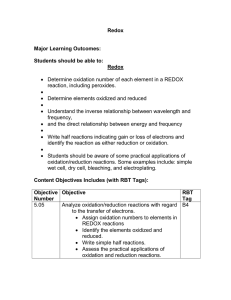
Chemistry IGCSE Redox Name: _______________________________ REDUCTION 1 Date: ________ Redox OXIDATION A Closed System A chemical reaction is a closed system whereby a substance can only be oxidised when there is another substance getting reduced A reaction in one substance is always in the expense of another substance A + C B + D oxidised reduced 2 Oxidising and Reducing Agents A reaction in a substance is caused by another Eg. When A undergoes oxidation, B is the oxidising agent When B undergoes reduction, A is the reducing agent OXIDISING AGENT: Causes oxidation of another substance, itself is reduced. 3 REDUCING AGENT: Causes reduction of another substance, itself is oxidised. Defining Redox 1 - Transfer of oxygen atoms OXIDATION: Gain of oxygen REDUCTION: Loss of oxygen loses oxygen to become Cu 2 CuO + Mg à MgO + Cu OXIDATION: Mg (Reducing agent) REDUCTION: CuO (Oxidising agent) gains oxygen to become MgO 4 Defining Redox 2 - Transfer of electrons OXIDATION: Loss of electrons REDUCTION: Gain of electrons loses electron to become Na+ 2 Na + Cl2 à 2 NaCl OXIDATION: Na (Reducing agent) REDUCTION: Cl2 (Oxidising agent) gains electron to become Cl- 5 Writing Half-equations Ionic half-equations shows oxidation and reduction taking place in a reaction separately Oxidation (Loss of electrons) a) Metals !" → !"% + '( b) Non-metallic ions ) *)( → *) + + '( c) Hydroxide ions + *.( → *) + Reduction (Gain of electrons) a) Metallic ions ,-)% + ) '( → ,- ) .) * + + '( b) Non-metals 2 Cl,/) + )'( → ,/ ) c) Hydrogen ions . % + ) '( → .) 1 Prepared by Chermaine Lim (2019) Chemistry IGCSE Redox 1 For the following reactions, identify the substance that is oxidised, reduced and the respective agents in terms of gain/loss of electron. a) Mg + F2 MgF2 à Oxidised Oxidising Agent b) 2 Na + F2 + 2 KI à Oxidised F2 K+ Cl- 2 KCl 2 F2 Reducing Agent + Reduced KI Reducing Agent or Na I2 Cl2 Oxidising Agent d) Mg Reduced Na K+ I- F2 2 NaF à Oxidising Agent Cl2 Reducing Agent F2 Oxidised c) Reduced Mg I- KI or I- Cl2 CuO + Zn à ZnO + Cu Oxidised Zn Reduced Oxidising Agent CuO Reducing Agent CuO Zn Write the half equations for the following situations: a) Magnesium metal becomes magnesium ion by losing electrons. oxidised Magnesium metal is _________________. Mg —> Mg2+ b) + 2e Copper ion gains electrons to become copper metal. Copper ion is _________________. reduced Cu2+ c) + 2e —> Cu Hydrogen ions gain electron to become hydrogen gas. Hydrogen ions are _________________. d) Chloride ions become chlorine gas by losing electrons. Chloride ions are __________________. e) Bromine molecules gains electron to form bromide ions. Bromine molecules are _________________. f) Aluminium metal become aluminium ions by losing electrons. oxidised Aluminium metal is __________________. Al —> Al3+ + 3e 2 Prepared by Chermaine Lim (2019) Chemistry IGCSE Redox 3 Identify the substances from the list below whether they can take part in oxidation or reduction. Na Br- I2 Pb Mg2+ I- Cu2+ Pb2+ Cl- Mg OH- H+ Cu Fe3+ Na+ Cl2 Oxidation Na I- Pb Cl- Mg2+ Cu OH- Br- 6 Reduction Cu2+ I2 Mg Pb2+ Fe3+ H+ Na+ Cl2 Determining Oxidation States/Numbers Charge an element would have if it existed in a compound To a. b. c. determine O.S of substances: Elements & Molecules à Always zero Atoms in a compound à Sum of O.S of all atoms is zero Some atoms have fixed O.S. : Li, Na, K F O +1 -1 H -2 +1 d. Ions à Follows the charge of the ion e. Atoms in a polyatomic ion à Sum of O.S of all atoms in a polyatomic ion follows its charge f. IUPAC naming gives the O.S. of the transition metals 7 Defining Redox 3 - Increase/Decrease of O.S OXIDATION: Increase REDUCTION: Decrease +1 2HCl + spectator ion 1 Mg à 0 -1 +2 0 -1 MgCl2 + * follow charge of metal OXIDATION: Mg (Reducing agent) REDUCTION: H+ (Oxidising agent) H2 HCl Give the oxidation state for the following substances: a) Elements/Ions Element/Ion Na O2 b) Oxidation State Element/Ion C 0 O2- 0 Oxidation State 0 -2 Atoms in Compounds Element in Compound Oxidation State Element in Compound Oxidation State PbO2 +4 CuO +2 Na2SO3 +4 K2CrO4 +6 KMnO4 MnO2 +7 3 =4 Prepared by Chermaine Lim (2019) Chemistry IGCSE Redox 2 For the following reactions, identify the substance that is oxidised, reduced and the respective agents in terms of increase/decrease of oxidation state. a) b) 1 3 CuCl2 + 2 Al à 3 AlCl3 + 2 Cu Oxidised Reduced Oxidising Agent Reducing Agent Cl2 + 2 KI à 2 KCl + I2 Oxidised Reduced Oxidising Agent Reducing Agent A piece of zinc is immersed in a blue solution of copper (II) sulfate. a) Which is the more electropositive metal, zinc or copper? b) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the redox reaction occurring. 4 Prepared by Chermaine Lim (2019) Chemistry IGCSE Redox c) i) ii) d) i) ii) e) Identify the substance going through oxidation. Zinc Write the half equation for the oxidation reaction. Zn —> Zn2+ + 2e Identify the substance going through reduction. CuSO4 Write the half equation for the reduction reaction. Cu2+ + 2e —> Cu A piece of silver in immersed in copper (II) sulfate solution now. Compare this reaction with that of zinc. Explain your answer. No changes. silver is less reactive compared to copper. 2 A piece of magnesium is immersed in a zinc nitrate solution. a) Which is the more electropositive metal, zinc or magnesium? magnesium b) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the redox reaction occurring. c) i) d) Mg + Identify the substance going through oxidation. Mg ii) Write the half equation for the oxidation reaction. i) Identify the substance going through reduction. ii) e) Zn(NO3)2 —> Mg(NO3)2 + Zn Mg —> Mg2+ + 2e Zn(NO3)2 Write the half equation for the reduction reaction. Zn2+ + 2e —> Zn A piece of copper in immersed in zinc nitrate solution now. Compare this reaction with that of magnesium. Explain your answer. No changes. Copper is less reactive than zinc. 3 Chlorine gas is bubbled into a solution of potassium bromide. a) Which is the more electronegative halogen, chlorine or bromine? Chlorine 5 Prepared by Chermaine Lim (2019) Chemistry IGCSE Redox b) c) d) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the redox reaction occurring. Cl2 + i) 2KCl + Br2 Identify the substance going through oxidation. KBr ii) Write the half equation for the oxidation reaction. i) Identify the substance going through reduction. ii) e) 2KBr —> 2Br- —> Br2 + 2e Cl2 Write the half equation for the reduction reaction. Cl2 + 2e —> 2Cl- Iodine vapour is bubbled into the potassium bromide solution now. Compare this reaction with that of chlorine. Explain your answer. No changes. Iodine is less reactive than chlorine 4 Fluorine gas is bubbled into a solution of potassium chloride. a) Which is the more electronegative halogen, chlorine or fluorine? b) Write a balanced chemical equation to show the redox reaction occurring. c) i) Identify the substance going through oxidation. ii) Write the half equation for the oxidation reaction. i) Identify the substance going through reduction. ii) Write the half equation for the reduction reaction. d) 6 Prepared by Chermaine Lim (2019)