Early Civilizations: From Early Humans to Mesopotamian Empires
advertisement

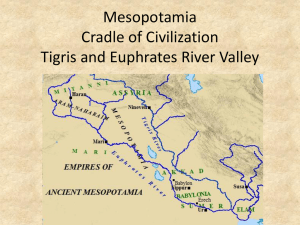
Chapter 1 The First Civilizations Section 1- Early Humans Who puts our history together? History is the story of humans in the past. Historians- People who study and write about the past. Archaeologists- Hunt for evidence buried in the ground. They dig up artifacts and fossils. Anthropologists- Focus on human society. They study how humans developed and how they related to one another Paleolithic or Old Stone Age 2.5 million years ago – 8000 B.C. Hunter-Gatherers- They hunted animals, caught fish, ate insects, and gathered nuts, berries, fruits, grains and plants. Nomads- People who regularly moved from place to place. Women gathered berries, grains and watched over children, men hunted animals. The Ice Ages 100,000 B.C.- 8000 B.C. (During the Paleolithic Era) • Long periods of extreme cold • The discovery of fire helped people survive. Food was easier to digest and lasted longer and the fire kept them warm. • Humans had to adapt by changing their diet, building sturdier shelters and using animal furs to make warm clothing Language, Art, Religion and Tools Humans created a language which made it easier to work together and pass on knowledge. Humans crushed colored rock to create paint. They would paint scenes of animals inside caves. Early humans used flint to create tools and weapons Neolithic Era or New Stone Age 8000 B.C.- 4000 B.C. People learned how to grow food and domesticated animals for their meat, milk and wool. For the first time, people could stay in one place to grow grains and vegetables. They began farming and stopped being hunter-gatherers! Villages were started in Europe, India, Egypt, China and Mexico. The shift to settled life meant people a larger food supply. Humans could now specialize in different kinds of jobs to create goods they did not have. People were now creating pottery, farming tools, and weapons made of copper. Section 2Mesopotamian Civilization Civilizations- Complex societies that have cities, organized governments, art, religion, class divisions and a writing system. Rivers provided: Water for farming Fish Freshwater A to drink way to travel and trade Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is known as “the land between the rivers” because it is bounded by the Tigris and Euphrates river. Farmers used irrigation to water their crops. Many cities formed in southern Mesopotamia known as Sumer. The Sumerian cities became separate city-states and had their own governments. These citystates would often go to war with each other. Sumerian Culture Sumerians believed in many gods. Each city-state built a grand temple called a ziggurat, which means “mountain of god” or “The hill of heaven”. Artisans- Skilled workers who made metal products, cloth or pottery. There were 3 social classes in Sumer: Upper class (kings, priests), middle class (artisans, merchants), and lower class (enslaved people). Sumerian Culture (continued) Men headed the household and were able to go to school. Sumerians developed a form of writing called cuneiform in order to keep track of business deals. Scribes- Record keepers. Sumerian’s wrote “The Epic of Gilgamesh”, the world’s oldest known story. Sumerians invented the plow, the wagon and the sailboat. Sumerians created the 60-minute hour, 60-second minute,360 degree circle and the 12 month calendar! Mesopotamia is known as the “CRADLE OF CIVILIZATION!” King Sargon, King Hammurabi and the Code of Hammurabi Led by King Sargon, in 2340 B.C. the Akkadians from northern Mesopotamia conquered all of Mesopotamia. Empire- A group of many different lands under one ruler. Sargon’s empire lasted for more than 200 years before falling to invaders. In the 1800’s B.C. a new group took over Mesopotamia and built the city of Babylon. Their Babylonian King Hammurabi created his own Empire. King Hammurabi also created the Code of Hammurabi, a collection of laws collected from all city-states that covered every area of life. Section 3The First Empires The Assyrians The Assyrian empire was created about 1,000 years after King Kammurabi. To defend their land, the Assyrians built a large army. The Assyrian army was strong because it was well organized. It had: Foot soldiers Archers Chariot riders Men on horseback Iron weapons (Learned how to make them from the Hittites) When Assyrians would capture a city, they would set fire to its buildings and take the people to foreign lands. Assyrian kings divided their empire into provinces, or political districts. The king would then choose a government official to collect taxes and enforce laws. The Assyrians (continued) The capital of the Assyrian Empire was in Nineveh. One of the worlds largest libraries was in Nineveh and held more than 25,000 books. Assyrians cruel treatment of people led to many rebellions. The Chaldeans rebelled against the Assyrians and captured Nineveh in 612 B.C. This marked the end of the Assyrian Empire. The Chaldeans Most of the Chaldeans were the descendants of the Babylonian people who made up Hammurabi’s empire. They rebuilt the city of Babylon after the fall of the Assyrian Empire. King Nebuchadnezzer (King Neb) was the ruler of the Chaldeans. Under his rule, Babylon became one of the world’s largest and richest cities. King Neb built the Hanging Gardens for his wife.