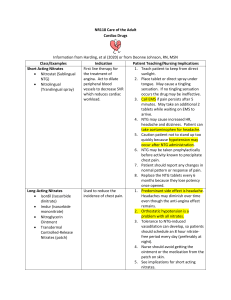
Cardio Cases Case #1 – diltiazem, heparin, warfarin A 45-year-old female presents to the emergency room with complaints of a “racing heart” and palpitations. EKG reveals atrial fibrillation with heart rate 150-160 bpm. The patient weight is 160 pounds. The patient denies knowledge of previous Afib. 1. Is the patient at risk for thrombus formation that could lead to MI or CVA? Why? 2. The patient is complaining of dizziness and weakness. She appears pale and diaphoretic. Why? 3. Imagine her blood pressure. What is it? 4. For each medication below, what is the intended effect? diltiazem 0.25mg/kg IV over 5 minutes, followed by 10 mg/hr continuous IV administration initiate low dose heparin protocol warfarin 5 mg PO daily Case #2 – morphine, aspirin, nitroglycerin, clopidogrel A 55-year-old male presents to the emergency room with complaints of chest pain that woke him up from sleep. The patient appears diaphoretic and anxious. He describes the chest pain as “crushing” and “heavy.” waist circumference 42 inches, BMI 31.2 fasting blood glucose 110 mg/dL, LDL 155, HDL 36, Triglycerides 189 BP 145/76 Home medications: aspirin 81 mg PO daily, niacin 500 mg PO every night. Cardio Cases 1. What is metabolic syndrome? Thoughts about his home medications? 2. For each medication below, what is the intended effect? Aspirin chewable 81 mg x 4 tablets, PO stat, instruct patient to chew Morphine 2-5 mg IV prn for chest pain Nitroglycerin 0.5 mg SL prn, may repeat x 2, 5 minutes apart 3. The patient begins to complain of a headache and dizziness. Why? What actions should the nurse perform? 4. The patient is transferred to the cardiac cath lab for diagnostic testing and treatment. A 90% blockage of the right coronary artery (RCA) was diagnosed; treatment include angioplasty and stent placement. An order was placed for clopidogrel 600 mg PO stat, followed by 75 mg PO daily. What is the purpose of the medication order? 5. What patient teaching should be included for a patient discharged home on sublingual nitroglycerin tablets? Cardio Cases Case #3 – digoxin, furosemide, ACE-inhibitors A 74-year-old woman lives independently at home and manages the disease heart failure well. While she struggles walking down her long, gravel driveway to the mailbox, she is able to care for her home and cook simple meals in the kitchen. The home health nurse checks in with her every other day to review her daily weight / BP / HR log and to draw any routine blood work. During a medication a review, the nurse notes the patient is taking the following medications: 1. For each medication below, what is the intended effect and HOW will it achieve it? furosemide 20 mg PO twice a day lisinopril 5 mg PO twice a day digoxin 250 mcg PO once a day During a home healthcare visit, the nurse noticed the patient had been growing progressively weaker; she was not able to walk short distances or cook her own meals. The nurse insisted she seek immediate medical attention. The patient presents with ankle edema, dyspnea on exertion, and orthopnea. On admission, she is severely dyspneic and can answer questions only with oneword phrases. She is diaphoretic, with a heart rate of 132 beats/min and blood pressure 98/70. She is extremely anxious. 2. For each medication below, what is the intended effect and HOW will it achieve it? furosemide 40 mg IV stat, repeat every 12 hours digoxin 0.5 mg IV stat, then 0.125 every 6 hours for 3 doses morphine 2 mg IV stat, then 2 mg IV PRN for dyspnea or chest pain Cardio Cases 3. The physician also orders an EKG now, repeat prior to each digoxin dose / BMP once & daily / BNP & serum digoxin level now. What is the significance with these orders? EKG BMP (basic metabolic panel) BNP (brain natriuretic peptide) serum digoxin level 4. Review the lab values provided. What do they indicate? What should the nurse do next? digoxin 0.4 ng/mL BNP 975 pg/mL (no need to memorize normal) K 3.2 mEq/L Cr 1.1 BUN 24 Cardio Cases 5. You are assisting the patient complete her menu selection. What foods should the patient include? 6. Consider the addition of spironolactone 12.5 mg PO twice a day – Why is spironolactone often concurrently administered with furosemide? 7. Upon discharge, what patient teaching should the nurse provide regarding the administration of digoxin? This should be a very long list.