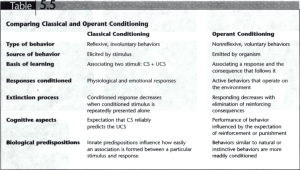
Psychology Study Guide Ch. 6, 7, & 8 6.1 Pavlov classical conditioning (type of associative learning) Stimulus → response Thorndlike operant conditioning Stimulus Response → Reinforcer Antecedents events that precede behavior Reflex reaction to stimulus 6.2 Pavlov experiment Neutral Stimulus- stimulus with no reaction Unconditioned Stimulus- gives a response without prior experience. Unconditioned response- response that requires no previous experience. Conditioned stimulus- NS paired with a US to create a learned response. Conditioned Response- Learned response from NS and US. Extinction- Weakening of a learned response by not reinforcing a response. Stimulus generalization- the learned ability to respond to stimuli similar to the conditioned stimuli. Stimulus discriminatin- the ability to respond differently to similar stimuli. Acquisition- when a response is reinforced. Expectancies- anticipation of future events. 6.3 Conditioned Emotional Response (CER)- response linked to a non emotion stimulus from classical conditioning. (amygdala - fight or flight) SYstematic desensitization- method of reducing fear by gradually exposing people to the object of fear. Vicarious classical conditioning- classical conditioning brought by observing another person react to a certain stimulus. 6.4 Operant conditioning- learning based on positive and negative consequences. Skinner Box (operant conditioning chamber)- designed to test animals operant conditioning. Law of effect- Responses that lead to desirable results are repeated. Response chain- series of actions that lead to reinforcement. Linked series of actions Ex. dog going through obstacles and then being rewarded at the end Shaping- Reinforcement of increasingly close approximations of a desired response. Extinction- weakening of a learned response. Positive and negative reinforcements and punishments 6.5 Operant stimulus generalization- tendency to respond to stimuli similar to those that precede reinforcements. Observational Learning Rote vs discovery learning Rote takes place mechanically through repetition. Facts and principles (memorization) Discovery based on insight and understanding Bobo doll Modeling people imitate what they see. Process of Observational Learning Modeling and Media What people observe is what they imitate Children see the violence happening online which is why parents are concerned about children being aggressive The neurology of Imitation Frontal lobe neurons fire when performing certain actions or observing others. The brain’s mirroring of another action might trigger imitation or empathy. Chapter 7 ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Memory ○ Memory has three steps in order to remember and use information. First is encoding. The information needs to be imbedded into the brain through one or more of the various techniques. Then comes storage where the information is pushed into the back of the memory until it is time to be used which is when retrieval occurs. Types of memory ○ There are several types of Emory including short term, long term, and many more. These first two simple memory systems include how intricate and important the information is which influences how long it is remembered. Short term is information held for a short period of time. Long term is information that is kept for an extensive amount of time and usually more easily remembered. An example for short term may be the vocab terms for a test but long term could be your moms name or birthday. Sensory Memory ○ First steps of short term memory. Holds information for short periods of time, usually a few seconds. Exact record of intake of information. Large amounts for short period. Iconic Memory ○ Mental image or visual representation Echoic Memory ○ Auditory system of listening brief memory of what occurs right then and there which trails for a little longer. Atkinson-Shifrin model ○ This graph shows the possible paths information can take when moving through memory processes. ○ Short term memory ○ Small amounts of info for 12 secs. Working memory ○ ANother version of short term memory. Thinking and problem solving Maintenance Rehearsal ○ Silent repetition or review of info. For short term memory. Digit span ○ Magic number 7 ○ Amount of numbers your brain can remember. Chunking ○ ● ● Grouping things into familiar sets in order to better remember something. Serial Position effect ○ This is the idea where you better remember the beginning and end of sequences and not the middle. Chapter 8 ● Experiential processing ○ Passive effortless and automatic ■ Watching TV ● Reflective processing ○ Active effortful and controlled ■ Listening to a lecture and taking notes ● Stroop task ○ Automatic processing disrupt cognitive ● ● They Image ○ Can be used for memory or thinking ■ Mental image give visual interpretation for memory ■ Able to zoom in and out of mental images Concept ○ Mental category for classifying things based on common feature or propporties ■ Concept formation ● Conjunctive ○ Class of objects that has two or more features in common ■ Both are red and triangles ● Relational ○ Defined by relation between object and its surroundings ■ Greater than ■ Lopsided ● Disjunctive ○ Concept defined by a least one of the possible features ■ Object must be blue or circular ■ Organizing concepts ● Superordinate ○ General category ■ Vehicles ● Basic ○ ● ● Common features ■ Boat, car, truck Subordinate ○ Exemplars ■ SUV, Yhat, Sudan Language ○ Words and symbols that are combined with rules to make a communication system and are used for thinking ● Synesthesia ○ One sense is associated with another ■ Hear color ● Schemas ○ Language ● Endangered Languages ○ Thousands with limited amounts of next generation speakers ● Building blocks of language ○ Semantics ■ The study of meanings in words ○ Phonemes ■ Basic speech sounds ○ Morphemes ■ Speech sounds collected into units ○ Syntax ■ Rule of ordering words when creating sentences ○ Grammar ■ Rules combining words into meaningful language units into speech and writing ○ Transformation rule ■ Sentences can be changed to past present and future tense ● Biology of Language ○ Broca's Area ■ Speaking ○ Wernicie’s Area ■ Listening and encoding ● Animal Communication ○ Communication vs language ■ Animal communication is limited to basics ● Flee, danger, ect. ● Development of Language ○ Cooing and babbling ■ Starting to pronounce syllables and phoneyms ○ Communicating ■ Baby talk ■ Baby sign language ○ Single words ○ ○ ■ Phonemes and morphemes Telegraphic speech ■ Two word sentences ■ Not grammatically correct