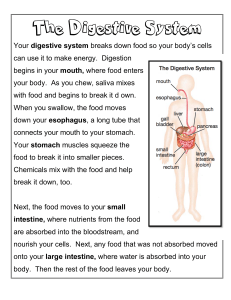
HUMAN BODY SYSTEM 14 APRIL 2019 WHAT IS DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? 1. Take in food (ingestion) 2. Digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. Remove undigestable food from body (feces) WHAT IS CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? • Transport materials to and from cells WHAT IS NERVOUS SYSTEM? 1. Gathers and interprets information 2. Responds to information 3. Helps maintain homeostasis WHAT IS EXCRETORY SYSTEM? 1. Removes waste products from cellular metabolism (urea, water, CO2) 2. Filters blood WHAT IS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM? Takes in oxygen and removes carbon dioxide and water Respiration: Respiration refers to a person’s breathing and the movement of air into and out of the lungs. The respiratory system provides oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration and removes the waste product carbon dioxide. WHAT IS SKELETAL SYSTEM? 1. Protects organs 2. Provides shape, support 3. Stores materials (fats, minerals) 4. Produces blood cells 5. Allows movement WHAT IS MUSCULAR SYSTEM? Allows for movement by contracting and relaxing WHAT IS REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM? Allows organisms to reproduce which prevents their species from becoming extinct. HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Recall: WHAT IS DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? 1. Take in food (ingestion) 2. Digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. Remove undigestable food from body (feces) 3 TYPES OF FOOD • Carbohydrate • Protein • Fats MOUTH • The mouth is where the digestive tract begins. Enzymes released into the mouth start the process of digestion. WHAT ARE ENZYMES? (RECAP) TEETH/TOOTH • Teeth are the organs of chewing, which is also known as mastication. • Break down into smaller substances, leading to an increase of surface area. • By age 7, 32 permanent or secondary teeth are developed & are divided into 4 types: incisors (for cutting) , Canines (for tearing) , Premolars (for crushing), and Molars (for grinding). these teeth follow the human dental formula of 2-12-3. TONGUE AND SALIVA The tongue , made of skeletal muscle, manipulates the food during mastication. It also contains taste buds to detect taste sensations (intrinsic). Food particles are mixed with saliva during mastication , resulting in a moist lump called bolus for easier passage into or pharynx . GULLET OR OESOPHAGUS It carries swallowed masses of chewed food along its length, from mouth to stomach. How can we swallow while lying down and without the help or gravity? - Peristalsis! PERISTALSIS The involuntary constriction and relaxation of the muscles of the intestine or another canal, creating wave-like movements that push the contents of the canal forward. STOMACH • A pouch-like organ primarily designed for food storage (for 2-4 hours), some physical/ mechanical and chemical digestion also occur • Churns, mixes and stores food • Digestion takes 2 forms– Physical and Chemical digestion • Stomach contributes to both forms of digestions SMALL INTESTINE • A long tube, with a small diameter (about 1 inch), extending from stomach to large intestine • The small intestine is the part of the intestines where 90% of the digestion and absorption of food occurs, the other 10% taking place in the stomach and large intestine. • The main function of the small intestine is absorption of nutrients and minerals from food. LARGE INTESTINE • The last segment of the GI tract , with a large diameter (2-3 inches) • Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored as feces before being removed by defecation • Make your feces compact RECTUM AND ANUS • The rectum is a chamber that begins at the end of the large intestine, and ends at the anus