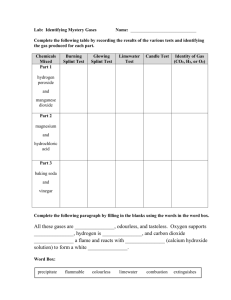
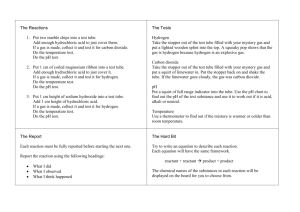
Reactant --> Product Law of Conservation of Mass: the mass of reactant = mass of product Factors that increase the Rate of Reaction: Temperature Catalyst Concentration (amount) Surface Area Acid + Metal = Salt + Hydrogen Gas Test for Hydrogen gas: Pop Test Word equation: Calcium + Hydrochloric Acid → Calcium Chloride + Hydrogen gas Chemical Equation: Ca + HCl → CaCl + H Acid + Base = Salt + Water Test: Litmus Paper Word equation: Hydrochloric Acid + Sodium Hydroxide → Sodium Chloride + Water Chemical Equation: HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O Common Acids: Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Nitric Acid (HNO3) Sulphuric Acid (H2SO4) Ethanoic Acid (CH3COOH) Acid + Carbonate = Salt + Carbon Dioxide Test for Carbon Dioxide: Mix Carbon Dioxide with limewater. If the limewater changes colour that means Carbon Dioxide is present. Word equation: Nitric Acid + Copper Carbonate → Copper Nitrate + Water + Carbon Dioxide Chemical Equation: 2HNO3 + CuCO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + H2O + CO2 Thermal Decomposition Definition: a single reactant is heated to a high temperature until it breaks apart to form several reactants. Composition/Synthesis Definition: when two reactants combine to form a single reactant Combustion Definition: a reaction in which something reacts with oxygen Fuel + Oxygen → Energy Solubility (how well a substance dissolves in another substance) Definition: two solutions are mixed together to form a insoluble (cannot dissolve) product called a solid precipitate. Balancing Chemical Equations