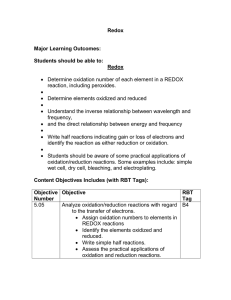
Practice Redox Problem: balance the following redox reaction in acidic solution: S(s) + NO3-(aq) --> SO2(g) + NO(g) Solution: The equation is: S + NO3- ---> SO2 + NO Oxidation half-reaction: S ---> SO2 S + 2H2O ---> SO2 +4H+ + 4eReduction half-reaction: NO3- ---> NO’] NO3- + 4H+ + 3e- ---> NO+2H2O To have the same number of electrons in both half-reactions, multiply the oxidation reaction by 3 and multiply the reduction reaction by 4. After this, add the two half-reactions together and then cancel: 4NO3- +3S +16H+ +6H2O ---> 3SO2 + 12H+ + 4NO +8H2O 4NO3- + 3S +4H+ ---> 3SO2 + 4NO + 2H2O Balancing redox reactions Describing the overall electrochemical reaction for a redox process requires a balancing of the component half reactions for oxidation and reduction. For reactions in aqueous solution, this general involves adding H+ , OH- ion, H2O and electrons to compensate the oxidation changes. Acid medium In acid medium H+ ions and water are added to half reactions to balance the overall reaction. For example, when manganese (II) reacts with sodium bismuthate. The reaction is balanced by scaling the two half-cell reactions to involve the same number of electrons (i.e. multiplying the oxidation reaction by the number of electrons in the reduction step and vice versa). Addition gives: Reaction balanced: Similarly for a propane fuel cell under acidic conditions: Balancing the number of electrons involved gives: Equation balanced: Basic medium In basic medium OH- ions and water are added to half reactions to balance the overall reaction. For example, in the reaction between potassium permanganate and sodium sulfite: Balancing the number of electrons in the two half-cell reactions gives: Equation balanced: A piece of iron, e.g. an iron nail, is dropped into a solution of copper sulphate. The nail gets coated with copper metal. Write the reaction that takes place, and the redox equation. Which atom has reduced, and which was oxidised. Fe + CuSO4 ----> FeSO4 + Cu Fe + Cu2+ + SO42- ----> Fe2+ + SO42- + Cu Now, the SO42- is unchanged left and right sides of the equation, so has not been oxidised nor reduced. Redox Reaction: Fe + Cu2+ ----> Fe2+ + Cu Iron Fe was oxidised to Fe2+, Cu2+ was reduced to Cu Pure zinc metal is placed into dilute hydrochloric acid. Hydrogen gas H2 is given off. Write the general equation and the redox equation. Which atom has reduced, and which was oxidised. Zn + HCl ----> ZnCl2 + H2 gas Zn + 2H+ + 2Cl- ----> Zn2+ + 2Cl- + H2 gas Redox Reaction: Zn + 2H+ ----> Zn2+ + H2 gas Zinc is oxidised to Zn2+, H+ is reduced to H2 gas