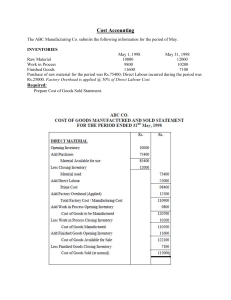
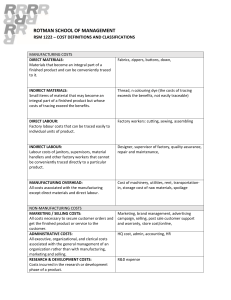
Grade 11 0 Introduction to cost accounting: Manufacturing Grade 11 Cost accounting includes/ takes into account all costs incurred to manufacture and sell a product. Key concepts: Direct materials cost: refers to the raw materials used during the manufacturing process in order to manufacture finished products. For example, milk would be considered a raw material in the production of cheese. Direct labour cost: this refers to the cost of workers directly involved in the manufacturing process. Prime costs: this refers to total direct costs incurred in the manufacturing process. Direct materials cost + Direct labour cost Indirect materials cost: materials that are used in the production process but cannot be traced to the finished/final product. An example, cleaning materials for the factory cannot be traced in the finished product but they are necessary to clean the factory. Indirect labour: this refers to the labour that supports the production process but is not directly involved in production of the finished product. For example, factory cleaners are not directly involved in the production but they are necessary to keep the factory clean. Factory overheads: this refers to all the costs incurred in order to run the factory other that direct materials and direct labour, such as indirect materials, indirect labour, depreciation of factory equipment or vehicles, factory insurance, rent expense (allocated to factory), water and electricity (allocated to factory).