Accounting Fundamentals: Financial vs. Management, Conventions, Cash Flow
advertisement

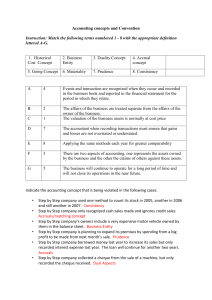
Lecture 3 Topics • Financial Vs. Management accounting • Accounting Conventions (Rules) • Profit Vs. Cash Flow 1 Financial Vs. Management accounting • Reports – general or specific, external/internal • Level of detail – aggregate vs. considerable detail • Regulations – no adherence in mgt accounting • Reporting interval – yearly vs. Daily • Time orientation – past vs. Present and future • Range & quality of information – monetary vs. 2 Accounting Conventions • • • • • Historical Cost – acquisition cost Going Concern – for the foreseeable future Business Entity – business & owner separate Dual Aspect – 2 aspects to each transaction Prudence – exercise caution, recognise expected losses. If in doubt choose the lower reported profit • Money measurement – convert to a common measure • Accruals/Matching – estimate accruals and prepayments 3 Accounting conventions • Realisation – record when legal title passes • Materiality – don’t follow rules to absurdity 4 Historical Cost • Assets included at original cost • Reliable evidence to support figures • Current values may be more relevant but are more subjective • Where NRV of current assets falls below cost, use NRV • NRV = SP – selling costs 5 Going Concern • Business will continue in operation into the foreseeable future • No intention to liquidate • Value of assets and liabilities otherwise affected 6 Business Entity • Business and owners treated as separate and distinct • Owners are seen as claimants of the business 7 Dual Aspect • Each transaction has two aspects • Ensures Balance Sheet balances 8 Prudence • FS should err on the side of caution • Both actual and anticipated losses are recorded in full • Profits are not recognised until realised reasonably certain that profit will be received • Prudence prevails over other conventions 9 Stable Monetary Unit • Assumes that money will not change in value over time • Ignores inflation • High inflation, BS understated • Revaluations of Land and Buildings 10 Balance Sheet Non-current Assets Premises Motor Vehicles Current Assets Inventories Debtors Bank Current Liabilities Creditors Net current assets Total assets less current liabilities Non-current Liabilities Loan Total assets less liabilities Equity Share capital Other reserves Accumulated revenue € 110,000 5,000 115,000 3,600 600 13,000 17,200 2,000 15,200 130,200 50,000 80,200 20,000 60,000 200 80,200 11 Accruals Convention • • • • • Look at transaction/ activity date Not cash transaction Revenues may not represent cash received Expenses may not represent payments made Net profit will not equal net cash generated for the period 12 Profit Vs. Cash Flow • Revenues earned are recorded in I/S • Expenses incurred are recorded in I/S • Cash received in CFS • Cash paid in CFS • Profit may not equal cash generated 13 Interpreting the Balance Sheet • Allows financial position of entity to be examined • Can assess liquidity of business • Can observe mix of assets • Can evaluate financial structure of entity 14