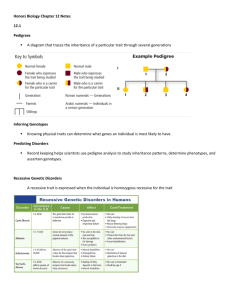
Chapter 2: Modern Genetics Section 1: Human Inheritance Traits Controlled by Single Genes In humans: Widow’s peak vs. no widow’s peak Dimples vs. no dimples Hair on fingers vs. no hair on fingers In pea plants: Short vs. tall Seed color (yellow vs. green) Multiple Alleles Not all human traits controlled by a single gene have just two alleles!!!!! Multiple Alleles: three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait Ex: pudding A gene may have multiple alleles, but a person can carry only two of those alleles due to chromosomes existing in pairs. Multiple Alleles Example: Blood Type A=codominant B=codominant AB O=recessive Example: Height Four genes contol height in humans Example: Skin color Some traits show a large number of phenotypes because traits are controlled by many genes. The genes act together as a group to form a single trait. Environment Effects Diet/ nutrition can affect a person’s height Lack of protein, mineral, and vitamins https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fPCtvQIStSg Male or Female? Within the 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell lies a single pair of chromosomes called the sex chromosomes. Control whether you are male or female Only pair that don’t always match Females: two sex chromosomes match XX Male: two sex chromosomes don’t match XY See Punnett square Sex-Linked Genes Sex-Linked Genes: genes located on X and Y chromosomes Some traits occur more often in one sex than other Genes carried sex chromosomes Sex linked genes have dominant and recessive alleles There is allele that goes with the Y chromosome. Whatever allele is attached to the X chromosome is the trait that the male will inherit. Because males have only one X Chromosome, males are more likely to have sex-linked traits controlled by recessive alleles. Sex-Linked Genes See punnett square on pg. 55 Carrier: a person who has one recessive allele for a trait and one dominant allele Pedigrees Pedigree: a chart or “family tree” that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait See pg. 56 Section 2: Human Genetic Disorders Genetic Disorders Genetic Disorder: an abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes Caused by mutations, or changes in a person’s DNA During meiosis Mutations present in parent’s cell and passed on to offspring Cystic Fibrosis Body produces abnormally thick mucus in the lungs and intestines Makes it hard to breathe Difficult to digest Bacteria growth causing lung damage Carried on a recessive allele Common among people whose ancestors are from Northern Europe No cure Sickle-Cell Disease Affects the blood and the production of protein called hemoglobin Hemoglobin carries oxygen in red blood cells Suffer from lack of oxygen in the blood and experience pain and weakness Allele is common in people of African Ancestry Codominant Allele No symptoms if heterozygous No cure Hemophilia A person’s blood clots very slowly Does not produce one of the proteins need for normal blood clotting A person can bleed to death from a minor cut or scrape Recessive allele on the X chromosome Sex linked disorder males more likely to have it Avoid sports Down Syndrome Too few or too many chromosomes Extra copy of chromosome 21 Chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis Have distinctive physical appearance Diagnosing Genetic Disorders Past: Doctors used Punnett Squares to predict genetic disorders Today: Doctors use amniocentesis and karyotypes Amniocentesis: procedure to determine whether bay will have genetic disorder Doctor uses long needle to extract fluid surrounding baby that contains baby’s cells Karyotypes: picture of all the chromosomes in a cell Some families turn to genetic counselors to help understand their chances of having a baby with a genetic disorder https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XyX59LtClXE Section 3: Advances in Genetics Developing Organisms with Desirable Traits Selective Breeding: process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation Cannot control which allele is passed on Inbreeding: crossing two individuals that have identical or similar sets of alleles Purebreds: Pea Plants, dogs, horses, etc. Increase probability that organism may inherit alleles that lead to genetic disorders Hybridization: breeders cross two genetically different individuals Get the “best” of both parents Most crops produced this way Cloning Clone: organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it was produced Exact same genes!!!! Cloning Plants-> Cutting Cloning Animals: Dolly example Removed egg cell from one sheep, then replaced nucleus with a nucleus of a cell from a six year old sheep Then implanted the egg into a uterus of a third sheep https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tELZEPcgKkE Used for transplants Genetic Engineering Genetic Engineering: process in which genes from one organism is transferred into the DNA of another organism “gene splicing” Produces medicines, improve food crops, and may cure genetic disorders Insert human genes into cells of bacteria and animals to produce human protein Gene Therapy Gene Therapy: inserting working copies of a gene directly into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder Used to produce working protein to replace the non-working protein that cause the disorder https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bLI1Gfb0ynw DNA Fingerprinting Except for identical twins, no two people have the same DNA. Similar to DNA, no two people have same fingerprints. Each person has a different fingerprint (patterns) Used to solve crimes, identification, etc. The Human Genome Project Genome: all the DNA in one cell of an organism Estimate 3 billion DNA base pairs or 35,000 genes The main goal of the Human Genome Project is to identify the DNA sequence of every gene in the human genome. Gain a better understanding of human development What makes the body work and what causes things to go wrong Lead to new treatments for genetic disorders https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MvuYATh7Y74