Cell Boundaries
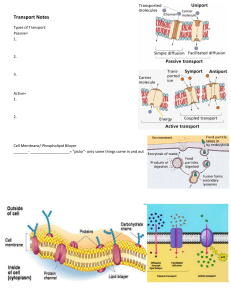
The Cell Membrane
The Cell Membrane
Thin, flexible barrier
Regulates what enters and leaves
Protects and supports
aka: Phospholipid Bilayer .
Consists of: hydrophilic head
(water liking) and a hydrophobic tail.
(water avoiding)
Phospholipid Bilayer: Fluid Mosaic Model
Also has
Proteins – doorways
Carbohydrates – name tags
Cholesterol – keeps membrane flexible
Therefore referred to as a “fluid mosaic” of different molecules.
Cell Boundaries
The Function of the
Plasma Membrane
The Cell Membrane
Cells want nutrients
Cells get rid of wastes
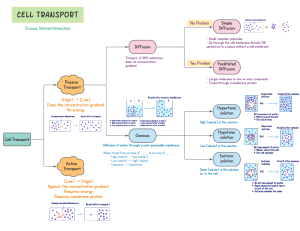
Two ways:
Passive Transport – No Cell Energy (ATP) needed
Active Transport – Cell Energy (ATP) required
Passive Transport - Diffusion
Passive Transport – Facilitated
Diffusion
Passive Transport - Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules through a cell membrane.
Concentration gradient depends on amount of dissolved particles (like salt) inside and outside the cell.
Isotonic Solution
Concentration of a dissolved substance
(solute) is the same inside and outside the cell.
Isotonic = Dynamic equilibrium.
Cell stays same size.
Isotonic Solution
Hypotonic Solution
Concentration of the solute is low outside the cell and higher inside the cell.
Water moves INTO the cell.
Cell gets BIG like the
O in hyp
O tonic
Hypotonic Solution
Hypertonic Solution
Concentration of the solute is higher outside the cell and lower inside the cell.
Water
E xits the cell.
Think of the “E” in hyp
E rtonic
Cell shrinks.
Hypertonic Solution
Assignment
Draw and Label Figure 23, 24 and 25 on page 204-205.
Complete the Osmosis worksheet.