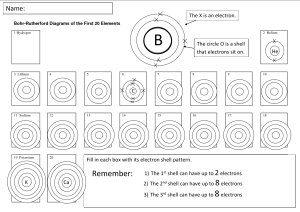
Electron Vocabulary Bohr Model – model of an atom which shows each individual proton, neutron, and electron. It shows the protons and neutrons at the center with electrons circling the outside. (electron cloud) – the area of an atom outside the nucleus where the electrons fly around electron shell – the electrons in the electron cloud are organized into shells. This is because of a complex system of repulsion and attraction between the protons and electrons within an atom. (unimportant fun fact: shells are divided into “sub-shells” and sub-shells are divided into “orbitals”.) Octet Rule – aka 2-8-8 Rule – only a certain number of electrons fit in each electron shell. first shell – First area the electrons go, but only up to two (2) electrons can fit in the first shell. second shell – After the first shell is full, more electrons will start filling the second shell. The second shell can hold up to eight (8) electrons. electrons in the 2nd shell have more energy than those in the 1st shell. third shell – Electrons go to the third shell after shell #2 is full. elections in the 3rd shell have more energy than elections in the 2nd shell. valence shell – The outermost shell with electrons. valence electrons – The electrons in the valence shell. ===================================== Electron Dot Diagram – aka Lewis Dot Diagram – a certain method of drawing an atom. The valence electrons are represented as dots around the outside of the element symbol. ===================================== Complete Octet - when the valence shell is full, we say it has as "Complete Octet". This is a chemically stable, "happy", state for every element. Atoms with a naturally incomplete octet can complete their octet by borrowing, donating, or sharing electrons with other atoms. Electrons being shared and traded is what creates chemical bonds between atoms! ===================================== (isotope) – an atom of the same element as another but with a different number of neutrons (ion) – an atom with a positive or negative (non-zero) net charge. This happens when the number of electrons is not equal to the number of protons. cation - an ion with a positive charge. happens when there are less electrons than protons. anion – an ion with a negative charge. happens when there are more electrons than protons. (chemical bond) – the connection between two atoms in a molecule. happens when their elections interact. covalent bond – a chemical bond made when two atoms share their elections to fill each other’s election shells. ionic bond – a chemical bond that occurs when the opposite charges of an anion and a cation attract each other. metallic bond – a chemical bond between metallic elements when valence elections are massively shared across a large number of atoms. electronegativity – a measure of how strongly a given element or atom will attract electrons from other atoms ionization energy – the amount of energy it takes to remove an election from a given atom.