Cell Membrane Structure: Hydrophobic & Hydrophilic Properties

Biology
Matthieu-Pierre Currie
October 21, 2019
Homework
Question:
Explain how hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties contribute to the arrangement of molecules in a membrane.
Answer:
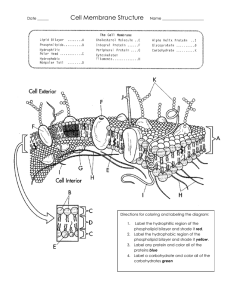
Phospholipids form the basis of the cell membrane with the head containing a phosphate and glycerol group and the tail containing a fatty acid group. Therefore, the head would be polar or hydrophilic whilst the tail would be non-polar or hydrophobic thus the phospholipid is to be considered amphipathic due to the dual hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties.
Consequently, due to the amphipathic nature of phospholipids and the attraction between the hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails in water the phospholipids form a bilayer. Structurally, the hydrophilic phosphate heads would be facing outwards with the hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails facing inwards as represented by the fluid mosaic model.
Furthermore, the amphipathic nature of the phospholipids contributes to the positioning molecules such as proteins, cholesterol and carbohydrates found in membrane structure.
Extrinsic proteins are hydrophilic on their surface and thus are not embedded in the membrane but attached to the surface of integral proteins or anchored onto the membrane surface. Integral proteins possess mostly hydrophobic surface thus found embedded within the membrane in the hydrocarbon chains with the portions of the protein protruding through the regions of the phosphate heads being hydrophilic at the ends.
Cholesterol is only present in animal cells but nevertheless the amphipathic nature contributes to its positioning. Cholesterol is primarily hydrophobic but at one end is hydrophilic due to the presence of a hydroxyl group in its molecular structure. As a result, most of the cholesterol molecule is found embedded within the membrane in the hydrocarbon chains but the hydrophilic portion is attracted to the phosphate head and thus the molecule is found in between the phospholipids in the membrane.
Carbohydrates found in the cell membrane structure are hydrophilic and consequently found on the outside attached to the hydrophilic phosphate heads to form glycolipids, attached to the hydrophilic portion of integral proteins to form glycoproteins or attached to the hydrophilic surface of integral proteins to form glycoproteins.