Podcast #4 Imperialism 2.0
Second wave imperialism in Modern History o After New World Colonization (Gold, God, Glory) o Silver, conversion, Haciendas, etc.
Need by NICs: o Expansion of many European nations
Ie. GBR o Massive amounts of raw materials o Markets
US: expanded o Conquered Philippines, Cuba, Puerto Rico, Pacific Islands from Spain in 1898 war
Spain: contracted o Lost colonies in Central/South America
England: expanded o EIC taken over by crown o Raj in India o Opium smuggling to China
Ottomans: contracted o Lost territory
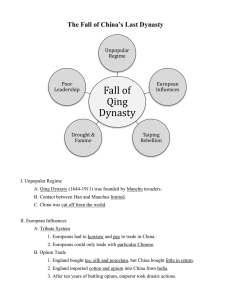
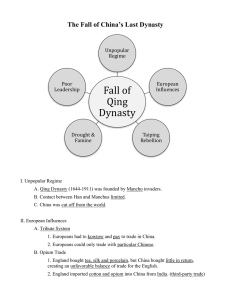
China-England Trade o Hong traders would force international tradesman to meet in Canton and pay tributes (in silver or trade) o England could not pay for the trade (they didn’t even have goods that the Chinese would accept) o Britain smuggled in opium produced in India
This became profitable for British as Chinese became addicted to the drug
British no longer had to pay in silver and they were making profits off the opium o Opium wars:
Britain= “free trade”. Really was to sell opium
China was no match to the industrial country o Treaty of Nanjing:
Unfair
Extra territoriality (Diplomatic immunity)
5 ports had to be open to GBR
Allow missionaries in o Taipeng Rebellion:
Religious movement motivated by change in perspective of history
Qing was weakening from rebellion (lent a hand to decentralization)
Asked local warlords to crush rebellion
30 million died o Self strengthening movement:
Shipbuilding yard
Industry
Modernize military
Foreign dept (International relations)
Translate western texts (scientific/mathematic texts) o Spheres of Influence
Regions that were controlled by other nations (ie. Those listed below)
Japan
Germany
France
GBR o 100 Days or Reform:
Attempt to reform Chinese education (most western education) and streamline bureaucracy
Manchu leaders and conservative Confucians wanted to crush rebellion so they executed those involved. o Boxers (trained in martial arts. Had religious)
They wanted to stop the western influence on China
(particularly in North, near Russia)
They were defeated by Russians in a battle
They were also executed by local warlords o Decentralization of China
Local warlords were splitting the empire
Last civil service examination in 1905
Final emperor deposed in 1911
China’s future unsure (entered tumultuous future)
Japan o Had to impose reforms
China vs Japan:
China began 1800s as it normally had (A lot of
Neoconfucianism). Secular government
Japan was ethnically homogeneous
Japan was even more secluded (Dutch port in Nagasaki) o Where they learned about Western ideas
Japan was demanded unequal treaty by US o Demanded extraterritoriality o Ended this and with other nations in 1898
Maji Restoration (Incredible reforms greater than RUS/CHN)
Ended feudalism
Political power centralized (give power back to emperor)
Did not make major changes but subtle changes that seemed to fit into normal Japanese society (while
Western ideas were implemented)
Parliament (German style. Emperor could appoint his ministers)
Banned samurai class (But had them learn trade and business in US and Europe)
Rapid industrialization o One of fastest most successful o Cartel families (very powerful). Came from
Samurai o Yashuda Family (Yashuda Maji owns many insurance companies today) o Mitsubishi
Members of parliament were responsive to needs of wealthy o Because 5% of men voted (and were wealthiest men)
Sino Japanese War o Japan vs. China for control of Korea
Baltic Fleet (Russian) o Japanese sunk fleet in 5hrs
Asian power had defeated a NIC European power