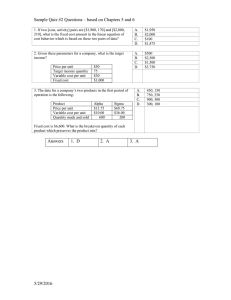
Managerial Accounting Insights from Fixed and Variable Costs Today’s Agenda • Ramona’s Charity Auction – Simple calculation; do all entrepreneurs do it? • GM Jobs Bank – The Danger of Fixed Costs • Breakeven calculations for Chinese airlines • McDonald’s Breakeven – Number of customers per store per hour – Sales Price or Contribution Margin? Breakeven Analysis Ramona’s Charity Banquet Ramona helped organize a charity banquet and raffle. • The raffle prize was a brand new car costing $18,000. (This was back in 1985, so that was a pretty nice car.) • The caterer charged $40 per person for the banquet. • The charity sold tickets to the banquet for $250 each. Questions 1. How many people had to attend the banquet in order for the charity to break even? 2. Do you think the charity performed the breakeven calculation? Explain. Breakeven Computation Total Fixed Costs --------------------------------Contribution Margin per Unit (Sales Price per unit - Variable Cost per unit) Breakeven Analysis Ramona’s Charity Banquet $18,000 for the car --------------------------------Contribution Margin per Person ($250 per person - $40 per person) $18,000 ÷ $210 per person = 86 people to breakeven Breakeven Analysis Ramona’s Charity Banquet Do you think the charity performed the breakeven calculation? Almost certainly ….. NOT. Why not? • Numbers are boring; starting a business or organizing a charity banquet is supposed to be exciting. • Numbers are scary. • Many people (most people?) just don’t think of using data in making decisions. Breakeven Analysis Ramona’s Charity Banquet A HUGE benefit of financial analysis in general and breakeven analysis in particular is that it can Counteract the natural over-optimism of entrepreneurs. The Dangers of Fixed Costs General Motors Jobs Bank • Jobs Bank initiated in 1984. • Insurance against overseas outsourcing of union jobs. • At the time, the Big Three had 75% U.S. market share. Questions 1. Is direct labor a fixed cost or a variable cost? 2. Does the existence of the Jobs Bank change your answer to (1)? Explain. 3. Under what circumstances would the Jobs Bank become a very costly program for the Big Three? The Dangers of Fixed Costs General Motors Jobs Bank 1. Is direct labor a fixed cost or a variable cost? Traditionally, direct labor is the perfect example of a variable cost. The Dangers of Fixed Costs General Motors Jobs Bank 2. Does the existence of the Jobs Bank change your answer to (1)? Explain. • From the standpoint of the UAW, the entire point of the Jobs Bank was to change direct labor from a variable cost to a fixed cost. • Thus, the Big Three automakers would know that even if production was outsourced overseas, they would still have the same fixed labor costs in the United States. The Dangers of Fixed Costs General Motors Jobs Bank 3. Under what circumstances would the Jobs Bank become a very costly program for the Big Three? • • The Jobs Bank would become very costly if production were to drop and yet Jobs Bank workers still had to be paid. Combined U.S. market share for the Big Three fell below 50% for the first time in 2007. In 2006, GM itself had 7,500 workers in the Jobs Bank. Including the cost of benefits, the Jobs Bank cost GM about $1 billion in 2006 alone … $1 billion to pay workers who were not working on building cars. The Dangers of Fixed Costs For A Small Business Owner Fixed costs have to be paid even when … • • • • • • You are just getting your business started. Your business is experiencing a seasonal downturn. The local economy is a little slow right now. You want to take a vacation. You get sick and can’t run your business. Your customers are a little slow in paying you. The Secret to Financial Security Spend less than you make!!!! One key practice: Keep Fixed Costs Low • • • Housing payment Installment payments for credit purchases Cable/Internet/Phone bill China Airline Industry Fixed and Variable Costs China Airline Industry Three Largest Chinese Airlines Air China State ownership 52.2% Major hubs Beijing Shanghai Chengdu Stock listings Shanghai Hong Kong London China Southern 50.3% Guangzhou Beijing China Eastern 59.7% Shanghai (Pudong) Shanghai (Hongqiao) Shanghai Hong Kong New York Shanghai Hong Kong New York China Airline Industry Three Largest Chinese Airlines China Airline Industry Cathay Pacific and Singapore Airlines Cathay Pacific – Founded in 1946. “Over the Hump” – Headquarters in Hong Kong – Significant ownership by Swire Group – Acquired Dragonair, complex transaction Singapore Airlines – Headquarters in Singapore – Majority owned by Singapore government China Airline Industry The Importance of Shanghai –How large is Shanghai? • Between 24 and 34 million people, depending on whether you count just the city or the entire metropolitan area. • Most populous city in China –Is Shanghai important to Chinese business? • The key Chinese financial center (in competition with Hong Kong) • One of the world’s largest ports Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China For 2007 (in billions) Revenue ¥ Variable costs Fixed costs Net income Passengers carried (thousands) Average number of seats per flight Average length of a flight (kilometers) Number of flights ¥ (RMB) (RMB) (RMB) China Eastern 43.1 ¥ (2.9) (40.0) 0.20 ¥ China Southern 54.5 ¥ (4.1) (48.4) 2.00 ¥ Air China 51.3 ¥ (2.8) (44.4) 4.10 ¥ 39,161.4 163 1,460 327,426 56,903.0 178 1,436 470,043 37,256.2 164 1,880 276,446 (RMB restated) (RMB restated) Cathay Singapore Pacific Airlines 70.8 ¥ 80.8 (2.8) (4.0) (61.3) (66.0) 6.70 ¥ 10.80 23,253.0 264 3,518 119,943 19,120.0 311 4,785 76,471 Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China For 2007 ¥ Variable cost per passenger ¥ Contribution margin per passenger ¥ Revenue per passenger Contribution margin percentage Fixed cost per flight ¥ (RMB) (RMB) China Eastern 1,101 74 1,027 93.3% 122,165 China Southern 958 72 886 92.5% 102,969 ¥ ¥ ¥ ¥ (RMB) ¥ ¥ ¥ ¥ Air China 1,377 75 1,302 94.6% 160,610 (RMB restated) (RMB restated) ¥ ¥ ¥ ¥ Cathay Pacific 3,045 120 2,925 96.1% 511,077 ¥ ¥ ¥ ¥ Singapore Airlines 4,226 209 4,017 95.1% 863,067 Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China Questions 1. Does an airline ever want to see a plane take off with empty seats on board? Explain. 2. Using the data for fixed cost per flight and for contribution margin per passenger, compute the breakeven number of passengers per flight for China Eastern. 3. Using your answer in (2) and the average number of seats per flight, for China Eastern compute the “breakeven passenger load factor” which is the percentage of seats that must be purchased, on average, for the airline to break even. 4. Comment on the results of your computation in (3). Do you think that the “breakeven passenger load factor” is an important number for an airline? Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China 1. Does an airline ever want to see a plane take off with empty seats on board? Explain. NO!! The variable cost of putting a passenger in a seat is just RMB70 for the Chinese airlines. Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China 2. Using the data for fixed cost per flight and for contribution margin per passenger, compute the breakeven number of passengers per flight for China Eastern. Fixed cost per flight ¥ ÷ Contribution margin per passenger ¥ Breakven number of passengers 122,165 ¥ 1,027 ¥ 102,969 ¥ 886 ¥ 160,610 ¥ 1,302 ¥ 511,077 ¥ 2,925 ¥ 119.0 116.2 123.4 174.7 863,067 4,017 214.9 Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China 3. Using your answer in (2) and the average number of seats per flight, for China Eastern compute the “breakeven passenger load factor” which is the percentage of seats that must be purchased, on average, for the airline to break even. Breakven number of passengers ÷ Average number of seats per flight 119.0 163 116.2 178 123.4 164 174.7 264 214.9 311 Breakeven passenger load factor 73.2% 65.3% 75.2% 66.2% 69.1% Breakeven Application Airline Industry in China 4. Comment on the results of your computation in (3). Do you think that the “breakeven passenger load factor” is an important number for an airline? • YES!! • Many airlines publicly report their “breakeven passenger load factor.” • This one number is an efficient way to summarize how an airline is balancing its revenues and its costs in changing economic conditions. Breakeven Application McDonald’s 6,399 company-owned stores (in millions of U.S. dollars) Sales Food & Packaging (variable) Payroll & Benefits: Variable Fixed Occupancy (fixed) Operating income 2010 $ 16,233 (5,300) $ (3,247) (874) (3,638) 3,174 Breakeven Application McDonald’s Questions 1. What is McDonald’s contribution margin ratio? 2. The average sale per customer visit to McDonald’s is $3.28. What is the contribution margin per visit? 3. With 6,399 company-owned stores, what is the fixed cost per store per year? 4. Assume that each store is open 16 hours per day, 365 days per year. What is the fixed cost per store per hour? 5. Combine your answers to (2) and (4). How many customers must visit the average McDonald’s store PER HOUR in order for McDonald’s to break even? Breakeven Application McDonald’s 1. What is McDonald’s contribution margin ratio? (in millions of U.S. $) Sales Food & Packaging (variable) Payroll & Benefits (variable) Contribution Margin Payroll & Benefits (fixed) Occupancy (fixed) Operating income Contribution Margin Ratio Contribution Margin ÷ Sales $ 2010 16,233 (5,300) (3,247) 7,686 (874) (3,638) 3,174 $ $ 7,686 16,233 $ 47.3% Breakeven Application McDonald’s 2. The average sale per customer visit to McDonald’s is $3.28. What is the contribution margin per visit? Sales per customer × Contribution Margin Ratio $ 3.28 47.3% Contribution margin per customer $ 1.55 Breakeven Application McDonald’s 3. With 6,399 company-owned stores, what is the fixed cost per store per year? Payroll & Benefits (fixed) Occupancy (fixed) Total Fixed Costs ÷ Number of stores Fixed cost per store per year (in millions) $ 874 3,638 $ 4,512 6,399 $ 705,110 Breakeven Application McDonald’s 4. Assume that each store is open 16 hours per day, 365 days per year. What is the fixed cost per store per hour? Fixed cost per Store per year $ 705,110 ÷ 365 days × 16 hours per day 5,840 Fixed cost per store per hour $ 120.74 Breakeven Application McDonald’s 5. Combine your answers to (2) and (4). How many customers must visit the average McDonald’s store PER HOUR in order for McDonald’s to break even? $120.74 fixed cost per store per hour ---------------------------------------------------$1.55 contribution margin per customer 78 customers per store per hour breakeven McDonald’s One More Dollar to Spend Assume that a customer has one more dollar in her or his pocket to spend. Would McDonald’s prefer that the customer spend that dollar on a hamburger or on french fries? Explain. McDonald’s One More Dollar to Spend Which should the company care about: • Sales? • Contribution Margin? Today’s Agenda • Ramona’s Charity Auction – Simple calculation; do all entrepreneurs do it? • GM Jobs Bank – The Danger of Fixed Costs • Breakeven calculations for Chinese airlines • McDonald’s Breakeven – Number of customers per store per hour – Sales Price or Contribution Margin?