Developmental Psychology Theories: Freud, Erikson, Piaget & More
advertisement
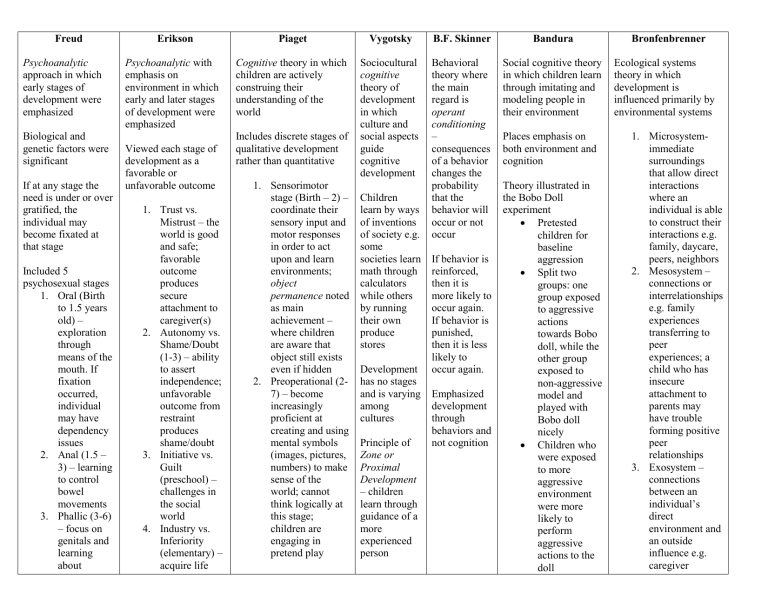
Freud Psychoanalytic approach in which early stages of development were emphasized Biological and genetic factors were significant If at any stage the need is under or over gratified, the individual may become fixated at that stage Included 5 psychosexual stages 1. Oral (Birth to 1.5 years old) – exploration through means of the mouth. If fixation occurred, individual may have dependency issues 2. Anal (1.5 – 3) – learning to control bowel movements 3. Phallic (3-6) – focus on genitals and learning about Erikson Psychoanalytic with emphasis on environment in which early and later stages of development were emphasized Viewed each stage of development as a favorable or unfavorable outcome 1. Trust vs. Mistrust – the world is good and safe; favorable outcome produces secure attachment to caregiver(s) 2. Autonomy vs. Shame/Doubt (1-3) – ability to assert independence; unfavorable outcome from restraint produces shame/doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt (preschool) – challenges in the social world 4. Industry vs. Inferiority (elementary) – acquire life Piaget Vygotsky B.F. Skinner Bandura Cognitive theory in which children are actively construing their understanding of the world Sociocultural cognitive theory of development in which culture and social aspects guide cognitive development Behavioral theory where the main regard is operant conditioning – consequences of a behavior changes the probability that the behavior will occur or not occur Social cognitive theory in which children learn through imitating and modeling people in their environment Includes discrete stages of qualitative development rather than quantitative 1. Sensorimotor stage (Birth – 2) – coordinate their sensory input and motor responses in order to act upon and learn environments; object permanence noted as main achievement – where children are aware that object still exists even if hidden 2. Preoperational (27) – become increasingly proficient at creating and using mental symbols (images, pictures, numbers) to make sense of the world; cannot think logically at this stage; children are engaging in pretend play Children learn by ways of inventions of society e.g. some societies learn math through calculators while others by running their own produce stores Development has no stages and is varying among cultures Principle of Zone or Proximal Development – children learn through guidance of a more experienced person If behavior is reinforced, then it is more likely to occur again. If behavior is punished, then it is less likely to occur again. Emphasized development through behaviors and not cognition Places emphasis on both environment and cognition Theory illustrated in the Bobo Doll experiment Pretested children for baseline aggression Split two groups: one group exposed to aggressive actions towards Bobo doll, while the other group exposed to non-aggressive model and played with Bobo doll nicely Children who were exposed to more aggressive environment were more likely to perform aggressive actions to the doll Bronfenbrenner Ecological systems theory in which development is influenced primarily by environmental systems 1. Microsystemimmediate surroundings that allow direct interactions where an individual is able to construct their interactions e.g. family, daycare, peers, neighbors 2. Mesosystem – connections or interrelationships e.g. family experiences transferring to peer experiences; a child who has insecure attachment to parents may have trouble forming positive peer relationships 3. Exosystem – connections between an individual’s direct environment and an outside influence e.g. caregiver male/female differences. Oedipus Rex complex arises 4. Latency – (6 to puberty) sexual interests are repressed in order to grow in social and intellectual skills. Fixation can develop into immaturity. 5. Genital (puberty onwards) – source of pleasure extends beyond family members Weaknesses – too abstract and difficult to test scientifically skills such as math and literacy 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion (adolescence) – the search for identity and that commitment to a specific identity 6. Generativity vs. Stagnation (middle adulthood) – having a job, investing in yourself 7. Integrity vs. Despair (late adulthood) – reflection of the past 3. Concreteoperational (7-11) – internal mental activities that require logic; e.g. conservation knowing that juice in a narrow glass is the same amount of juice in a short stubby glass 4. Formaloperational (1112+) – thinking extends beyond factual/observable and thinking can be hypothetical Weaknesses – do not consider cultural and social aspects across cultures Weaknesses – limited to Western culture; abstract References Mcleod, S. (2018, June 6). Theories of Development. Retrieved from https://www.simplypsychology.org/piaget.html Santrock, J. W. (2018). A topical approach to life-span development. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education. working more hours with less time at home can influence development 4. Macrosystem – larger cultural context where development occurs e.g. laws in society