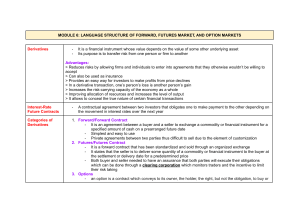
Forex- foreign exchange market Is a global decentralized or "over the counter" exchange happens to both parties present Market trading of currency Currency - Current – Circulation Money in any form when it's use Activities Buying Selling Trading/Exchange Participants. 1. Commercial banks & security leaders 2. Commercial companies MNC 3. Central Banks 4. Investment Management firms. 5. Non-bank foreign exchange- money changer 6. Retail foreign exchange traders- brokers 7. Money transfer or remittance company, Bureuax de change Fixed exchange rate: decided by the government Floating exchange rate regime: 1. International parity conditions - equal conditions relative purchasing power parity, interest rate parity, Domestic Fisher effect, International Fisher effect. 2. Balance of payments model- focuses largely on tradable goods and services, ignoring the increasing role of global capital flow 3. Asset market model - views currencies as an important asset class for constructing investment portfolios. For shorter time frames (less than a few days) Economic factors Economic policy comprises government Government Budget Deficities or surpluses Balance of trade levels and trends Inflation levels and trends Economic growth and health Productivity of an economy Political conditions Internal, regional, and international political conditions and events can have a profound effect on currency markets. Market Psychology Market psychology and trader perceptions influence the foreign exchange market in a variety of ways Flights to quality Long-term trends Buy the rumor, sell the fact Economic numbers Technical trading consideration Financial Instruments Spot - A spot transaction is a two-day delivery transaction, as opposed to the futures contracts, which are usually three months. Forward- One way to deal with the foreign exchange risk is to engage in a forward transaction Non -deliverable forward (NDF) -are derivatives that have no real deliver-ability. Swap - In a swap, two parties exchange currencies for a certain length of time and agree to reverse the transaction at a later date. These are not standardized contracts and are not traded through an exchange. Futures -Futures are standardized forward contracts and are usually traded on an exchange created for this purpose. The average contract length is roughly 3 months. Option - Is a derivative where the owner has the right but not the obligation to exchange money denominated in one currency into another currency at a pre-agreed exchange rate on a specified date. Tolentino, Hazel Ann De Paz, Jahziel Anne