Cell Theory & Biology: Structure, Respiration, & Experiments
advertisement

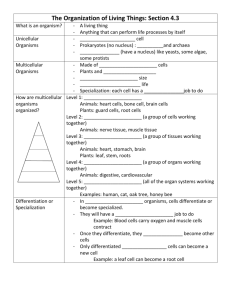
THE CELL THEORY MICROBIOLOGY The study of microscopic organisms that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. WHAT IS A CELL? A Cell is the basic structure which makes up all living organisms. A cell can exist by itself (unicellular) or with many other cells (multicellular) THE CELL THEORY 1. All Living Things are Made up of Cells 2. Cells are the Basic Unit of Life 3. All Cells Come From Pre-Existing Cells Copy me into your books ROBERT HOOKE Copy me into your books Robert Hooke was the first person to view and describe cells under a microscope. EXPERIMENT: PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Aim: To view and compare the differences of plant and animal cells. Method: 1. Set up the microscope and turn on. 2. Collect a pre-prepared slide and place under the microscope using the stage clips. 3. Ensure the objective lens is on low, and using the adjustment knob, bring into focus. 4. Draw a cell. 5. Remove the slide, and repeat with the other preprepared slide. EXPERIMENT: PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS Results: Plant cell: Animal Cell: EXPERIMENT: ONION SLIDES Aim: To make an onion slide and investigate the cells in the onion. Method: 1. Cut a small piece of onion and carefully remove the skin on the onion 2. Place the skin on the slide 3. Add 1-2 drops of iodine solution 4. Lower the coverslip over the onion skin 5. Remove excess stain 6. View under microscope on low power 7. Draw a labelled cell EXPERIMENT: ONION SLIDES Results: EXPERIMENT: ONION SLIDES Conclusion: An onion cell is a plant cell because it has a cell wall. 3 DIFFERENT TYPES OF CELLS Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacteria Cell ANIMAL CELL Copy me into your books PLANT CELL Copy me into your books DIFFERENCES OF PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL Animal Cell Plant Cell Small Vacuole (some) Large Vacuole No Chloroplasts Chloroplasts No Cell Wall Cell Wall Copy table into your books FUNCTION OF ORGANELLES Copy me into your books Cell Organelle Function Nucleus Controls the activities of a living cell Cytoplasm Jelly-like substance which fills most of the cell Mitochondria The site of cellular respiration. Where energy is made in the cell Vacuole Water storage Cell Membrane Thin layer surrounding the cell which controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell Cell Wall* Tough outer layer of a plant cell that helps keeps its shape Chloroplasts* Found only in plant cells which contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis BACTERIA CELL The Simplest type of cell CELLULAR RESPIRATION Mitochondria CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular respiration occurs inside mitochondria. This process involves glucose (from the food we eat) and oxygen to react together to form water, carbon dioxide and energy. This energy is used by our bodies to help us function. (Sugar) IMPORTANCE OF RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is important because it provides energy for the living organism to perform all other necessary functions to maintain life. RESPIRATION AND BREATHING It is important not to confuse respiration with breathing. Respiration is a chemical reaction that occurs in the mitochondria inside cells. Breathing is a process performed by multicellular organisms that have lungs or gills to exchange gases with the environment. Breathing usually involves taking oxygen into the body and expelling carbon dioxide back into the environment. EXPERIMENT: EXTRACTING CHLOROPHYLL Aim: To extract chlorophyll from leaves and investigate the colour of leaves without chlorophyll. Method: 1. Pick a leaf from a tree 2. Boil the leaf in a beaker of water for 2 minutes. 3. Pour 20mL of ethanol into a small beaker and place leaf inside 4. Place beaker in hot water bath 5. Record Results EXPERIMENT: EXTRACTING CHLOROPHYLL Results: Colour Before Colour After Ethanol Leaf Clear Green EXPERIMENT: EXTRACTING CHLOROPHYLL Conclusion: We found that chlorophyll is green and gives leaves the appearance of the colour green. This is because the leaf turned clear and the ethanol turned green. UNICELLULAR AND MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS Unicellular organisms are organisms which are made up of only one cell. An example of a unicellular organism is bacteria. MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS Multicellular organisms are organisms which are made up of more than one cell. There are different types of cells in multicellular organisms because they carry out different functions. These are called specialised cells. Examples of multicellular organisms are plants and animals. CELLS, TISSUE, ORGANS, SYSTEMS, ORGANISM All living organisms are made up of cells. A bunch of cells together are called tissue. Organs such as the heart, lungs, liver are made up of tissue. And it is these organs that then make up different systems in the body such as the circulatory, respiratory and digestive system. There are various systems in the body which make up an entire organism, which is you and me! SPECIALISED CELLS Different types of cells have different cell components to enable them to carry out their specific roles. These differences in the structure and function of cells can be used to classify them