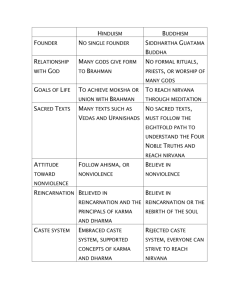
Moksha - Liberation E perience characteri ed b infinite being, infinite a areness, infinite bliss Completel be ond e periences of this orld Monism: All is Brahman Most Hindus belie e in Monism Doctrine that all realit is ultimatel one Belief that all forms of realit share a COMMON ESSENCE - Brahman Ultimate Realit (Brahman) can be understood through in ard contemplation of the self Ultimate realit ithin is Atman - the eternal Self Parts of Atman make up Brahman! La and Order: Di ine Principles in the World Karma Karma functions HAND IN HAND ith SAMSARA - determines nature of each reincarnation Moral la of cause and effect: states that e er action produces an outcome that is justified b the action s moral orthiness Determines all the particular circumstances and situations of one s life *An indi idual s karmic record sta s ith the self from reincarnation to reincarnation* Karma determines life form into hich the atman (self) is born Dharma La of Karma: holds people responsible for actions Appl ing this requires standard for determining rightness/ rongness of actions This standard: DHARMA (ethical dut based on di ine order of realit ) Dharma is the complete rule of life For e er acti it , there is a a of acting that conforms to Dharma Four sources: Di ine re elation (sacred scriptures) Sacred tradition (from generation to generation) Practices of those considered isest in societ Conscience Shifts focus from satisf ing pri ate cra ings to caring for others + limits one s pursuits Ka a, e a a f ca e a d effec , ba ed d a a, e ca d ,a d ,D a a c ec ed ca de Person s dharma: determined b e de , ca e, a e f fe Ka a ba ed D a a! Dharma of Women: t picall emphasi ed obedience to men Primar role: elfare of famil Limited education and career Thought to ha e more integrit Dharma of Men: tied more to caste + stage of life Doing One s Job: The Caste S stem Four distinct classes Brahmin: Priests Kshatri a: Warriors and Administrators Vaish a: Producers Shudras: Ser ants and Laborers Additional categor for outcastes - those considered to be outside of societ altogether Also kno n as Harijan ( God s Children ); ha e onl recentl gotten some legal rights Subdi ided into >3000 categories Correspond to different occupations for men For omen: caste determines ho the can marr Ca e e : d ba ed e ed One is simpl born to lifelong cast identit This identit : determined b karma - directs soul into hate er situation it deser es Karma can be seen to justif the caste s stem itself People do not just happen to be born outcastes: the deser e this lo l status because of their stinking conduct in pre ious li es/lifetimes Ka a de e e ca e de , ca e, , de e e ec f c DHARMA e a e ac Acting One s Age: Four Stages of Life Upon undergoing initiation ritual at pubert , Hindu bo enters first stage: of student Lasts until marriage Second stage: Householder Pursuing a career and raising a famil are central Women and husbands together in ol ed in this stage Third stage: Birth of the first grandchild Forest d eller stage Fourth stage: sann asin ( andering ascetic) For forest d ellers ho are read to return to societ but remain DETACHED from normal attractions/distractions of social life Engaged ith the orld but NOT ATTACHED to it Seeking One s Desire: Four Goals of Life Important: Liberation from samsara (c cle of rebirth) is summit of spiritual fulfillment Moksha: ULTIMATE GOAL of life (1) Sensual Pleasure Kama - pleasure Ultimate goal of life Mainl pleasures of sensual lo e - is to be embraced b hosoe er desires is (as long as lo ers remain in limits of DHARMA) (2) Material Success Yearning for Artha: material success (and social po er/prestige that follo s it) Hinduism celebrates goal of ARTHA E entuall pro es unfulfilling; people e perience earning to stri e for something BEYOND PURSUITS that pro ide for onl personal & material needs (3) Harmon ith Dharma basedondivine Dharma: general principle of ethical dut No the thing that is MOST desired Deep jo of li ing in harmon ith dharma is kno n firsthand (4) Bliss of Moksha All Hindus destined to seek 4th goal Infinite being, a areness, bliss of Moksha Three Paths to Liberation (MOKSHA) For the Acti e: Ka a Marga ( Path of the Works ) Most people (for hom ph sical acti ities come naturall ) choose liberation through Karma Marga Also kno n as: Karma Yoga Has to do ith li ing in accordance ith Dharma Performing action ithout attachment to outcome Selfless Ser ice Cease to identif ith the ego Heart is purified: egoism/selfishness is anished; creates space for pure lo e, compassion, etc. Ma E e ce: D e beca e F e DHARMA ( e e) a d acce ae e c e For the Philosophical: J a a Marga ( The Path of Kno ledge ) Intended for those ith talent for philosophical reflection Shortest (but steepest) ascent to liberation Requires great amount of time: (for) learning + meditation Most practical for BRAHMIN class order ofreality Ma e E e ce: A a ed e e a ce ed e f e a e f ea E periential dimension of Hinduism! Reached through f dc e a f e e f, e perience brings full a areness of truth, certitude that has po er to transform kno er (leading to liberation) Sa d be e d ff c a : e e d a d e ec be d e e e f a ea e a eO e eD e. For the Emotional: Bhakti Marga ( The Path to De otion ) Yoga of De otion Said to be easiest of paths - can be practiced b an one (regardless of mental/ph sical abilities) + does not require e tensi e ogic practices Pa f e c e e ea ,a a ce, a ed, , e c. Replaces feelings ith jo , di ine ecstas , bliss, etc. Vedanta: Fine thread made of Pure Lo e (Prem) hich connects heart ith Di ine This thread: ESSENCE OF BHAKTI Has been l ing dormant in heart since beginning of creation, hidden b la ers of ignorance and suffering But no matter ho deep one goes, this thread (Di ine connection) can ne er be broken Creates deep YEARNING of Soul for JOY and BLISS Bhakti: To be lo e - to be into icated ith Di ine Lo e U f be e LOVE ITSELF A atar Incarnation (li ing embodiment) of a deit Commonl of Vishnu - sent to earth to accomplish Di ine purpose Bhaga ad Gita Most popular sacred te t of Hindu Religion Rele ant to man aspects of Hinduism Most closel associated ith BHAKTI YOGA/MARGA Content of Bhaga ad Gita ackno ledges fruitfulness of path of orks and path of kno ledge but tends to fa or path of DEVOTION Caste S stem Toda Marriage across caste lines is still taboo for some families India s rapid economic e pansion and booming high-tech sector: BIGGEST change to alle iate problems of caste s stem (that pre ailed through centuries) Turning AWAY reser ation of ell-pa ing jobs for some and menial jobs for others Hiring of thousands of orkers: b foreign and domestic high-tech firms Some Dalits - rising into India s middle class International companies (talent is #1 issue) ha e also made difference T o Indias - one rich and one poor India s caste s stem can NO LONGER full contain the socioeconomic change the countr is undergoing Different religions, occupations, and le els of education - no longer correlated ith caste IMPORTANT! Limited access to education and resources - still a problem for some Dalits Missionar schools and go ernment-sponsored education ha e helped