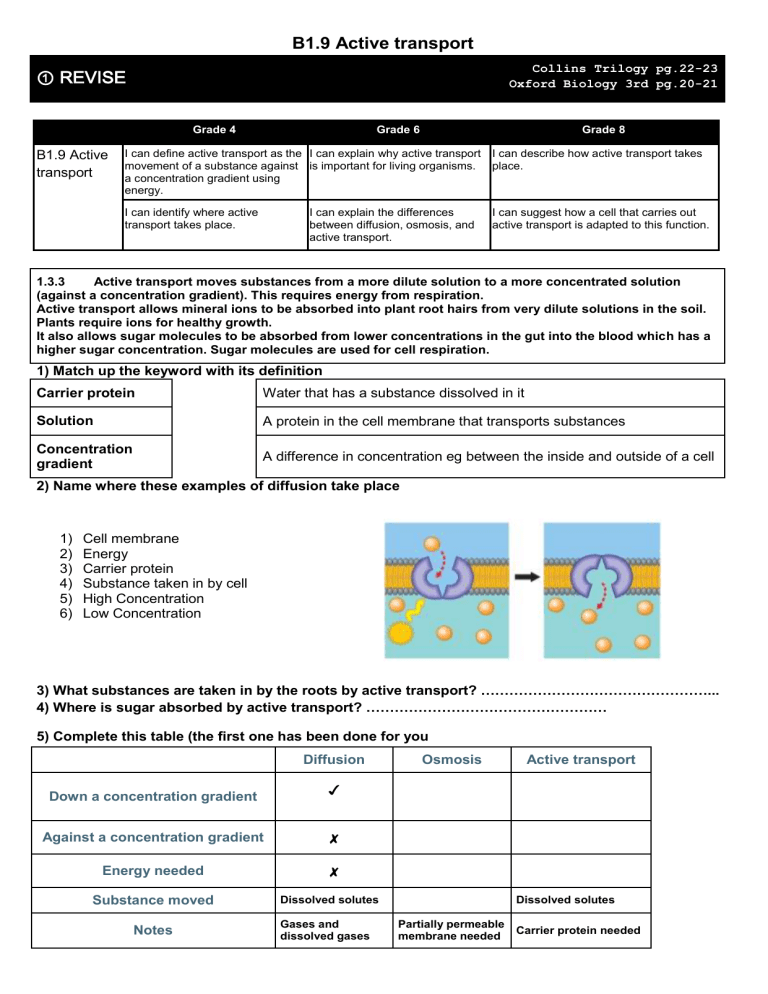
B1.9 Active transport Collins Trilogy pg.22-23 Oxford Biology 3rd pg.20-21 ① REVISE Grade 4 B1.9 Active transport Grade 6 Grade 8 I can define active transport as the I can explain why active transport I can describe how active transport takes movement of a substance against is important for living organisms. place. a concentration gradient using energy. I can identify where active transport takes place. I can explain the differences between diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. I can suggest how a cell that carries out active transport is adapted to this function. 1.3.3 Active transport moves substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution (against a concentration gradient). This requires energy from respiration. Active transport allows mineral ions to be absorbed into plant root hairs from very dilute solutions in the soil. Plants require ions for healthy growth. It also allows sugar molecules to be absorbed from lower concentrations in the gut into the blood which has a higher sugar concentration. Sugar molecules are used for cell respiration. 1) Match up the keyword with its definition Carrier protein Water that has a substance dissolved in it Solution A protein in the cell membrane that transports substances Concentration gradient A difference in concentration eg between the inside and outside of a cell 2) Name where these examples of diffusion take place 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Cell membrane Energy Carrier protein Substance taken in by cell High Concentration Low Concentration 3) What substances are taken in by the roots by active transport? …………………………………………... 4) Where is sugar absorbed by active transport? …………………………………………… 5) Complete this table (the first one has been done for you Diffusion Down a concentration gradient ✗ Energy needed ✗ Notes Active transport ✓ Against a concentration gradient Substance moved Osmosis Dissolved solutes Gases and dissolved gases Dissolved solutes Partially permeable membrane needed Carrier protein needed also diffuse TEST YOURSELF ② Grade 3 What is active transport? ……………………………………………………………………….………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………… …………………………………………………………….………………………………………….. Describe an example of active transport in the roots of a plant ……………………………………………………………………….………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………… …………………………………………………………….………………………………………….. Describe an example of active transport in the gut of an animal ……………………………………………………………………….………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………… …………………………………………………………….…………………………………………. Grade 6 Explain the difference between Active transport and Diffusion. (Make sure you mention a) the direction that particles move b) the role of carrier proteins c) the presence of a membrane d) the need for a source of energy ……………………………………………………………………….………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………… …………………………………………………………….…………………………………………………… ………………………….……………………………………………………………………………………… …………………….…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………….……………………………………………………………………………….……………… ……………………………………………………….………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………….……………………………………………………………… …………………………………………….…………………………………………………………………… ………….……………………………………………………………………………………………………… …….…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… .……………………………………………………………………………….……………………………… ………………………………………….………………………………………… Grade 8 Describe what is happening in the diagram to the right. …………………………………………………………… ………….………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………….… …………………………………………………………… …………………………………………….……………… ….………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………… ….………………….……………….…………………… Explain why a root hair cell has a large surface area and many mitochondria but no chloroplasts. …………………………………………………………… ………….………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………….… …………………………………………………………… …………………………………………….……………… ….………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………… ….………………….……………….……………………… …………………...…………………………………...