Cells - Uplift Education
advertisement

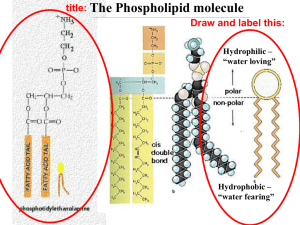
August 25-26, 2014 What do these all have in common? Real cells differ greatly from each other and from a ‘generalized cell’ in order to carry out different functions. Cells differ in: • Size • Shape • Number & type of organelles How well do you remember the structures of the cell? Earn bragging rights by being the first to match up the structure with the function. Afterwards, use the same papers to label a generalized cell diagram. With a partner, answer the 4 questions on your guided notes. … 5 minutes Identify special features of each cell that help them do their specific functions. What special features do you see? What special features do you see? - Microvilli to increase surface area for absorption of nutrients - Tight junctions between cells to prevent digestive enzymes from leaking into the tissue of the small intestine. What special features do you see? What special features do you see? - Small to fit through capillaries - No organelles or nucleus to maximize area for carrying oxygen What special feature do you see? What special feature do you see? cilia – to help move mucus over surface of the trachea What is the difference between microvilli and cilia? What is the difference between microvilli and cilia? - Microvilli are extensions of cell membrane, cilia are proteins - Microvilli increase SA for absorption, cilia move substances Read your textbook for more examples! Selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the environment. What does ‘selectively permeable’ mean? Only some materials can cross the membrane Selective permeability is necessary for the cell to maintain the correct internal environment for physiological functions. Phospholipids ◦ Make up the majority of the membrane ◦ Arranged in a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads outside, and hydrophobic tails inside Hydrophilic = ___________ Hydrophilic molecules are __________ like water. Hydrophobic = ____________ Hydrophobic molecules are __________ like oil. Phospholipids ◦ Make up the majority of the membrane ◦ Arranged in a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads outside, and hydrophobic tails inside Hydrophilic = water loving Hydrophilic molecules are polar like water. Hydrophobic = water fearing Hydrophobic molecules are nonpolar like oil. Phospholipids The structure of phospholipids is the key to their function! Hydrophilic heads can interact with watery external environment and watery cytoplasm. Hydrophobic tails reduce the diffusion of water and other charged or polar substances across the membrane. Cholesterol ◦ Makes the cell membrane more rigid and less permeable to water Proteins ◦ Act as enzymes, pores, carriers, and hormone receptors, and structural elements Glycoproteins and Glycolipids ◦ Glyco = sugar! ◦ Influence cell interactions (e.g. identifying cell as ‘self’) and molecule transport Talk with a partner then share as a class Scholar on the left answers … ◦ What are the 4 membrane components? ◦ Which component has most functions? Why? Scholar on the right answers … ◦ Name 4 functions of membrane proteins ◦ Which two components are primarily responsible for reducing fluid loss through the cell? What do those components have in common? For each sheet, The vocabulary word(s) and definition(s) should be written in large letters A diagram should be drawn. Must be accurate, neat, and visually appealing! Vocab minisheets / Study! What were our objectives and how well did you learn about them? How did what we do today connect to our unit statements? What learner profile trait did we demonstrate? TOK connection: What are the primary ‘ways of knowing’ that lead to our scientific knowledge of cells? Draw and label a cell. At least 5 of the components should be labeled with name and function.