US History Chapter 5 Review: French & Indian War to Revolution
advertisement

US History
YOU DO NOT HAVE MY PERMISSION TO POST THIS IN ANY OTHER LOCATION OR
Fort Burrows
TO MAKE COPIES OR TO DOWN LOAD.
REVIEW with Answers Chapter 5
French and Indian War – war between France and Britain that ended France’s power in North America
Albany Plan of Union – the attempt to create one general government for the 13 colonies;
proposed by Benjamin Franklin
Plains of Abraham – a field near Quebec on the St. Lawrence River;
site of a major British victory over the French
Treaty of Paris – 1763 Treaty that ended the French and Indian War
makeshift – put together quickly as a temporary substitute
surveyor – a person who determines the size, location, or boundaries of an area of land
skirmish – a short often unplanned battle between small groups or soldiers
popular sovereignty – ultimate power and final authority for a law, rest with the citizens’ votes
Republicanism – power to the people to exercise their power by delegating it to representatives chosen by
them through elections
federalism – power is divided between the central government, by the Constitution, and all other powers
go to state government
separation of powers – national governments’ power is divided among three separate branches
checks and balance – each branch of the government has controls (checks) over the other two branches
limited government – government power is limited by the rule of law which is the Constitution
individual rights – personal freedoms, personal protections, and equality under the law
Pontiac’s War – 1763 conflict between Indians and British over Indian land near the Great Lakes
Proclamation of 1763 – law that forbid English colonist to settle West of the Appalachian Mountains
Stamp Act – 1765 law placed duties on legal documents, newspapers, almanacs, playing cards, & dice
petition – formal written request to someone in authority, signed by a group
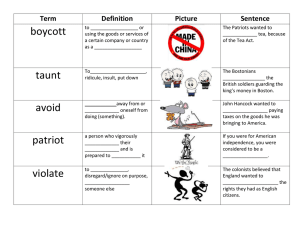
boycott – refusal to buy certain goods and services
repeal – cancel
Townshend Acts – 1767 laws that taxed glass, paper, paint, lead, and tea
writ of assistance – legal document that allowed British customs to inspect a ship’s cargo without
giving a reason
Boston Massacre – 1770 conflict between colonist and British troops in which colonists were killed
committee of correspondence – letter writing campaign that became a major tool of protest in the
colonies
proclamation – an official formal public announcement
crest – the top line of a mountain or hill
province – an administrative district or division of a country
controversial – giving rise to a different and opposing views
duties – taxes or tariffs
intolerable – unbearable
writ – a written order by a court of law
Tea Act – 1773 law that let the British East India Company bypasses tea merchants and sell directly
to colonists
Boston Tea Party – 1773 protest colonists dressed as Indians and dumped British tea into the harbor
Intolerable Acts – 1774 laws passed to punish Boston for Tea Party
Quebec Act – law to set up government in Canada and protect the rights of French Catholics
First Continental Congress – 1774 meeting in Philadelphia of delegates from 12 colonies
militia – army of citizens who serve as soldiers during an emergency
1 of Review w/Answers Chapter 5 SEPT 2019
US History
YOU DO NOT HAVE MY PERMISSION TO POST THIS IN ANY OTHER LOCATION OR
Fort Burrows
TO MAKE COPIES OR TO DOWN LOAD.
minuteman – colonial militia volunteer who was prepared to fight in a minute’s notice
battles of Lexington and Concord – 1775 conflict between Massachusetts colonists and British
soldiers that started the Revolutionary War
trespass – to go onto or into someone’s property without any right
bypass – to avoid by going around
scorned – rejected or dismissed as unworthy of respect
enlist – to enroll oneself in the armed forces
artifact – object used to understand how a group lived in the past
Unalienable Right {also known as natural rights}– right cannot be taken away without legal justice
abolitionist – person against slavery
abolition – act of abolish, stopping slavery
patriot – one that supports all aspects of their country’s independence
Match the correct Colony to the correct description.
Middle Colonies
New England Colonies
Southern Colonies
1. This colonies’ economy was based on rice, indigo and tobacco plantations ?
Southern Colonies
2. This colonies’ economy was based on farming, ranching and skilled artisans/crafts ?
Middle Colonies
3. This colonies’ economy was based on whaling, shipbuilding and sawmill ports ?
New England Colonies
4. How did Pontiac react when the French told him that the Treaty of Paris had been signed ?
he was disappointed that the French would no longer offer aid
5. What colonial claim regarding the Boston Massacre is supported by these allegations ?
Crispus Attucks - Victim of the Boston Massacre died in 1770
James Caldwell - I was an innocent bystander when I was shot in 1770
Patrick Carr - I was shot and killed by British soldiers in 1770
Samuel Gray - I was attacked by British soldiers and died in 1770
John Maverick - Last thing I heard was musket fire in 1770
that the British soldiers fired on unarmed colonists
6. What did the British Parliament do to the colonists after the Boston Tea Party ?
passed the four (4) Intolerable Acts
7. Why did the colonist resent British regulations such as the Sugar & Stamp Acts ?
the colonist felt it was taxation without representation
8. List the parts of the four (4) Intolerable Acts ?
1. shut down port in Boston
2. Parliament forbade colonist from holding town meetings without governor’s permission
3. custom officers were to be tried in Canada instead of Massachusetts
4. Quartering Act - colonists had to let the British soldiers in their homes for housing
9. What is the correct chronological order for these historical dates ?
9. Know the year each event happened in…
1. FOC 1639
2. HOB 1619
3. Mayflower Compact 1620
4. Magna Carta 1215
10. On March 5, 1770, 5 colonists were killed at in Boston, so why did Samuel Adams name the
event the ‘Boston Massacre’ ? he wanted colonists to move to action against British oppression
2 of Review w/Answers Chapter 5 SEPT 2019
US History
YOU DO NOT HAVE MY PERMISSION TO POST THIS IN ANY OTHER LOCATION OR
Fort Burrows
TO MAKE COPIES OR TO DOWN LOAD.
11. What did British troops do to create the fall of New France ?
they captured Quebec
12. Name the four (4) new colonial leaders as the conflict with Britain escalated ?
From Massachusetts:
From Virginia:
1. Samuel Adams
1. George Washington
2. John Adams
2. Patrick Henry
13. What kept colonists from settling West of Appalachian Mountains ?
Proclamation of 1763
14. In the mid-1700s, where was France and Britain competing for land, rivers, and trade … ?
Ohio River Valley
15. What is Patrick Henry’s message when he states, “Give me liberty, or give me death!”?
freedom is worth dying for
16. Fighting broke out at Lexington and Concord for what reason ?
British were trying to seize colonial arms in Concord
17. The Proclamation of 1763 stated that colonists could not settle beyond which geographical
features ?
Appalachian Mountains
18. Complete the timeline with events from U.S. history ?
1763 - French and Indian War Ends
1765 - Stamp Act
1770 - Boston Massacre
1775 - Battles of Lexington and Concord
1776 - Declaration of Independence
19. What were the 1st battles of the American Revolution ?
battles of Lexington and Concord
20. What four (4) ways did the colonists respond to the Tea Act ?
1. served coffee
2. served liberty tea
3. boycotted the British tea
4. kept Company from unloading cargo
21. What is the BEST primary source for studying the founding of the American colonies ?
a journal writing by a witness or participant
22. What was the French fort’s name that General Amherst captured ?
It was also France’s most important fort in Canada.
Louisbourg
23. What were the three (3) things accomplished from the signing of the Treaty of Paris ?
1. brought the long conflict to an end
2. marked the end of the French power in North America
3. allowed Britain to gain control of Canada
24. Why did Ben Franklin’s Albany Plan of Union not get approved ?
colonies did not want to give up any power to a central council
25. What did Ben Franklin use as a frame of reference to create the Albany Plan of Union ?
political structure of the League of the Iroquois
26. 1639 – plan of government in Puritan colony which expanded the idea of representative
government
FOC
27. 1620 – agreement by Pilgrims for ruling Plymouth to ensure the general good of colony
Mayflower Compact
28 1619 – marked the beginning of representative government in the English colonies –
House of Burgess
29. 1215 – British document stated citizens have basic rights and monarchs have to obey the law
Magna Carta
30. 1607 - 1st permanent English settlement - Jamestown, VA
3 of Review w/Answers Chapter 5 SEPT 2019
US History
YOU DO NOT HAVE MY PERMISSION TO POST THIS IN ANY OTHER LOCATION OR
Fort Burrows
TO MAKE COPIES OR TO DOWN LOAD.
31.
What did the British troops do to surprise the French at Quebec ?
climbed a steep wall at night
32. Why did Parliament raise taxes in the colonies after 1763 ?
thought colonists should help pay for French and Indian war debts
33. Name the country that posed the most serious threat to the English colonies in North America
in 1750 ?
France
34. Why did the British issue the Proclamation Line of 1763 ?
to avoid conflicts with Native Americans in the Ohio Valley
35. Why did the colonists say “The Mohawks are come!”
colonists disguised as Mohawks dumped tea into Boston Harbor
36. How did the French and Indian War lead to the American Revolution ?
The British government taxed the colonists to help pay for the war debts
37. How did the colonists demonstrate their opposition to British actions and hurt their trade.
they boycott British goods
38. Colonial traders profited greatly from the Triangular Trade and traded with the colonies of
European nations other than England.
How would the traders responded if England started to strictly enforce the Navigation Acts ?
1. protest
2. ask for exemptions
39. Why did many of the colonial traders ignore the Navigation Act Law and bought sugar and
molasses from non-English colonies in the West Indies ?
demand for such products was high and so were the profits
40. William Blackstone published Commentaries on the Laws of England. Blackstone had
reviewed the entire history of English law. He was a member of Parliament and also a judge
in England. He believed what type of law was the highest and best form of law.
common law
41. Which event brought William and Mary of the Netherlands to begin ruling England in 1688 ?
Glorious Revolution
42. By the mid-1700s, the major powers of Europe; Britain, France, Spain, & Netherlands
competed for trade and were locked in a worldwide struggle for empires.
Why did France want to maintain its hold over the Ohio River Valley ?
they wanted to control the fur trade in the region
43. What causes created the French and Indian War to happen in North America ?
the British were building forts in the Ohio River Valley
44. Great Britain defeated the French and signed the Treaty of Paris, what was their gains ?
1. all lands east of the Mississippi except New Orleans
2. French lost control over Canada
45. What was the original reasoning behind the Proclamation of 1763?
to protect Indians in the western lands
46. What events led to the repeal of the Stamp Act in 1766 ?
1. petition to the king
2. a boycott of British exports
47. What did Mercy Otis Warren do to achieve recognition as one of the leading patriots ?
wrote plays that made fun of the British officials
48. Colonists, as a group, struggled with the Intolerable Acts.
What agreements did the colonies create democratically together ?
to stop exporting to Britain
4 of Review w/Answers Chapter 5 SEPT 2019