Management & Cost Accounting Class Notes
advertisement

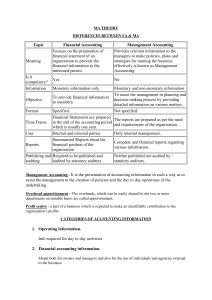
MECN 7032 – Management and cost accounting Class notes – 15/05/2019 Chapter 1: Accounting can be divided in 4 areas: Bookkeeping o Bean counting – records transactions, journal entries, ledgers o May even go to income statement and balance sheet o Capturing transactions and recording Financial accounting o Putting financial statements together o Analyzing and interpreting them o Income statement, Balance sheet, Cash flow statement Cost accounting o Large portion of this course o How we capture costs and methodologies we use in different situations o E.g. paint factory – process costing – continuous process o E.g. Nissan factory – Split in production line – joint product costing o 3 costs – material, labour and overhead (challenge in all methodologies, how to measure and allocate properly) o Way in which we apply costing methodology to the environment in which we operate in o Bean counting – week 1 Management accounting o Applies to financial accounting and cost accounting o Having proper information to make decisions o Used internally for planning, directing, motivating and controlling operation o Analysis and interpretation and case studies – week 2 Cost and management accounting – internal use Financial accounting – external use Planning Strategic – long term planning by top management Managerial – short to medium term planning done by middle management Operational – short term planning for daily operations Control Variance analysis – what we estimate vs. what has happened? Do we keep a product line going? Do we make or buy? Chapter 2 – Fundamental aspects of cost accounting - Cost – resource we use to achieve a particular objective Purpose Direct costs Direct material – actual materials that go into making the item Direct labour – People who are hands on – involved in making the item – e.g. machinist in clothing factory, not foreman Direct material + Direct labour + Direct expenses (overheads) = Prime costs/Direct costs Behaviour Fixed – quantity is irrelevant – not activity based Variable costs – changes with level of output, can be theoretically removed if not producing Semi – variable – e.g. Telephone line Stepped fixed Chapter 5: Manufacturing overheads All indirect costs accumulated within the manufacturing process that cannot be traced to single product Allocation and apportionment Internally