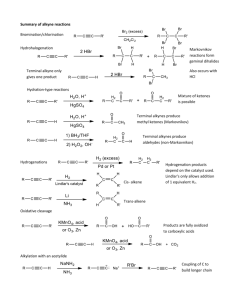
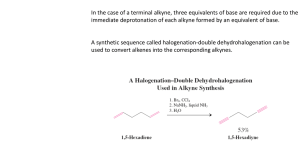
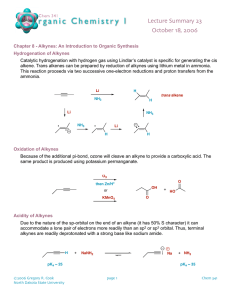
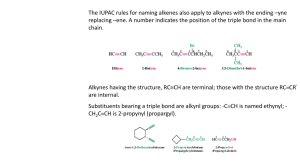
CHE143 ORGANIC AND ALKYNES ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY Structure and nomenclature Physical properties Synthesis Reactions P r e p a r e d b y: Siti Munirah Muda STRUCTURE AND NOMENCLATURE • Alkynes contain a carbon—carbon triple bond. • Terminal alkynes have the triple bond at the end of the carbon chain so that a hydrogen atom is directly bonded to a carbon atom of the triple bond. • Internal alkynes have a carbon atom bonded to each carbon atom of the triple bond. • An alkyne has the general molecular formula C n H 2n-2 , giving it four fewer hydrogens than the maximum possible for the number of carbons present. Thus, the triple bond introduces two degrees of unsaturation. • Recall that the triple bond consists of 2 bonds and 1 bond. • Each carbon is sp hybridized with a linear geometry and bond angles of 1800. IUPAC NOMENCLATURE OF ALKYNES 1. 2. 3. Find the longest chain containing the triple bond and change the corresponding “-ane” ending to “-yne” The chain is numbered in direction that gives the triple bond, the lower number Give the location and name of each substituent (alphabetical order) as a prefix to the name of the main chain. NOMENCLATURE OF ALKYNES STRUCTURES HC Examples C CH3 COMMON NAMES IUPAC Acetylene ethyne methyl acetylene propyne dimethyl acetylene 2-butyne ethyl acetylene 1-butyne Give the IUPAC name for each of the following PROBLEM: IUPAC NAMES? Draw the structure for each of the following a) b) c) d) e) f) g) 1-chloro-3-hexyne 4-bromo-2-pentyne 4,4-dimethyl-1-pentyne 3-chloropropyne 1,6-heptadiyne 6,6-dimethyl-3-octyne 5-cycloheptyne PHYSICAL PROPERTIES Quite similar to those of alkanes and alkenes with similar carbon skeletons. All are insoluble in water and soluble in nonpolar solvents such as hexane. Less dense than water Alkynes are more linear than alkenes, causing alkynes to have stronger van der Waals interaction. As a result, alkyne has a higher BP than alkene containing the same number of carbons. Physical proper ties of some low molecular weight alkynes SYNTHESIS OF ALKYNES ALKYLATION OF ACETYLENE DOUBLE DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDE DEHYDROGENATION SYNTHESIS OF ALKYNES 1. ALKYLATION OF ACET YLENE General equation Alkylation of acetylene involves a sequence of two separate operations. An alkyl halide is added to the solution of sodium acetylide and form an alkynes. SYNTHESIS OF ALKYNES Examples:- PRACTICE Outline efficient synthesis of each of the following alkynes from acetylene and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents a) 1-heptyne b) 2-heptyne c) 3-heptyne SYNTHESIS OF ALKYNES 2) DOUBLE DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDE Prepare an alkyne by elimination reactions. Double dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalide SYNTHESIS OF ALKYNES Examples:- SYNTHESIS OF ALKYNES 3) DEHYDROGENATION Multiple bonds are form by removing a hydrogen chemically. REACTION OF ALKYNES 1) HYDROHALOGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN HALIDE) 2) HYDROGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN) 3) HALOGENATION (ADDITION OF HALOGEN) 4) HYDRATION (ADDITION OF WATER) HYDROHALOGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN HALIDE) General equation Alkynes react with one molar equivalent of hydrogen chloride or hydrogen bromide to form haloalkenes, and with two molar equivalents to form geminal dihalides. Both addition are regioselective and follow Markovnikov’s rule. Example: Mechanism Major product Example Minor product Practice Major product HYDROHALOGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN HALIDE) -- cont Anti Markovnikov addition of hydrogen bromide to alkynes occurs when peroxides are present in the reaction mixture. These reaction take place through a free -radical mechanism HYDROGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN) General reaction Conditions for hydrogenation of alkynes are similar to those for alkenes.it also known as reduction reaction of alkynes. In the presence of finely divided platinum, palladium, nickel or rhodium, two molar equivalents of hydrogen add to the triple bond an alkyne to yield an alkane. Example:- HYDROGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN) -- cont Hydrogenation can be stopped at the alkene if the less active Lindlar catalyst used. The Lindlar catalyst is a finely divided Pd metal that has been precipitated onto a CaCO 3 support and then deactivated by treatment with lead acetate and quinoline, an aromatic amine . The hydrogenation occurs with syn stereochemistr y, giving a cis alkene product . General equation Example Lindlar catalyst HYDROGENATION (ADDITION OF HYDROGEN) -- cont Examples: HALOGENATION (ADDITION OF HALOGEN) Alkynes show the same kind of addition reactions with Cl and Br that alkenes do. With alkynes, the addition may occur once or twice, depending on the number of molar equivalents of halogen we used. HYDRATION (ADDITION OF WATER) Hydration of alkyne is expected to yield an alcohol. The alcohol would be a special kind, which hydroxyl group is a substituent on a carbon-carbon double bond. This type of alcohol is called an enol An important property of enol is their rapid isomerization to aldehydes or ketones under the conditions of their formation. HYDRATION (ADDITION OF WATER) -- cont EXERCISE