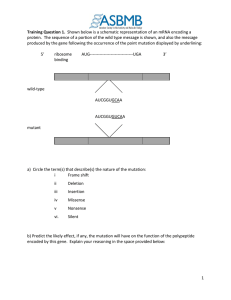
Lab: Building Proteins from RNA Student Guide Prelab Information Purpose Explore the molecular process of building proteins from the information carried by RNA using a laboratory procedure. Time Approximately 45 minutes Question How are proteins built using the information provided by a molecule of RNA? Prediction RNA determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins and polypeptides by a twostep process: transcription of DNA produces mRNA in the nucleus, then translation of the mRNA to tRNA takes place at the ribosome in the cytoplasm. Lab Procedure Materials: helicase human cell tRNA sequence protein structure chart Step 1: Transcribe the Information in DNA to mRNA (The animation will zoom from the human cell to the nucleus to the DNA strand.) a) Find and click the arrow that represents the direction in which the mRNA is built. Like DNA, mRNA is always built from the 5' direction to the 3'. b) Which RNA nucleotide can pair with the thymine (T) at the beginning of the strand? Drag it into the DNA antisense strand to make a pair. c) Complete nine (9) additional base pairs. Remember, there is no thymine (T) in RNA. The adenine (A) in the DNA needs to pair with uracil (U). d) After your mRNA sequence record is complete, click “Leave the Nucleus” to send the mRNA to the ribosome in the cell’s cytoplasm, where production of proteins will take place. Step 2: Locate Codons (You will continue to read mRNA from the 5′ end toward the 3′ end.) a) A codon is a sequence of three bases that indicates a unit of information in the RNA. A gene is a series of codons that results in the production of a protein. Identify the codons of the mRNA shown. The start codon for a gene is AUG, so start by dragging the blue start codon box over the AUG on the strand. (The start codon is already recorded on the data table.) b) Use the gray codon box to highlight additional codons three bases at a time. When you reach a stop codon (either UAA, UAG, or UGA) you will need to use the pink stop codon box. As you form codons, record them in Table 1. Step 3: Translate mRNA tRNA is composed of short sections of RNA that bond to the codons in mRNA. The screen shows a pool of tRNA anticodons, which carry the amino acids to the ribosome and attach to the mRNA when its sequence of base pairs is complementary with the mRNA in the ribosome. a) For each codon, you will find the correct tRNA anticodon and drag it to the ribosome. Start with the AUG codon in the ribosome. Find and drag its match, the UAC anticodon, to it. Record this Copyright © Edgenuity Inc. Student Guide (continued) pair and the amino acid Met to complete the first row of Table 2. b) Find the next anticodon you need to match the next mRNA codon you identified. Drag its anticodon to the ribosome. Record in the second row of Table 2. c) Remember, the ribosome can only handle two tRNA strands at a time. So, click the Dehydrate button to activate the process of dehydration synthesis, or the loss of water molecules during protein building. d) Continue to build the protein by joining amino acids to the chain in the correct order. Every amino acid joined to the protein results in the production of one more water molecule. Click Dehydrate to form the peptide bonds. W atch the water molecule counter and be sure to record all data in your data Table 2. When many amino acids are joined in sequence, this is a polypeptide chain. Copyright © Edgenuity Inc. Student Guide (continued) Sequence and Protein Structure Chart Image: Public domain. http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Aminoacids_table.svg Copyright © Edgenuity Inc. Student Guide (continued) Data Table 1: Codon sequences for mRNA molecule Codons AUG (start) Copyright © Edgenuity Inc. Student Guide (continued) Data Table 2: Translation of mRNA molecules Codons AUG (start) Copyright © Edgenuity Inc. tRNA Anticodons Amino Acid Number of Water Molecules Produced