Uploaded by
Aileen Concepcion M. Agustin
Heart Disease Murmurs & Characteristics Chart
advertisement
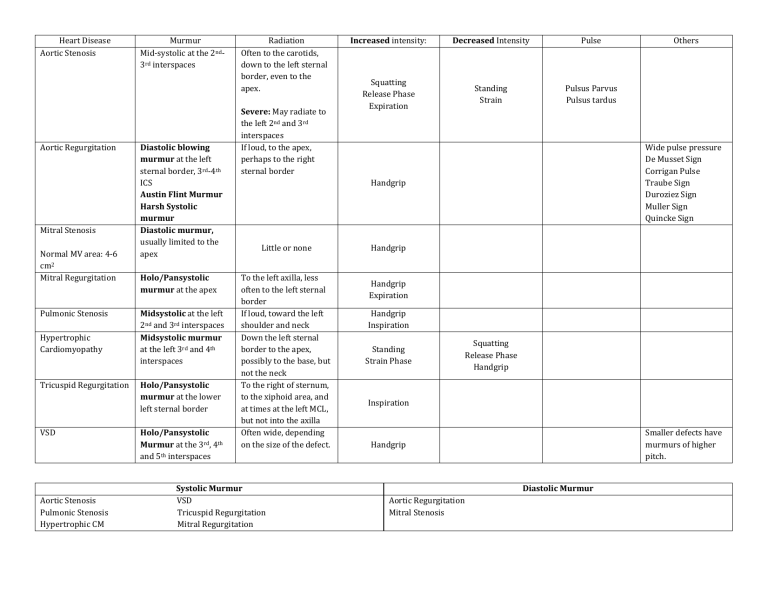
Heart Disease Aortic Stenosis Aortic Regurgitation Mitral Stenosis Normal MV area: 4-6 cm2 Mitral Regurgitation Pulmonic Stenosis Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Tricuspid Regurgitation VSD Aortic Stenosis Pulmonic Stenosis Hypertrophic CM Murmur Mid-systolic at the 2nd3rd interspaces Diastolic blowing murmur at the left sternal border, 3rd-4th ICS Austin Flint Murmur Harsh Systolic murmur Diastolic murmur, usually limited to the apex Holo/Pansystolic murmur at the apex Midsystolic at the left 2nd and 3rd interspaces Midsystolic murmur at the left 3rd and 4th interspaces Holo/Pansystolic murmur at the lower left sternal border Holo/Pansystolic Murmur at the 3rd, 4th and 5th interspaces Radiation Often to the carotids, down to the left sternal border, even to the apex. Severe: May radiate to the left 2nd and 3rd interspaces If loud, to the apex, perhaps to the right sternal border Increased intensity: Decreased Intensity Pulse Squatting Release Phase Expiration Standing Strain Pulsus Parvus Pulsus tardus Wide pulse pressure De Musset Sign Corrigan Pulse Traube Sign Duroziez Sign Muller Sign Quincke Sign Handgrip Little or none To the left axilla, less often to the left sternal border If loud, toward the left shoulder and neck Down the left sternal border to the apex, possibly to the base, but not the neck To the right of sternum, to the xiphoid area, and at times at the left MCL, but not into the axilla Often wide, depending on the size of the defect. Systolic Murmur VSD Tricuspid Regurgitation Mitral Regurgitation Others Handgrip Handgrip Expiration Handgrip Inspiration Standing Strain Phase Squatting Release Phase Handgrip Inspiration Smaller defects have murmurs of higher pitch. Handgrip Diastolic Murmur Aortic Regurgitation Mitral Stenosis









