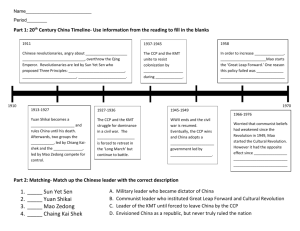
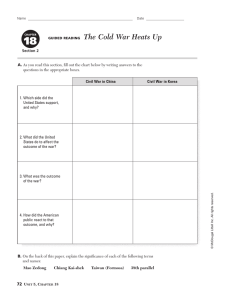
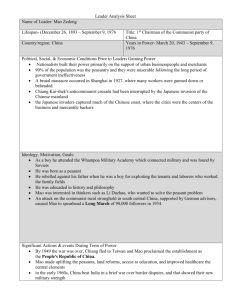
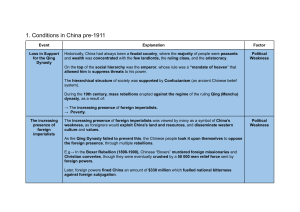
-85 percent of the population were peasants -with little evidence of mechanization -living conditions were basic -no running water or electricity and mud-track roads -most of peasantry lived on the edge of subsistence -peasants did not own their own land, but rented in from wealthy landlords who usually charged very high rents. rural poverty Economic Urban poverty -urban population remained tiny -China ’s small industrial sector which constituted less than 10 percent of China’s gross domestic product( GDP) -huge polarization in wealth between employers and workers. -most of peasantry lived on the edge of subsistence -potential power to affect real change Social division Casualties -A substantial change was that landlords were removed from their position of power and persecuted by local peasantry. The civil war’s impact on social structure the impact of the war of woman Impact of War -Foot binding -Peasants found that they owned land for the first time -woman were largely confined to the domestic duties of childbearing and maintaining the household. -improvement in the legal status and educational and political opportunities for woman, but only affected only the minority. Distinct differences an ideas about male and female roles in society persisted Educational opportunities -an increase in educational opportunities economic impact of the war -industrial production further weakened GMD Weakness of Political System -destroyed and disrupted significant areas of agricultural land corrupt Mao's rise to power CCP opposition to Mao:Mao’s particular interpretation of the dialectic put him at variance with the orthodox communists.Mao was accused of‘reckless adventurism’for assuming that the stages of proletarian revolution could be skipped at will. The odds of a CCP victory were initially very slim.The GMD was recognized by other powers (including the Soviet Union) as the legitimate government. : Persuasion and coercion Chiang the Southern Anhui Incident Chiang‘s leadership became increasingly dictatorial. Chiang The role of leaders Futian incident Mao Jiangxi Soviet ( Mao was dedicated to achieving a peasant revolution. ) GMD three principle of people GMD 1.nationalism 2.democracy 3.the People's welfare/livelihood CCP the ideology of the CCP The elimination of the bourgeoisie, communist party to lead the people to achieve the revolution nationalized -absolute power Dictatorship of the proletariat Ideology ( ( , ) ) Anti-landlord campaign CCP The ‘100 Flowers’ campaign The Use of force propaganda GMD the Southern Anhui Incident creating co-operative farms and then collective farm in the 1950s. -woman have the same rate of pay as men(no real change to woman’s lives)