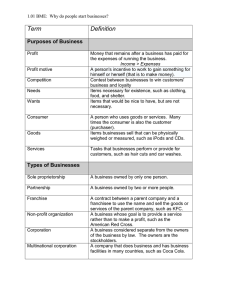
Fundamentals of Accounting Course I Accounting and the Business Environment Planning, recording, analyzing, and interpreting financial information is called accounting. A planned process for providing financial information that will be useful to management is called an accounting system. Organized summaries of a business’s financial activities are called accounting records. Accounting is the language of business. Many individuals in a business complete accounting forms and prepare accounting reports. Owners, managers, and accounting personnel use their knowledge of accounting to understand the information provided in the accounting reports. Regardless of their responsibilities in an organization, individuals can perform their jobs better if they know how to read the language of business. The development of accounting concepts and principles is closely related to the economic growth, as businesses grew, and outsiders increased their demand for financial information. A business is an organization that sells products or services to customers. One major goal of a business is to generate a profit, which is the difference between the sales price of the goods and services sold by the business and the cost of the resources used to provide these goods or services. The second major goal of a business is to stay liquid. Being liquid means being able to generate enough cash from selling goods or services to pay bills on time. A. Types of Business Organizations A business organization can be classified by what it provides to its customers. • Service companies perform services for customers. Some service companies require lots of expertise (legal, accounting, medical, or banking services), and others help with personal services (oil changing, painting, cleaning or hair styling). • Merchandise companies, also known as retail companies, sell products that are made by another company. • Manufacturing companies make their own products that are sold directly to the final customer or to other companies who distribute the products to customers. 1 Fundamentals of Accounting B. Forms of Business Organization A business organization can also be classified based on how it is organized. There are three basic forms of organization: • A proprietorship – has a single owner, called the proprietor, who is often the manager. It tends to be a small merchandising store or the professional business of a physician, attorney or accountant. The advantages of a proprietorship include ease of formation, total control by the owner and profits that are not shared. From the accounting point of view, each proprietorship is separate from his owner. The accounting reports of a proprietorship are separate from the owner’s personal financial records. From a legal perspective, the business is the proprietor. If the organization stop operating, the owner is personally responsible for all the debts that the business owed to creditors. In this course, we begin discussing the accounting process by looking at a proprietorship. • A partnership – joins two or more individuals as co-owners. Each owner is a partner. It is a business such as a retail store or a professional organization of attorneys or accountants. It is small or medium-sized, but it can have an unlimited number of partners. Accounting treats the partnership as a separate organization, distinct from the personal, financial affairs of each partner. But again, from a legal perspective, a partnership is the partners. If the organization stops operating, the partners are personally responsible for all debts that the organization owes to creditors. • A corporation – is owned by stockholders or shareholders. Stockholders purchase an ownership interest in a corporation by buying shares of its stock. Corporations can be small, with one stockholder, but usually they are quite large because they get funds from their owners, as investors or stockholders. A corporation begins when the state approves its article of incorporation. It is a legal entity separate from its owners that conducts business in its own name. The most common forms of corporations are: - limited liability companies (LLC) – A limited liability company is a corporate structure whereby the members of the company are not personally 2 Fundamentals of Accounting liable for the company's debts or liabilities. Limited liability companies are hybrid entities that combine the characteristics of a corporation and a partnership or sole proprietorship. - joint-stock companies (JSC) – a business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their shares (certificates of ownership). The accounting records of a corporation are separate from the records of its owners. However, unlike the proprietorship and the partnership, the owners of a corporation do not lose personal assets if the corporation goes bankrupt and is unable to pay its bills. So, the amount that the stockholders risk when buying stock is the amount that they paid for it. This limited liability of stockholders for corporate debts explains why corporations are so popular. C. Organization Accountability Accountability is the responsibility for one’s actions. Organization accountability is the organization’s fiduciary responsibility to manage its resources carefully. Many different individuals and groups of people, called stakeholders (this category includes invertors, creditors, suppliers, employees, customers, government agencies, and investees), have an interest in organizations, especially in these activities that most directly affect them. A business’s activities can be grouped into three categories: • Financing activities. Organizations and their management attract investors and creditors who provide cash or other assets to them. In exchange, they use these resources responsibly to operate the business profitably, and repay amounts owed when due while maintaining a positive cash balance. • Investing activities. Organizations and their management obtain items needed to operate the business. Some of these are physical, long-term assets as building space, equipment, and furniture. Others include stock in or loans to other companies as a way of 3 Fundamentals of Accounting using extra cash profitably. In exchange, organizations and their management pay suppliers and investees for these items in a timely manner. • Operating activities. Organizations and their management generate a profit from the sale of goods and services. First, they purchase economic resources and use them in order to . In exchange for the used resources, suppliers and employees are paid on time and management provides a safe a work environment. Next, customers buy goods and services. In exchange, management provides quality goods and services in a timely manner. Finally, organizations and their management meet various regulatory obligations to the National Tax Administration Agency, Ministry of Public Finance and other central or local government agencies by reporting financial information, paying taxes, and obeying laws. D. Financial Accounting and Management Accounting To satisfy the needs of stakeholders, managers are required to provide information that communicates the decisions made and the results obtained from those decisions. Because organizations are accountable to others for actions taken, managers communicate using accounting as the language of business. From this position, accounting is the information system that measures business activity, processes results of activities into reports, and communicates the results to decision makers. Thus, organization accountability requires two forms of accounting based on who is being communicated with: • Financial accounting for external reporting; • Management accounting for internal planning, control, and decision making. Financial accounting produces reports called financial statements that show financial information about a business. These historical, objective reports, based on applying some certain rules, communicate financial information in monetary terms (national currency) to its external stakeholders and must follow the current regulations, known as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). GAAP are the rules that govern financial accounting and must be followed when preparing financial statements. 4 Fundamentals of Accounting Financial statements allow investors and creditors to make investment decision, based on financial indicators which are contained in them. They allow suppliers and customers to determine the financial condition of a business. Finally, they are used by the organizations for reporting to regulatory agencies. Management accounting provides financial and nonfinancial information inside the organization. This forward-looking information helps managers plan, control, and make decisions consistent with the fiduciary role managers have in operating a business. Management accounting information must be useful, and the benefits of this information must be greater than the costs of obtaining it. However, because it is used internally, it does not need to fallow GAAP. 5