Cell Physiology Summary: Metabolism, Respiration, Protein Synthesis
advertisement

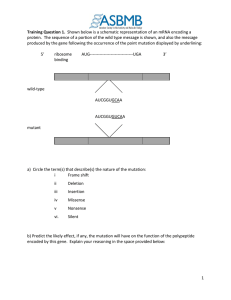
SUMMARY OF CELL PHYSIOLOGY METABOLISM = anabolism (build up rx that store energy) + catabolism (breakdown rx that release energy) CELL RESPIRATION = Conversion of glucose energy to ATP energy Glycolysis – occurs anywhere in the cell without O2 o Glucose enters into the cell and is cut in ½ releasing enough energy to produce 2ATP molecules o The remnants of the broken glucose are called pyruvic acid Kreb’s cycle – occurs only in the mitochondrial matrix o Pyruvic acid enters into the mitochondria for further decomposition o Through a series of chemical reactions, the energy contained in pyruvic acid is transferred to 2 ATP molecules o CO2 is produced o Electron carriers are also synthesized Electron transport chain – occurs only in the mitochondria and requires O2 o Electron carriers from previous reactions are shuttled across the cristae within the mitochondria and produce another 32 molecules of ATP o H2O is produced PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Transcription o Occurs in nucleus where information on chromosomal gene is copied to mRNA molecule via complementary base pairing A—U T—A C—G G—C o RNA polymerase unwinds DNA and complementarily copies DNA based on nitrogenous base pairing A-U and C-G Translation o Released mRNA molecule migrates out of the nucleus and binds to a ribosome o The ribosome reads the base sequence on mRNA and allows tRNA to dock when mRNA codon complements to tRNA anticodon o The tRNA molecule then drops off its amino acid as it is bonded to the growing chain of amino acids o When a stop codon is read, the protein is released to be packaged by the ER and modified by the Golgi apparatus before release from the cell Jennifer Reaves, JSCC Savannah