, of this type of cell reaction? sacrificial protection or stop iron/steel rusting [1] or galvanising …………………………………………………………………………………………………[1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (b) Cells can be set up with inert electrodes and the electrolytes as oxidant and reductant. voltmeter V electron flow carbon electrode (inert) carbon electrode (inert) Potassium iodide(aq) Potassium manganate(VII)(aq) salt bridge (allows ions to move from one beaker to another) The potassium manganate(VII) is the oxidant and the potassium iodide is the reductant. (i) Describe the colour change that would be observed in the left hand beaker. pink or purple [1] to colourless or decolourised [1] NOT red NOT clear …………………………………………………………………………………………………[2] (ii) Write an ionic equation for the reaction in the right hand beaker. 2I– – 2e → I2 …………………………………………………………………………………………………[2] May-2006 Electrolysis-Past papers questions (i) The electrolysis of molten strontium chloride produces strontium metal and chlorine. Write ionic equations for the reactions at the electrodes. negative electrode (cathode) …………..…………….………….……… positive electrode (anode) …………..……………………….……… [2] (ii) One of the products of the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous strontium chloride is chlorine. Name the other two. …………..………………………………………………………………… [2] Nov-2005 (i) h ydroc hloric acid [1] (ii) Sr 2 + + 2e = Sr [1] 2C l – – 2e = C l 2 [1] or 2C l – = C l 2 + 2e (iii ) hydr ogen [1] and stront ium hydr oxi de [ 1] [2] Nov-2005 (b) Aqueous copper(II) sulphate solution can be electrolysed using carbon electrodes. The ions present in the solution are as follows. Cu2+(aq), SO 24− (aq), H+(aq), OH– (aq) (i) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the negative electrode (cathode). ............................................................................................................[1] (ii) A colourless gas was given off at the positive electrode (anode) and the solution changes from blue to colourless. Explain these observations. ............................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................[2] (c) Aqueous copper(II) sulphate can be electrolysed using copper electrodes. The reaction at the negative electrode is the same but the positive electrode becomes smaller and the solution remains blue. (i) Write a word equation for the reaction at the positive electrode. ............................................................................................................[1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (ii) Explain why the colour of the solution does not change. ............................................................................................................ ............................................................................................................[2] (iii) What is the large scale use of this electrolysis? ............................................................................................................[1] May-2004 (b) (i) Cu2+ + 2e = Cu [1] (ii) gas is oxygen [1] (copper(II) sulphate) changes to sulphuric acid [1] or copper ions removed from solution (c) (i) copper atoms - electrons = copper ions [1] accept correct symbol equation (ii) concentration of copper ions does not change or [1] amount or number of copper ions does not change copper ions are removed and then replaced [1] or copper is transferred from anode to cathode (iii) refining copper or plating (core) [1] or extraction of boulder copper May-2004 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 1. Copper is purified by electrolysis. (a) Complete the following. The positive electrode (anode) is made from…………………………………. The negative electrode (cathode) is made from …………………..………… The electrolyte is aqueous ………………… ………………………………[3] (b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (anode). …………………….………………………………...………………..………. [2] (c) (i) Give two reasons why copper is used, in electric wiring, …………………………………..…………………….. ……………………………………………………………………..………. [2] in cooking utensils., …………………………..……………………….. ……………………….……………………………………………..………. [2] (ii) Give another use of copper. ……………………………………………………………………..………. [1] [Total: 10] May-2008 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 2. Lead bromide was placed in a tube and connected to an electrical circuit as shown below. d.c.power supply bulb LEAD BROMIDE TOXIC heat The lead bromide was heated until molten. A brown gas was given off. (a) State one other expected observation. ………………………………………….……………………….………………………………[1] (b) (i)Suggest a suitable material to make the electrodes. …………..………………………….……………………………….………………………….[1] (ii)Indicate on the diagram the negative electrode (cathode). [1] (c) Name the brown gas. At what electrode will the gas be given off? ⋅ Name …………………..………………….…………………………………….………… ⋅ electrode ……………………………….………………………………...………………[2] (d) Why is this experiment carried out in a fume cupboard? …………..………………………….……………………………….…………………………[1] May-June - 2004 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 3. The diagram shows the apparatus used to find out the effect of an electric current on a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride. (a) On the diagram label the electrodes [1] (b)Give three observations when the circuit is switched on. 1……………………….………………………………………………………………………… 2……………………….………………………………………………………………………… 3……………………….……………………………………………….………………………[3] (c) (i)Name the product at the positive electrode (anode). ……………………….……………………………………….…………………………………[1] (ii)State a test for this product and the result of the test. test……….……………………………………….………………………………………[1] result ……………………….………………………………………………………………[1] May-June-2006 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 4. Impure copper is extracted from the ore. This copper is refined by electrolysis. (a) Name; the material used for the positive electrode (anode), ……………………..…………………………………………….……..………. [1] the material used for the negative electrode (cathode), …………………………………………………………………….………………[1] a suitable electrolyte. …………………………………………………………………….………………[1] (b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction at the negative electrode. …………………………………………………………………….………………[1] (c) One use of this pure copper is electrical conductors, another is to make alloys. Name the metal that is alloyed with copper to make brass. …………………………………………………………………….………………[1] Nov-2005 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 5. The diagram shows the apparatus used to pass an electric current through concentrated hydrochloric acid. chlorine (a) Label the electrodes. hydroge n [1] (b) Give two observations when the current is switched on. 1……….…………………………………..……………………………………………. 2……….…………………………………..………………………………………… [2] (c) Give a test for the product at the negative electrode (cathode). test ……….…………………………..……………………………………………. result ……….………………..……………………………………………………. [2] oct-Nov-2005 Electrolysis-Past papers questions 6. Electricity was passed through a concentrated solution of sodium chloride containing Universal Indicator. positive electrode − + carbon rods negative electrode Concentrated aqueous sodium chloride and universal indicator (a) Suggest a suitable material for the electrodes. carbon/graphite/any unreactive metal e.g. platinum/nickel………………….………..[1] Three observations were noted: 1- Bubbles of gas seen immediately at the negative electrode. 2- Bubbles of gas formed after some time at the positive electrode. 3- The solution turned blue around the negative electrode and colourless near the positive electrode. (b) Give a test to show that the gas observed in 1 is hydrogen. • Test ……lighted splint (1) ……………..……………….……..[1] • result … pops(1) ………………………………………………..[1] (c) Suggest why bubbles of gas were not seen immediately in 2. gas dissolves (in the solution) o.w.t.t.e [1]…………………………..……………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2] (d) (d)What causes the colour change in 3 at the negative electrode, …alkali/(sodium) hydroxide (1)………………………………..[1] the positive electrode? …chlorine/bleach (1) not chloride or chlorine ions………..[1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 7. A constant current was passed through aqueous copper(II) sulphate using inert electrodes as shown in the diagram below. Copper was deposited at one of the electrodes. A variable resistor + – D E (a) Name a suitable material for the inert electrodes. aqueous copper(II) sulphate ……………………………… [1] (b) At which electrode was copper deposited, D or E? ……………………………… [1] (c) What was seen at the other electrode? ............................................................................................................................................[1] (d) What was the colour of the electrolyte (i) at the start of the experiment, ................................................................................................................................... (ii)at the end of the experiment? ................................................................................................................................... [2] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 8. A metal cup can be coated in silver by electrolysis. The cup must be very clean and also rotated during the process, which is known as electroplating. metal electrode cup electrolyte (a) Should the metal cup be the anode or the cathode? .............................................................................................................................[1] (b)Identify the metal from which the electrode is made. ..............................................................................................................................[1] (c) Suggest a suitable electrolyte that could be used to electroplate this cup. ..............................................................................................................................[2] (d)Suggest why the cup must be (ii) very clean, ........................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................[1] (iii) rotated during the electrolysis. ........................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................[1] 2 (a) cathode / negative [1] (b) silver [1] (c) silver nitrate (1) solution (1) [2] // any silver salt not Cl -, I(d) (i) silver will not coat / stick or similar [1] (ii) to give even coating / all of it gets coated [1] [Total 6] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 9. A student electrolysed lead bromide and aqueous sodium chloride in the apparatus shown below. + - + A B carbon electrodes + C D molten lead bromide carbon electrodes aqueous sodium chloride heat Each of the electrodes is labelled with a letter. (a) Why was it necessary for lead bromide to be molten? ......................................................................................................................................[1] (b) (i)What was produced at electrode A? ................................................................................................................................... (ii) What was the appearance of this product? ................................................................................................................................... (iii) What was produced at electrode B? ................................................................................................................................... (iv) Where did this product collect? ................................................................................................................................... [4] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (c)Gases were produced at electrodes C and D. In each case name the gas and give a test to confirm its presence. (i) the gas produced at C ............................................................................... test for this gas ......................................................................................................... (ii) gas produced at D ,,.................................................................................... test for this gas ......................................................................................................... [4] (d) What change should be made so that sodium is produced at one of the electrodes? ..........................................................................................................................................[1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 10. The apparatus below was used to electrolyse water. X Y graphite electrodes H 2SO 4 (aq) (a) (i) Why was a small volume of sulphuric acid added to the water? ....................................................................................................................... (ii)Name the gas collected in tube X and give a test for this gas. gas ............................................................................................................................ test ............................................................................................................................ (iii) Name the gas collected in tube Y and give a test for this gas. gas ............................................................................................................................ test ........................................................................................................................[5] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (b) State how the volume of gas collected in tube X compares with the volume of gas collected in tube Y. ..................................................................................................................................... [1] (c) Name a gas that may be used to sterilise water and give a test for this gas. gas ................................................................................................................................... test .............................................................................................................................. [2] (d) A student added a small piece of sodium and a small piece of iron to separate samples of water. What observations were made? sodium .............................................................................................................................. .......................................................................................................................................... iron ................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... [3] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 11. A student electrolysed concentrated aqueous sodium chloride using the apparatus below. The solution also contained litmus solution. + - Carbon anode Carbon anode aqueous sodium chloride containing some litmus solution (a) (i)Name the gas produced at the anode (positive electrode). ......................................................................................................................................... [1] (ii) Suggest what happened to the colour of the solution around the anode as the electrolysis proceeded. …..………......................................................................................................................... [1] (iii) Why did this change take place? …….……….................................................................................................................... [1] (b) (i)Name the gas produced at the cathode (negative electrode). ..................................................................................................................................... [1] (ii) Give a test for this gas. ........................................................................................................................................ [1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions (iii) What happened to the colour of the solution around the cathode as the electrolysis proceeded? .............................................................................................................................. [1] (iv) Why did this change take place? .............................................................................................................................. [1] (c) The solution was replaced by a dilute solution of an acid. Suggest which acid would produce the same gases as those produced with concentrated aqueous sodium chloride. (d) Under what conditions does the electrolysis of sodium chloride produce sodium at one of the electrodes? [Total: 9] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 12. The diagram shows a cell that can be used to make electrical energy. voltmeter rod of metal X, Y or Z Magnesium rod electrolyte (a) Explain why distilled water is not used as the electrolyte. ............................................................................................................................................[1] (b) This table shows the results when rods of three metals, X, Y and Z, are used in separate experiments. All the metals are less reactive than magnesium. rod 1 magnesium rod 2 Voltmeter reading / V X 2.72 Y 0.78 Z 1.10 magnesium magnesium Place the metals in order of reactivity most reactive magnesium ……………………… ……………………… least reactive ……………………… Electrolysis-Past papers questions (c) A student places a rod of magnesium in aqueous silver nitrate. (i) Write an ionic equation, with state symbols, for the reaction which happened. ................................................................................................................................... (ii) What would you expect to see after the reaction had been taking place for some time? ............................................................................................................................................... ...........................................................................................................................................[3] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 13. This reaction can be used to generate electricity in a cell. (a) Write an ionic equation for the reaction between zinc and aqueous copper(II) sulphate. ..................................................................................................................................... [1] V electrode 2 (Zinc) copper electrode aqueous copper (II) sulphate (b) Drawn an arrow on the diagram to show the direction of the flow of electrons in the wire. [1] (c) The voltage of the cell was measured when the following metals were used as electrode 2. copper iron lead zinc Complete the table by entering the metals in the correct order. meter reading / V 1.10 metal 0.78 0.21 0.00 (d) When metal M was used as electrode 2, it produced a higher voltage than zinc. Suggest a name for metal M. ........................................................................................................................................................ [1] Electrolysis-Past papers questions 14. The diagram shows a cell for purifying copper. - + Pure copper cathode impure copper anode Electrolyte (aqueous copper (II) sulphate (a) Describe what you would observe during this electrolysis and write the equations for the reactions at the electrodes. (b) The electrodes and the electrolyte conduct electricity. (i) Explain how the structure of metals allows copper electrodes to conduct electricity. [1] (ii)Explain why solid copper(II) sulphate does not conduct electricity but an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulphate does conduct. (c)Describe how the apparatus shown in the diagram could be modified in order to electroplate an iron object, such as a knife, with nickel. (d) Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin. Bronze is less malleable than pure copper. Use ideas about the structure of metals and alloys to explain why bronze is less malleable than pure copper. Electrolysis-Past papers questions 15. An electric current can be generated by a simple electrochemical cell such as the one shown. V magnesium copper Electrolyte (magnesium sulphate) (a) Explain why the flow of electrons is in the direction shown in the diagram. [2] (b) Suggest why silver nitrate would not be a good electrolyte to use in this cell. [1]