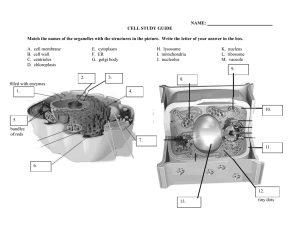
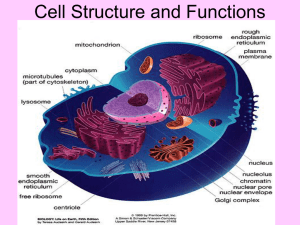
Chapter 2 Ultrastructure of cells Name: Page 52 Quick check 1 2 Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false. a Fossilised indirect signs of life could be cells. b A modern sign of life could be a footprint. c The first cells to appear on planet Earth were eukaryotic cells. d The Pilbara region of Western Australia is a source of direct and indirect evidence of early life on Earth. e Microbial mats occur in a variety of environments. What is the essential difference between a direct and an indirect sign of life? Answers 1 a False. Cells, living or fossilised, are direct evidence of life. b True. Signs of life result from past or present interactions of organisms with the environments in which they lived or live. c False. Life organised as eukaryotic cells appeared on Earth about 2.1 billion years ago or earlier, but much later than the first prokaryotic life forms. d True. Both cells (direct evidence) and the activity of cells (indirect evidence)have been found in this region. e True. Microbial mats can form on moist or submerged surfaces including lakebeds, on sediments such as mud or sand, on tidal flats, in hypersaline (very salty) pools, in fissures, around hot springs and even around deep ocean vents. 2 A direct sign is the cells themselves. The cells could be fossilised or living. An indirect sign is the evidence of activity of cells, for example, distinctive marks created by microbial mats. Page 57 Quick check 3 Given a choice of any kind of microscope, which kind might you choose to examine the following: a a living amoeba b the detailed ultrastructure of an animal cell c the surface of a layer of cells d the distribution of a specific protein in cells? 4 Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false. a A scanning electron microscope can be used to examine living cells. b The resolving power of a transmission electron microscope is much better that that of a light microscope. c All kinds of optical microscopes use visible light to illuminate the specimens to be viewed. d A microscope with a magnifying capability of several hundred thousand is likely to be a phase contrast microscope. © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 1 Chapter 2 answers Answers 3 a b c d 4 a b c d Light microscopes typically use visible light to examine cells, including living cells. Transmission electron microscopes (TEM) reveal the fine details of cell ultrastructure. Scanning electron microscopes (SEM) reveal surface detail and texture. Fluorescence microscopy uses fluorescent probes that bind to cell structures and to proteins to reveal the details of the structure and function of cells. False. The specimen viewed using an electron microscope is placed in conditions that are not life supporting. True. A transmission electron microscope can resolve down to a separation of less than 0.1 nm, making atoms visible. Resolution of light microscopes is about 0.2 μm (200 nm). False. In optical microscopy, specimens are illuminated by visible or ultraviolet light, or laser light that is focused on the specimen through the use of lenses. False. A phase contrast microscope would normally be used for magnifications of 400X or 1000X. Quick check 5 6 7 Identify whether each of the following is true or false, giving a brief explanation where needed. a A nucleus from a plant cell would be expected to have a nuclear envelope. b Prokaryotic cells do not have DNA. c A mature red blood cell has high energy needs and, in consequence, has large numbers of mitochondria. What is the difference between the cytosol and the cytoplasm of a cell? A cell has a cell wall. What conclusion can be drawn about the kind of organisms from which it came? Answers 5 6 7 a True. Both plant and animal cells have a nuclear envelope. b False. Prokaryotic cells contain DNA. The DNA is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. c False. Red blood cells are effectively just bags of haemoglobin that are carried passively around the bloodstream. Relative to other cells, red blood cells have very low energy needs that can be met by fermentation; mature red blood cells have no mitochondria. The cytosol is the fluid region within the cell and is surrounded by the plasma membrane of the cell. The cell organelles, excluding the nucleus, together with the cytosol form the cytoplasm of a cell. An organism with a cell wall could be one of the following: bacteria, archaea, fungi or plant. Page 68 Quick check 8 9 Identify whether each of the following is true or false. a The RNA of the ribosomes is made in the nucleolus. b Rough ER and smooth ER serve the same functions in a eukaryote cell. c The folding of a protein into its functional 3D shape takes place on the ribosomes. d Ribosomes are membrane-bound organelles that form part of the cell cytoplasm. e The channels of the Golgi complex are connected to those of the ER. A scientist wished to examine ribosomes in a liver cell. a Where should the scientist look: in the nucleus or the cytoplasm? © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 2 Chapter 2 answers 10 11 12 b What kind of microscope is likely to be used by the scientist: a light microscope or a transmission electron microscope? Explain. List one similarity between rough ER and smooth ER. Identify two differences between rough ER and smooth ER, one structural and one functional. The liver is an important organ in detoxification of harmful substances. What organelle in liver cells is active in this process? Answers 8 9 10 11 12 a True. rRNA is made in the nucleolus. b The functions are not exactly identical. Both the rough ER and the smooth ER are involved in transporting different materials within cells, the rough ER and the smooth ER also have other important functions that differ from one another. c False. Folding proteins into their correct functional shape or conformation occurs within the rough ER. d False. A ribosome is not surrounded by a membrane. e False. Transition vesicles connect the ER to the Golgi complex. a The scientist would look in the cytoplasm. b The scientist would use a transmission electron microscope. Ribosomes are only 0.03 μm in diameter. Both the rough ER and the smooth ER are involved in transporting different materials within cells. Rough ER has ribosomes and is involved in the processing and transport of proteins. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and has several functions, including the synthesis of lipids and detoxifying harmful substances. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum is important in the detoxification of hydrophobic products of metabolism and barbiturate drugs by converting them to water-soluble molecules. Page 75 Quick check 13 14 15 16 17 18 Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false, giving a brief explanation where needed. a Chloroplasts are enclosed within a single membrane. b Peroxisomes carry out the oxidation of long chain fatty acids. c The enzyme catalase is one of the many enzymes present in peroxisomes. d Chloroplasts are present in all plant cells. e Fatty acids enter peroxisomes by simple diffusion. f The fluid within lysosomes contains about 50 digestive enzymes. g Cell organelles operate independently of each other. Where in a plant cell would you find chloroplast-containing cells? Identify one difference between cilia and flagella. Identify one similarity between cilia and flagella: a in terms of structure b in terms of function. What is the cause of Pompe disease? In what cell organelle would you expect to find the following structures? a Stroma b Grana c Microtubules © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 3 Chapter 2 answers Answers 13 14 15 a False. Each chloroplast is enclosed in two membranes, termed an outer and an inner membrane. In addition, a third membrane is present internally and this is folded to create an intricate internal structure consisting of many flattened membrane layers called grana. b True. Peroxisomes carry out several functions in cellular metabolism, including the breakdown of long chain fatty acids. c True. About 50 peroxisomal enzymes have been identified to date, including catalase and peroxidase. d False. Cells of the plant not exposed to sunlight would not have chloroplasts. e False. Normally, a specific transport protein on the peroxisome membrane brings long chain fatty acids across the membrane into the peroxisomes for breakdown. f True. The fluid in these cell organelles contains a large number (about 50) of digestive enzymes. g False. Organelles within a eukaryotic cell do not act in isolation but have a high degree of interdependence. Chloroplast-containing cells would be found in the leaves and in the stems of plants. Cilia are shorter than flagella. 16 a Each cilium and flagellum is enclosed in a thin extension of the plasma membrane. Both cilia and flagella have the same arrangement of microtubules in their structure, with nine paired microtubules in an outer ring and two central microtubules. A microtubule consists of 13 protein filaments that form a hollow tube. b Cilia and flagella can both create movement. 17 Pompe disease is the result of an absent or a defective enzyme in lysosomes that breaks down glycogen. a The stroma is found within a chloroplast. b The grana are found within a chloroplast. c Microtubules can be found in cilia and flagella. 18 Page 79 Quick check 19 20 21 Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false. a The genomes of chloroplasts of eukaryotic cells are closely related to those of modern cyanobacteria. b Endosymbiosis occurred only in organisms on the ancient Earth. c Mitochondria are accepted as having once been free-living microbes. d Bacterial cells contain mitochondria. What is the difference between symbiosis and endosymbiosis? Identify two lines of evidence in support of the Endosymbiosis Theory. Answers 19 a True. Genomic comparisons indicate that chloroplasts are most closely related to modern cyanobacteria. b False. We can see examples living today including nitrogen-fixing bacteria that live in the cells of nodules on the roots of legumes, such as clovers, and single-celled algae that live inside the cells of corals. © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 4 Chapter 2 answers 20 21 c True. The theory of endosymbiosis is now generally accepted as explaining in part the origin of eukaryotic cells, in particular the origin of their chloroplasts and mitochondria. Mitochondria were once free-living prokaryotic microbes. d False. Bacteria do not have membrane-bound organelles. The term symbiosis refers to an interaction between two different kinds of organism living in close proximity in a situation where often each organism gains a benefit. Endosymbiosis is a special case of symbiosis where one of the organisms lives inside the other. The Endosymbiosis Theory is supported by ongoing biochemical and genetic comparisons of mitochondria and chloroplasts with prokaryotes. Page 80 Biochallenge Exploring lysosomes 1 a There are about 50 different enzymes present in a lysosome. b Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and polysaccharides and nucleic acids are digested by the enzymes. 2 a The acidic condition is necessary to give the right conditions for optimal enzyme activity. b If the membrane of the lysosome is broken and the digestive enzymes are released into the cell, the activity of the enzymes will not be at an optimal level. Many of the enzymes may be denatured at pH7. 3 a The hydrogen ion gradient is from the lysosome to the cytosol. b The hydrogen ions are moved by active transport into the cell. Energy is required as the hydrogen ions are being moved against a concentration gradient. 4 a Phagocytosis. This is an example of endocytosis. b The bacteria can be taken into the cell and is broken down by the cell. c Autophagy. This is the breakdown of non-functioning cell organelles that are old and/or damaged. © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 5 Chapter 2 answers Page 81 Chapter review questions 1 An example of a possible concept map is as follows. 2 Some possible answers are in the table below. Location How assists in cell functioning nucleus A nuclear envelope controls the passage of material into and out of the nucleus. mitochondria The highly folded inner membrane is the site of respiratory enzyme action. endoplasmic reticulum Membrane forms a transport channel. Golgi complex Membranes are used to package material for export. lysosomes The membrane protects the rest of the cell from the digestive enzymes contained within the sac. 3 a b c d e f g h Nucleus Cell membrane Mitochondria Ribosome Golgi complex Lysosome Peroxisomes Chloroplast 4 a Largest to smallest: (iv) organ, (ii) tissue, (i) cell, (vii) nucleus, (vi) nucleolus, (iii) mitochondrion, (v) ribosome b Outside to inside the leaf: (ii) cell wall, (iii) plasma membrane, (iv) cytosol, (i) nuclear membrane, (v) nucleolus © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 6 Chapter 2 answers 5 6 a All cells from plants, animals and bacteria possess ribosomes, DNA and a plasma membrane. b If each cell contained mitochondria the cell could not be a bacterial cell. Bacteria do not have membrane bound organelles. c The cell could be either a plant or animal cell as lysosomes are present. Note that in plants vacuoles containing a similar range of enzymes carry out the same function as an animal lysosome. Some experts call these lysosome-like vacuoles, while others simply call them plant lysosomes. a i The presence of a nuclear envelope would distinguish a plant cell from a bacterial cell. ii The presence of a cell wall would distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. b The presence of a cell wall would be more robust evidence as not all plant cells have chloroplasts. 7 a Energy requirements for the heart muscle cells are high as the cardiac muscle fibres contract frequently. This energy is supplied by the mitochondria. Large numbers of mitochondria provide the high energy demanded by the heart muscle. b Cells that secrete lipids would require large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum as the outer membrane surface of the smooth ER is a site of synthesis of lipids; these lipids are then enclosed in a small section of the smooth ER membrane that breaks off and transports the lipids to sites within the cell where they are exported from the cell. c Red blood cells do not have DNA. They lack the genetic instructions required for the formation of protein. d Cells with a prominent Golgi complex are secretory cells, for example, pancreatic cells which secrete insulin. Cells lacking a Golgi complex are not secretory cells. 8 a (a): 20 minutes; (b): 40 minutes; (c): 5 minutes Correct order for viewing is: (c) followed by (a) followed by (b). b When radioactively labelled amino acids are incorporated into a cell, the amino acids are synthesised into proteins in the rough endoplasmic reticulum, (c). The radioactively labelled protein then moves to the Golgi complex where it is packaged for secretion. The radioactive protein moves in vesicles to the cell surface where it is secreted by exocytosis into the surrounding environment, (b). 9 a This enslaving refers to the idea that some primitive microbes were taken inside another cell. b The ‘brethren’ are the primitive microbes. c These primitive microbes may have given the host cell an advantage such as a new source of energy or a more constant oxygen supply. d The ‘brethren’ may have received a more constant supply of food or a more stable environment in which to live. © John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 7