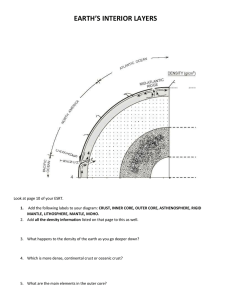
CLG# 5 Layer Thickness Temperature Composition Crust Oceanic (5km to 10 km) Continental (30 km to 50km) about 200 °C to 400 °C oxygen (46.6%), silicon (27.7), aluminum (8.1), iron (5.0), calcium (3.6), potassium (2.8), sodium (2.6), and magnesium (2.1). Mantle 2,900 km 500° to 900 °C Outer Core 2,200 km 4400 °C to 6100 °C iron and nickel Inner Core 1250 km 6,000°C nickel-iron alloy made up of rock containing silicon, iron, magnesium, aluminium, oxygen and other minerals. DISCONTINUITIES Conrad Discontinuity- corresponds to the sub-horizontal boundary in continental crust at which the seismic wave velocity increases in a discontinuous way. Moho Discontinuity- lies almost entirely within the lithosphere; only beneath midocean ridges Repetti Discontinuity- between upper and lower mantle. Guttenberg Discontinuity- Between lower mantle and outer core Lehman Discontinuity- Between outer and inner core Which wave is detected first in the Earth’s surface? Seismic Wave Crust Mantle Outer Core Inner Core P wave Yes (but are slowed in the boundary of the crust and mantle) Yes Yes Yes S wave Yes Yes No (passing from the mantle to the core are absorbed because s waves cannot be transmitted through liquids. ) No The wave is the P wave or primary wave. This is the fastest kind of seismic wave, and, consequently, the first to 'arrive' at a seismic station. The P wave can move through solid rock and fluids, like water or the liquid layers of the earth. Lithosphere- the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle. Asthenosphere- the upper layer of the earth's mantle, below the lithosphere, in which there is relatively low resistance to plastic flow and convection is thought to occur. Tectonic plates are pieces of Earth's crust and uppermost mantle