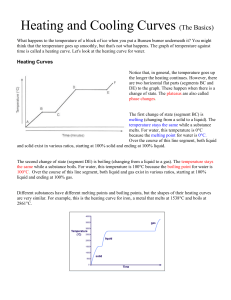
Honors Chemistry Unit 2 • Physical Behavior of Matter STUDY Classification of Matter: Describe the difference between atoms, compounds, and mixtures (heterogeneous and homogeneous) Describe how atoms combine to make different types of matter Interpret models representing atoms, compounds, mixtures, solids, liquids, and gases Energetic Nature of Phase Changes: Explain physical equilibrium: liquid waterwater vapor. Vapor pressure depends on temperature and concentration of particles in solution. (conceptual only – no calculations) Explain how the energy (kinetic and potential) of the particles of a substance changes when heated, cooled, or changing phase. Develop and use models to illustrate that energy at the macroscopic scale can be accounted for as a combination of energy associated with the motions of particles and energy associated with the relative position of particles. Identify pressure as well as temperature as a determining factor for phase of matter. Contrast heat and temperature, including temperature as a measure of average kinetic energy, and appropriately use the units Joule, Celsius, and Kelvin. GUIDE Explain phase change calculations in terms of heat absorbed or released (endothermic vs. exothermic processes). Phase Diagrams Interpret the phase diagrams of water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2) Use phase diagrams to determine information such as o phase at a given temperature and pressure o boiling point or melting point at a given pressure o triple point of a material. Heat Transfer Recognize that, for a closed system, energy is neither lost nor gained only transferred between components of the system. Explain the direction in which heat flows Describe energy as a quantitative property of a system that depends on the motion and interactions of matter within that system Complete calculations of: 𝑞𝑞 = 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚∆𝑇𝑇, 𝑞𝑞 = 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝐻𝑓𝑓 , and 𝑞𝑞 = 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝐻𝑣𝑣 using laboratory data Heating and Cooling Curves: Behavior of Gases Explain heating and cooling curves (heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, specific heat, melting point, and boiling point) Describe an ideal gas in terms of the kinetic molecular theory Define and use the terms and/or symbols for: specific heat capacity, heat of fusion, heat of vaporization. Explain the significance of plateaus and the physical states of each segment of heating and cooling curves Complete calculations of: 𝑞𝑞 = 𝑚𝑚𝑚𝑚∆𝑇𝑇, 𝑞𝑞 = 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝐻𝑓𝑓 , and 𝑞𝑞 = 𝑚𝑚𝐻𝐻𝑣𝑣 using heating/cooling curve data Explain the relationships among pressure, temperature, volume, and quantity of gas, both qualitatively and quantitatively Identify graphs representing relationships among pressure, temperature, and volume Solve problems using the following formulas: o o o 𝑃𝑃1 𝑉𝑉1 = 𝑃𝑃2 𝑉𝑉2 𝑃𝑃1 𝑇𝑇1 𝑉𝑉1 𝑇𝑇1 𝑃𝑃 = 𝑇𝑇2 = 2 𝑉𝑉2 𝑇𝑇2