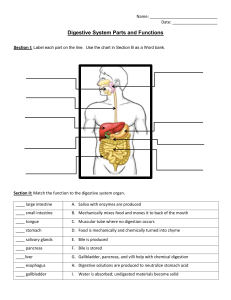
Chapter 23: Interactive Physiology: Digestive System Digestive System: Orientation 1. Absorption is the movement of nutrients and water across the GI epithelium into the blood or ___________________. Digestive System: Orientation 2. The inner lining of the mucosa is lined with simple _______________________ epithelial cells. 3. Smooth muscle in the muscularis externa produce peristalsis and ________________________________. 4. The enteric nervous system is comprised of the submucosal plexus and the ________________________ plexus. 5. The esophagus conveys a _______________________ to the stomach and enters at the cardia region. . 6. Most digestion and absorption occurs in the _______________________________________. 7. List the 3 regions of the small intestine. ____________________________, ______________________________ , and ______________________________________ 8. The shortest small intestine region is the __________________________ and the longest is the _______________. 9. The function of the plicae circularis is to increase ______________________________________. 10. The microvilli on the columnar cells of villi form the ______________________________ border. 11. The smooth muscle bands of the large intestine are called _____________________________________. 12. The __________________________ sphincter prevents the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus. 13. The _________________________valve prevents reflux from the large intestines into the small intestines. 14. The _________________________sphincter controls the rate of gastric emptying into the duodenum. 15. The ____________________ anal sphincter is comprised of skeletal muscle and must be relaxed to defecate. 16. Bile is produced by the _______________ is stored in the ___________________ and is necessary for fat digestion. Digestive System: Control of the Digestive System 1. Sight, smell and thoughts of food trigger salivation and gastric secretions during the ___________________ phase. 2. Parasympathetic impulses ___________________ digestion and sympathetic impulses _______________ digestion. 3. Intrinsic reflexes which connect different areas of the GI tract are called ________________________ reflexes. 4. The neurotransmitter of the postganglionic fibers of parasympathetic fibers is ____________________________. 5. The neurotransmitter of the postganglionic fibers of sympathetic fibers is ______________________________. 6. Gastrin is secreted from the pyloric region of the stomach and stimulates ___________________ secretion. 7. CCK is secreted from the __________________________ and causes the _____________________ to contract and the pancreas to secrete enzymes. 8. Secretin is released from the duodenum and causes the liver and pancreas to secrete _________ into the duodenum. Page 1 Digestive System: Motility 1. The function of chewing is the ________________________breakdown of food and to mix the food with saliva. 2. The esophagus is a conduit between the ____________________________ and the stomach. 3. A typical swallow of a bolus takes ____________________ to reach the stomach by peristalsis. 4. The stomach can stretch to accommodate a large meal by ____________________________ relaxation. 5. Food is mixed and moved out of the stomach by _______________________________________. 6. During the intestinal phase, fat in the duodenum triggers the release of the hormone ______________________. 7. Acid in the duodenum triggers the release of the hormone _______________________________. 8. The motility of the small intestine during digestion is _________________ which mixes the chyme and brings it in contact with the absorptive epithelium. 9. The major function of the large intestine is in storing and concentrating ________________________________. 10. During the defecation reflex the rectum contracts and the ___________________anal sphincter relaxes involuntarily. Digestive System: Secretion 1. The total amount of fluid entering the digestive tract in a given day is _____________________ liters. 2. In a given day you produce 1 and ½ liters of saliva and ________________ liters of gastric juice. 3. Saliva contains lysozyme and _______________________ which are antimicrobial. 4. Saliva contains the enzyme __________________________ which begins the digestion of carbohydrates. 5. ____________________ stimulation of salivary glands produces large amounts of watery saliva containing enzymes. 6. In the gastric glands, parietal cells secrete _________________________ and ____________________________. 7. Chief cells secrete ___________________________ which gets activated to the protease ____________________. 8. _________________ secreted from the gastric glands protects the stomach lining from the HCl. 9. Chyme in the stomach is nearly sterile due to the ________________________________. 10. HCl activates _______________________ to pepsin which digest proteins. 11. Pancreatic juice enters the duodenum through the ___________________________ sphincter. 12. The liver and pancreas both secrete __________________________ into the duodenum which helps to neutralize the acidic chyme from the stomach. 13. The enterohepatic circulation involves the circuit of __________________ from liver to small intestines to blood to hepatic portal vein back to the liver. Digestive System: Digestion and Absorption 1. The most abundant dietary carbohydrates are 3 disaccharides and ___________________________. 2. Sucrose is digested to ___________________and fructose. Lactose is digested to _______________ and galactose. Page 2 3. Proteins are digested to ______________________________ and peptides. 4. Protein digestion begins in the ____________________________________ with pepsin. 5. Indigestible fibers contained in fruit and vegetables make up dietary ____________________________. 6. Most of the water and salt that enter the GI tract are absorbed in the ______________________________. 7. The last stage of carbohydrate digestion is to break them down by ________________________enzymes into monsaccharides which are absorbable. 8. List the 3 major pancreatic proteases. __________________ _____________________ __________________ 9. Large fat drops are broken into smaller fat drops by ________________________ in the small intestine. 10. ___________________ salts keep small fat droplets in solution by a process called emulsification. 11. Lipase digests triglycerides and those products are surrounded by bile salts to form _________________________ 12. Finally chylomicrons are absorbed into _____________________________________. Page 3