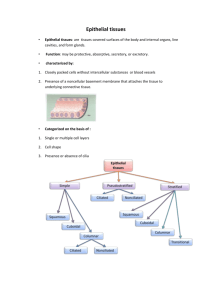
Epithelial tissue is tightly packed cells and has minimal extracellular matrix. It covers the body and organ surfaces, lines body cavities and organ cavities, forms glands. Can be simple (one layer), stratified (2 or more), and pseudostratified (appears layered). Keratinized: found in epidermis and superficial layer of dead cells. Lacks nucleus and filled with keratin. Non keratinized: all cells are alive and kept moist with secretions. Visible cell nuclei. Found in oral cavity, esophagus, vagina, and anus Functions: Physical protection, selective permeability, secretion, and sensation. Types Characteristics ● 1. Simple Squamous ● ● One cell layer, irregular floor tiles, with a buldging nucleus; attached to basement membrane directly Thinnest possible barrier for diffusion, filtration, and secretion from serous membranes to occur Location: lines air sacs in lungs (alveoli), lymph vessels and lumen vessels (endotheliam), and serous membranes of body cavities (mesothelium) 2. Simple Cuboidal ● ● ● Absorbs and secretes between filtrate and blood Secretory tissue of most glands and small ducts Location: kidney tubules, thyroid gland follicles, surface of ovary, secretory regions of ducts and glands 3. Non-cilated Simple Columnar ● ● ● Taller than they are wide, nucleus in basal region, apical regions may have microvilli, may contain goblet cells that secrete mucin Absorption and secretion; mucin Location: inner lining of digestive tract (stomach, small and large intestine 4. Cilated Simple Columnar ● ● Secrete mucin and help movement in apical surface by cilia; oocyte movement through uterine tube Lining bronchioles of lung and uterine tube 5. Cilated Psuedostratified Columnar ● ● ● ● ● Singles layer of cells with varying heights, all cells connect to basement membrane BUT not all cells reach apical surface Goblet cells (secrete mucin through ducts making moist) and cilia Protection, move mucin along apical surface by cilia Cilated form in most of upper resp. Tract including trachea Line larger air ways of respiratory, nasal cavity, pharynx, trache, bronchi, and larynx 6. Noncilated Psuedo. Columnar 7. Keratinized Stratified Squamous ● ● ● Single layer with varying heights Protection RARE - lining of the part of male urethra and epididymis ● Multiple cell layers. Apical cells are dead and filled with protein keratin Protect underlying tissue from abrasion ● 7. Non-Keratinized ● Epidermis of skin ● ● ● Superficial cells alive and kept moist Protection of underlying tissue Lines oral cavity, phayrnx, larynx, esophagus, vagina, and anus Withstand abrasion from ingested materials ● 8. Stratfied Cuboidal ● ● ● Two or more layers Protect and secrete Ducts of most exocrine glands and ovarian follicles ● ● Protect and secrete Large ducts of salivary glands, conjunctiva covering eye, and membranous part of male urethra ● Appearance varies depending on if relaxed or distended. Relaxed: apical cells are large and rounded. Distended: flattended cells at apical surface some binucleated Urine elimination Bladder, ureters, and part of 9. Stratified Columnar ● 10. Transitional ● ● ● urethra